Abstract
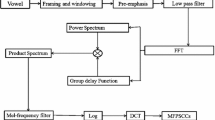
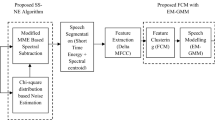
This paper proposes hybrid classification models and preprocessing methods for enhancing the consonant-vowel (CV) recognition in the presence of background noise. Background Noise is one of the major degradation in real-time environments which strongly effects the performance of speech recognition system. In this work, combined temporal and spectral processing (TSP) methods are explored for preprocessing to improve CV recognition performance. Proposed CV recognition method is carried out in two levels to reduce the similarity among large number of CV classes. In the first level vowel category of CV unit will be recognized, and in the second level consonant category will be recognized. At each level complementary evidences from hybrid models consisting of support vector machine (SVM) and hidden Markov models (HMM) are combined for enhancing the recognition performance. Performance of the proposed CV recognition system is evaluated on Telugu broadcast database for white and vehicle noise. The proposed preprocessing methods and hybrid classification models have improved the recognition performance compared to existed methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell, S. (1979). Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 27, 113–120.
Burges, C. J. (1998). A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2(2).
Collobert, R., & Bengio, S. (2001). Svmtorch: support vector machines for large-scale regression problems. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 1, 143–160.
Cui, X., & Alwan, A. (2005). Noise robust speech recognition using feature compensation based on polynomial regression of utterance snr. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 13(6), 1161–1172.
de la Torre, A., Peinado, A. M., Segura, J. C., Perez-Cordoba, J. L., Benitez, M. C., & Rubio, A. J. (2005). Histogram equalization of speech representation for robust speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 13(3), 355–366.
Ephrain, Y., & Malah, D. (1984). Speech enhancement using minimum mean square error short-time spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 32, 1109–1121.
Gales, M., Young, S., & Young, S. J. (1996). Robust continuous speech recognition using parallel model combination. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 4(5), 352–359.
Gangashetty, S. V. (2004). Neural network models for recognition of consonant-vowel units of speech in multiple languages. Ph.D. dissertation, IIT Madras, October.
Gangashetty, S. V., Sekhar, C. C., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2005a). Combining evidence from multiple classifiers for recognition of consonant-vowel units of speech in multiple languages. In Proc. of ICISIP (pp. 387–391).
Gangashetty, S. V., Sekhar, C. C., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2005b). Spotting multilingual consonant-vowel units of speech using neural networks. In An ISCA tutorial and research workshop on non-linear speech processing (pp. 287–297).
Hegde, R. M., Murthy, H. A., & Gadde, V. (2004). Continuous speech recognition using joint features derived from the modified group delay function and mfcc. In Proc. INTERSPEECH-ICSLP (pp. 905–908).
Hermanski, H., Morgan, N., & Hirsch, H. G. (1994). Recognition of speech in additive and convolutional noise based on rasta spectral processing. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal process.
Hermes, D. J. (1990). Vowel onset detection. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 87, 866–873.
Hermus, K., & Wambacq, P. (2004). Assessment of signal subspace based speech enhancement for noise robust speech recognition. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal process (pp. 945–948).
Hermus, K., Verhelst, W., & Wambacq, P. (2000). Optimized subspace weighting for robust speech recognition in additive noise environments. In Proc. of 6th international conference on spoken language processing (pp. 542–545).
Hilger, F., & Ney, H. (2006). Quantile based histogram equalization for noise robust large vocabulary speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 14(3), 845–854.
Ho, T. K., Hull, J. J., & Srihari, S. N. (1994). Decision combination in multiple classifier systems. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 16(1), 66–75.
Huang, J., & Zhao, Y. (1997). Energy-constrained signal subspace method for speech enhancement and recognition. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 4, 283–285.
Kamath, S., & Loizou, P. (2002). A multi-band spectral subtraction method for enhancing speech corrupted by colored noise. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal process, Orlando, USA.
Kim, D. K., & Gales, M. J. F. (2011). Noisy constrained maximum-likelihood linear regression for noise-robust speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 19(2), 315–325.
Kris, H., Patrick, W., & ham Hugo, V. (2007). A review of signal subspace speech enhancement and its application to noise robust speech recognition. EURASIP Journal on Applied Signal Processing, 195–209.
Krishnamoorthy, P., & Prasanna, S. R. M. (2011). Enhancement of noisy speech by temporal and spectral processing. Speech Communication, 53, 154–174.
Liao, H., & Gales, M. J. F. (2007). Adaptive training with joint uncertainty decoding for robust recognition of noisy data. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal process (pp. 389–392).
Mokbel, C., & Chollet, G. (1991). Speech recognition in adverse environments: speech enhancement and spectral transformations. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal process.
Moreno, P. J. (1996). Speech recognition in noisy environments. Ph.D. dissertation, Carnegie Mellon University.
Nolazco-Flores, J. A., & Young, S. (1993). CSS-PMC: a combined enhancement/compensation scheme for continuous speech recognition in noise (Technical Report). Cambridge University Engineering Department.
Ohkura, K., & Sugiyama, M. (1991). Speech recognition in a noisy environment using a noise reduction neural network and a codebook mapping technique. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal process.
Ozlem, K., Michael, L. S., Jasha, D., & Alex, A. (2010). Noise adaptive training for robust automatic speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 18(8), 1889–1901.
Picone, J. W. (1993). Signal modeling techniques in speech recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 81(9), 1215–1247.
Prasanna, S. M. (2004). Event-based analysis of speech. Ph.D. dissertation, IIT Madras, March.
Prasanna, S. R. M., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2005). Detection of vowel onset point events using excitation source information. In Proc. of interspeech (pp. 1133–1136).
Prasanna, S. M., Reddy, B. S., & Krishnamoorthy, P. (2009). Vowel onset point detection using source, spectral peaks, and modulation spectrum energies. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 17(4), 556–565.
Rabiner, L. R. (1989). A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. In Proc. of IEEE (pp. 257–286).
Rabiner, L. R., & Juang, B. H. (1993). Fundamentals of speech recognition. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Rao, K. S. (2011). Application of prosody models for developing speech systems in Indian languages. International Journal of Speech Technology, 14(1), 19–33.
Rao, K. S., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2009a). Intonation modeling for Indian languages. Computer Speech & Language, 23(2), 240–256.
Rao, K. S., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2009b). Duration modification using glottal closure instants and vowel onset points. Speech Communication, 51, 1263–1269.
Sekhar, C. C. (1996). Neural network models for recognition of stop consonant-vowel (scv) segments in continuous speech. Ph.D. dissertation, IIT Madras.
Sekhar, C. C., Lee, W. F., Takeda, K., & Itakura, F. (2003). Acoustic modeling of subword units using support vector machines. In Proceedings of WSLP.
Suh, Y., Ji, M., & Kim, H. (2007). Probabilistic class histogram equalization for robust speech recognition. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 14(4), 287–290.
Vaseghi, S. V., & Milner, B. P. (1997). Noise compensation methods for hidden Markov model speech recognition in adverse environments. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 5(1), 11–21.
Viiki, O., Bye, B., & Laurila, K. (1998). A recursive feature vector normalization approach for robust speech recognition in noise. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal process.
Vuppala, A. K., Chakrabarti, S., & Rao, K. S. (2010). Effect of speech coding on recognition of consonant-vowel (CV) units. In Proc. int. conf. contemporary computing. Springer communications in computer and information science (pp. 284–294).
Yegnanarayana, B., & Murthy, S. (2000). Enhancement of reverberant speech using lp residual signal. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 8, 267–281.
Yegnanarayana, B., Avendano, C., Hermansky, H., & Murthy, S. (1999). Speech enhancement using linear prediction residual. Speech Communication, 28, 25–42.
Yegnanarayana, B., Prasanna, S. R. M., Duraiswami, R., & Zotkin, D. (2005). Processing of reverberant speech for time-delay estimation. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 13, 1110–1118.
Young, S., Kershaw, D., Odell, J., Ollason, D., Valtchev, V., & Woodland, P. (2000). The HTK book version 3.0. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Yu, D., Deng, L., Droppo, J., Wu, J., Gong, Y., & Acero, A. (2008). A minimum-mean-square-error noise reduction algorithm on Mel-frequency cepstra for robust speech recognition. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal process (pp. 4041–4044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vuppala, A.K., Rao, K.S., Chakrabarti, S. et al. Recognition of consonant-vowel (CV) units under background noise using combined temporal and spectral preprocessing. Int J Speech Technol 14, 259–272 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-011-9101-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-011-9101-9