Abstract
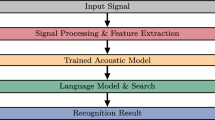
One major source of suboptimal performance in automatic continuous speech recognition systems is misrecognition of small words. In general, errors resulting from small words are much more than errors resulting from long words. Therefore, compounding some words (small or long) to produce longer words is welcome by speech recognition decoders. In this paper, we present a novel approach to artificially generate compound words using part of speech tagging. For this purpose, we consider two cases in Arabic speech where two words are pronounced without a silence period in between: a noun followed by an adjective, and a preposition followed by any word. To collect the candidate compound words, we use Stanford Arabic tagger to tag all words in our baseline transcription corpus. Then, compound words are generated whenever any of the two cases occur in a sequence of two words. The unique compound words are then added to the expanded pronunciation dictionary, as well as to the language model. Using Sphinx 3, we test the proposed method for a 5.4 hours speech corpus of modern standard Arabic. The results show a significant improvement, as the word error rate is reduced by 2.39%.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
AbuZeina, D., Al-Khatib, W., Elshafei, M., & Al-Muhtaseb, H. (2011). Cross-word Arabic pronunciation variation modeling for speech recognition. International Journal of Speech Technology.
Albared, M., Omar, N., Ab Aziz, M., Zakree, M., & Nazri, A. (2010). Automatic part of speech tagging for Arabic: an experiment using Bigram hidden Markov model. In RSKT’10 proceedings of the 5th international conference on rough set and knowledge technology.
Alghamdi, M., Almuhtasib, H., & Elshafei, M. (2004). Arabic phonological rules. Journal of King Saud University: Computer and Information Sciences, 16, 1–25.
Ali, M., Elshafei, M., Alghamdi, M., Almuhtaseb, H., & Alnajjar, A. (2009). Arabic phonetic dictionaries for speech recognition. Journal of Information Technology Research, 2(4), 67–80.
Al Shamsi, F., & Guessoum, A. (2006). A hidden Markov model-based PS tagger for Arabic.
Berton, A., Fetter, P., & Regel-Brietzmann, P. (1996). Compound words in large-vocabulary German speech recognition systems. In Proceedings of the international conference of speech and language processing (ICSLP).
Diab, M., Hacioglu, K., & Jurafsky, D. (2004). Automatic tagging of Arabic text: from raw text to base phrase chunks. In 5th meeting of the North American chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics/Human Language Technologies conference.
Elshafei, A. M. (1991). Toward an Arabic text-to-speech system. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 16(4B), 565–583.
Elshafei, M., Almuhtasib, H., & Alghamdi, M. (2002). Techniques for high quality text-to-speech. Information Sciences, 140(3–4), 255–267.
El Hadj, Y., Al-Sughayeir, I., & Al-Ansari, A. (2009). Arabic part-of-speech tagging using the sentence structure. In Proceedings of the second international conference on Arabic language resources and tools. The MEDAR Consortium.
Finke, M., & Waibel, A. (1997). Speakingmode dependent pronunciation modeling in large vocabulary conversational speech recognition. In EUROSPEECH-1997 (pp. 2379–2382).
IPA for Arabic (2011). http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:IPA_for_Arabic.
Jelinek, F. (1999). Statistical methods for speech recognition. In Language, speech and communication series. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Lei, X., Wang, W., & Stolcke, A. (2009). Data-driven lexicon expansion for Mandarin broadcast news and conversation speech recognition. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing. ICASSP 2009 (pp. 4329–4332). 19–24 April 2009. doi:10.1109/ICASSP.2009.4960587.
MITCogNet (2010). http://mitpdev.mit.edu/library/erefs/arbib/images/figures/A248_fig001.gif.
Plötz, T. Advanced stochastic protein sequence analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Bielefeld University, June 2005.
Stanford Log-linear Part-of-Speech Tagger (2011). http://nlp.stanford.edu/software/tagger.shtml.
Siegler, M. A., & Stern, R. M. (1995). On the effects of speech rate in large vocabulary speech recognition systems. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust. speech signal process (Vol. 1, pp. 612–615). Detroit.
Saon, G., & Padmanabhan, M. (2001). Data-driven approach to designing compound words for continuous speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 9(4):327–332
Sloboda, T., & Waibel, A. (1996). Dictionary learning for spontaneous speech recognition. In Proc. ICSLP-96 (pp. 2328–2331). Philadelphia, PA, USA.
Zhang, J., Gao, J., & Zhou, M. (2000). Extraction of Chinese compound words: an experimental study on a very large corpus. In Proceedings of the second workshop on Chinese language processing: held in conjunction with the 38th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 8 October, Hong Kong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
AbuZeina, D., Al-Khatib, W., Elshafei, M. et al. Toward enhanced Arabic speech recognition using part of speech tagging. Int J Speech Technol 14, 419–426 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-011-9121-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-011-9121-5