Abstract
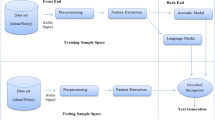
Speaker indexing referred in literature as speaker diarization is an important task in audio indexing and retrieval. Speaker indexing includes two important and usually separate stages, namely speaker segmentation and speaker clustering. Speaker indexing can be divided into online and offline categories. This paper mainly focuses on domain independent online speaker indexing. For this purpose, the proposed framework should be parameter free and no application specific parameters such as utterance duration or threshold settings are required. To reduce dependency on parameters, the traditional speaker segmentation is reformed to a voting based homogeneous speech segmentation, in which several approaches are applied in parallel to decide on the existence of a change point. In online indexing, data insufficiency is encountered at each time slice. In the proposed framework, a set of reference speaker models are used as side information to facilitate online tracking. To improve the indexing accuracy, adaptation approaches in eigen-voice decomposition space are proposed in this paper. To enhance the tracking performance from the computational cost point of view, an index structure of the reference models is proposed to speed up the search in the model space. The proposed framework is evaluated on the 2002 Rich Transcription Broadcast News and Conversational Telephone Speech Corpus (in Garofolo, NIST Rich Transcription, 2002) as well as a synthetic dataset. The indexing error of the proposed framework on telephone conversations, broadcast news and synthetic dataset are 7.51 %, 6.36 % and 9.34 %, respectively. Also, using the index tree structure approach, the tracking run time of the proposed framework is improved by 32 %.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajmera, J., McCowan, I., & Bourlard, H. (2004). Robust speaker change detection. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 11(8), 649–651.
Anguera, X., & Hernando, J. (2004). XBIC: nueva medida para segmentacion de locutor hacia el indexado automatico de la senal de voz. In III jornadas en tecnologia del habla, Valencia, Spain.
Anguera, X., Wooters, C., & Hernando, J. (2006). Frame purification for cluster comparison in speaker diarization. In Second international workshop on multimodal user authentication.
Attias, H. (1999). Inferring parameters and structure of latent variable models by variational Bayes. In 15th conf. uncertainty artif. intell., Stockholm, Sweden (pp. 21–30).
Barras, C., Zhu, X., Meignier, S., & Gauvain, J. L. (2006). Multistage speaker diarization of broadcast news. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 14(5), 1505–1512.
Berrani, S., Amsaleg, L., & Gros, P. (2003). Robust content-based image searches for copyright protection. In ACM workshop on multimedia databases, New Orleans, USA (pp. 70–77).
Bijankhan, M. (2002). Great farsdat database (Technical report). Iran Research center on Intelligent Signal Processing.
Bimbot, F., Magrin-Chagnolleau, I., & Mathan, L. (1995). Second order statistical measures for text-independent speaker identification. Speech Communication, 17(1–2), 177–192.
Boehm, C., & Pernkopf, F. (2009). Effective metric-based speaker segmentation in the frequency domain. In ICASSP (pp. 4081–4084).
Chen, S. S., & Gopalakrishnan, P. S. (1998). Clustering via the Bayesian information criterion with applications in speech recognition. In Proc. of ICASSP, USA (Vol. 2, pp. 645–648).
Chen, K., et al. (2000). Fast speaker adaptation using eigenspace-based maximum likelihood linear regression. In Interspeech (pp. 742–745).
Chu, S. M., Tang, H., & Huang, T. S. (2009). Fishervoice and semi-supervised speaker clustering. In ICASSP (pp. 4089–4092).
Davy, M., Doncarli, C., & Tourneret, J. (2000). Supervised classification using MCMC methods. In Proc. ICASSP (pp. 33–36).
Delacourt, P., & Wellekens, C. J. (2000). DISTBIC: a speaker based segmentation for audio indexing. Speech Communication, 32(1–2), 111–127.
Dempster, A., Laird, N., & Rubin, D. (1977). Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series B. Methodological, 39(1), 1C38.
Desobry, F., & Davy, M. (2003). Support vector-based online detection of abrupt changes. In ICASSP (Vol. 5, pp. 872–875).
Evans, N. W. D., Fredouille, C., & Bonastre, J. F. (2009). Speaker diarization using unsupervised discriminant analysis of inter-channel delay features. In ICASSP (pp. 4061–4064).
Fernandez, D., Otero, P. L., & Mateo, C. G. (2009). An adaptive threshold computation for unsupervised speaker segmentation. In Proc. of interspeech, Brighton, UK (pp. 843–849).
Garofolo, J. S., Lamel, L. F., Fisher, W. M., Fiscus, J. G., Pallett, D. S., & Dahlgren, N. L. (1993). In The DARPA TIMIT acoustic-phonetic continuous speech corpus CDROM. Linguistic data consortium.
Garofolo, J., et al. (2002). In NIST rich transcription 2002 evaluation: a preview. LREC.
Gauvain, J. L., Lamel, L., & Adda, G. (1998). Partitioning and transcription of broadcast news data. In Proc. of interspeech, Sydney, Australia (Vol. 4, pp. 1335–1338).
Han, K. J., & Narayanan, S. (2007). A robust stopping criterion for agglomerative hierarchical clustering in a speaker diarization system. In Proc. of interspeech, Antwerp, Belgium.
Han, K. J., & Narayanan, S. S. (2008). Agglomerative hierarchical speaker clustering using incremental Gaussian mixture cluster modeling. In Interspeech (pp. 20–23).
Huang, C. H., Chien, J. T., & Wang, H. M. (2004). A new eigenvoice approach to speaker adaptation. In International symposium on Chinese spoken language processing (ISCSLP), Hong Kong.
Hung, J., Wang, H., & Lee, L. (2000). Automatic metric based speech segmentation for broadcast news via principal component analysis. In Proc. of interspeech, Beijing, China.
Iso, K. (2010). Speaker clustering using vector quantization and spectral clustering. In ICASSP (pp. 4986–4989).
Izmirli, O. (2000). Using a spectral flatness based feature for audio segmentation and retrieval (Abstract). In Proc. of the international symposium on music information retrieval (ISMIR2000), Plymouth, Massachusetts, USA.
Jolliffe, I. T. (1986). Principal component analysis. Berlin: Springer.
Kemp, T., Schmidt, M., Westphal, M., & Waibel, A. (2000). Strategies for automatic segmentation of audio data. In Proc. of ICASSP, Istanbul, Turkey (Vol. 3, pp. 1423–1426).
Kim, H., Elter, D., & Sikora, T. (2005). Hybrid speaker-based segmentation system using model-level clustering. In Proc. of ICASSP, Philadelphia, USA (Vol. I, pp. 745–748).
Koshinaka, T., Nagatomo, K., & Shinoda, K. (2009). Online speaker clustering using incremental learning of an ergodic hidden Markov model. In ICASSP (pp. 4093–4096).
Kotti, M., Moschou, V., & Kotropoulos, C. (2008). Speaker segmentation and clustering. Signal Processing, 88(5), 1091–1124.
Kuhn, R., Junqua, J. C., Nguyen, P., & Niedzielski, N. (2000). Rapid speaker adaptation in eigenvoice space. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 8(4), 695–707.
Kullback, S., & Leibler, R. A. (1951). On information and sufficiency. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 22(1), 79–86.
Kwok, J. T., Mak, B., & Ho, S. (2004). Eigenvoice speaker adaptation via composite kernel PCA. In NIPS 16, Cambridge: MIT Press.
Kwon, S., & Narayanan, S. (2004a). Unsupervised speaker indexing using generic models. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 13, 1004–1013.
Kwon, S., & Narayanan, S. (2004b). Speaker model quantization for unsupervised speaker indexing. In Interspeech (pp. 1517–1520).
Lopez, J. F., & Ellis, D. P. W. (2000). Using acoustic condition clustering to improve acoustic change detection on broadcast news. In Proc. of interspeech, Beijing, China.
Lu, L., & Zhang, H. (2002). Speaker change detection and tracking in real-time news broadcast analysis. In Proc. of the ACM multimedia, France (pp. 602–610).
Lu, L., & Zhang, H. (2005). Unsupervised speaker segmentation and tracking in real-time audio content analysis. Multimedia Systems, 10(4), 332–343.
Mami, Y., & Charlet, D. (2002). Speaker identification by location in an optimal space of anchor models. In Proc. ICSLP, Denver, Colorado, USA (pp. 1333–1336).
Markov, K., & Nakamura, S. (2007). Never-ending learning with dynamic hidden Markov network. In Proc. of interspeech.
Markov, K., & Nakamura, S. (2008). Improved novelty detection for online GMM based speaker diarization. In Interspeech, Brisbane, Australia (pp. 363–366).
Moattar, M. H., & Homayounpour, M. M. (2009). A simple but efficient real-time voice activity detection algorithm. In 17th European signal processing conference (Eusipco) (pp. 2549–2553).
Moh, Y., Nguyen, P., & Junqua, J. C. (2003). Toward domain independent clustering. In Proc. of ICASSP (Vol. II, pp. 85–88).
Muthusamy, Y. K., et al. (1992). The OGI multi-language telephone speech corpus. In Interspeech (pp. 895–898).
Neal, R. M., & Hinton, G. E. (1998). A view of the EM algorithm that justifies incremental, sparse, and other variants. In Learning in graphical models (pp. 355–368). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Nguyen, T. H., Cheng, E. S., & Li, H. (2008). T-test distance and clustering criterion for speaker diarization. In Interspeech (pp. 36–39).
Nguyen, T. H., Li, H., & Cheng, E. S. (2009). Cluster criterion functions in spectral subspace and their application in speaker clustering. In ICASSP (pp. 4085–4088).
Ning, H., Liu, M., Tang, H., & Huang, T. (2006). A spectral clustering approach to speaker diarization. In Interspeech (pp. 2178–2181).
Nishida, M., & Kawahara, T. (2003). Unsupervised speaker indexing using speaker model selection based on Bayesian information criterion. In ICASSP (Vol. 1, pp. 172–175).
Omar, M., Chaudhari, U., & Ramaswamy, G. (2005). Blind change detection for audio segmentation. In ICASSP.
Otero, P. L., Fernandez, L. D., & Mateo, C. G. (2010). Novel strategies for reducing the false alarm rate in a speaker segmentation system. In Proc. of ICASSP (pp. 4970–4973).
Rabiner, L. R., & Juang, B. H. (1993). Fundamentals of speech recognition. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
Reynolds, D. A. (1995). Speaker identification and verification using Gaussian mixture speaker models. Speech Communication, 17(1–2), 91–108.
Reynolds, D. A., Quatieri, T. F., & Dunn, R. B. (2000). Speaker verification using adapted Gaussian mixture models. Digital Signal Processing, 10(1–3), 19–41.
Rodriguez, L. J., Penagarikano, M., & Bordel, G. (2007). A simple but effective approach to speaker tracking in broadcast news. In IbPRIA, part II (pp. 48–55).
RT (2009). The 2009 (RT09) rich transcription meeting recognition evaluation plan. http://www.itl.nist.gov/iad/mig//tests/rt/2009/docs/rt09-meeting-eval-plan-v2.pdf.
Schwarz, G. (1978). Estimating the dimension of a model. The Annals of Statistics, 6, 461–464.
Siegler, M. A., Jain, U., Raj, B., & Stern, R. M. (1997). Automatic segmentation, classification and clustering of broadcast news audio. In DARPA speech recognition workshop, Chantilly (pp. 97–99).
Sivakumaran, P., Fortuna, J., & Ariyaeeinia, A. (2001). On the use of the Bayesian information criterion in multiple speaker detection. In Eurospeech, Scandinavia.
Sun, H., et al. (2010). Speaker diarization system for RT-07 and RT-09 meeting room audio. In ICASSP (pp. 4982–4985).
Tang, H., Chu, S. M., & Huang, T. S. (2009). Generative model-based speaker clustering via mixture of von Mises-Fisher distributions. In ICASSP (pp. 4101–4104).
Tranter, S. E., Yu, K., Evermann, G., & Woodland, P. C. (2004). Generating and evaluating segmentations for automatic speech recognition of conversational telephone speech. In Proc. of ICASSP, Montreal, Canada (pp. 433–477).
Tritschler, A., & Gopinath, R. (1999). Improved speaker segmentation and segment clustering using the Bayesian information criterion. In EuroSpeech (pp. 679–682).
Tsai, W. H., Cheng, S. S., & Wang, H. M. (2007). Automatic speaker clustering using a voice characteristic reference space and maximum purity estimation. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 15(4), 1461–1474.
Valente, F., & Wellekens, C. (2004). Variational Bayesian speaker clustering. In Speaker odyssey, Toledo, Spain.
Valente, F., & Wellekens, C. (2005). Variational Bayesian adaptation for speaker clustering. In Proc. of ICASSP, Lisbon, Portugal.
Valente, F., Motlicek, P., & Vijayasenan, D. (2010). Variational Bayesian speaker diarization of meeting recordings. In ICASSP (pp. 4954–4957).
Wang, D., Lu, L., & Zhang, H. J. (2003). Speech segmentation without speech recognition. In Proc. of ICASSP, Hong Kong (Vol. 1, pp. 468–471).
Wang, W., Lv, P., Zhao, Q., & Yan, Y. (2007). A decision-tree-based online speaker clustering. In Lecture notes in computer science (Vol. 4477, pp. 555–562). Berlin: Springer.
Wu, J., & Chang, E. (2001). Cohorts based custom models for rapid speaker and dialect adaptation. In Proc. eurospeech (pp. 1261–1264).
Zamalloa, M., et al. (2010). Low latency online speaker tracking on the AMI corpus of meeting conversations. In ICASSP (pp. 4962–4965).
Zdansky, J. (2006). BINSEG: an efficient speaker-based segmentation technique. In Interspeech, Pennsylvania (pp. 2186–2189).
Zezula, P., Amato, G., Dohnal, V., & Batko, M. (2006). Similarity search: the metric space approach. In Advances in database systems (Vol. 32). ISBN 0-387-29146-6
Zhou, B., & Hansen, J. (2002). Improved structural maximum likelihood eigenspace mapping for rapid speaker adaptation. In Interspeech, Denver, Colorado (pp. 554–564).
Zhou, B., & Hansen, J. H. L. (2005). Efficient audio stream segmentation via the combined T2 statistic and the Bayesian information criterion. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 13(4), 467–474.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moattar, M.H., Homayounpour, M.M. A unified framework for domain independent online speaker indexing in eigen-voice space using an index tree of reference models. Int J Speech Technol 16, 381–401 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-013-9190-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-013-9190-8