Abstract
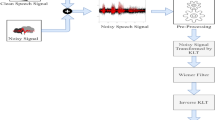
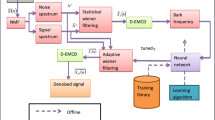
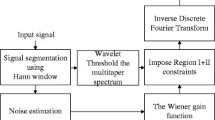
This paper proposes an adaptive Wiener filtering method for speech enhancement. This method depends on the adaptation of the filter transfer function from sample to sample based on the speech signal statistics; the local mean and the local variance. It is implemented in the time domain rather than in the frequency domain to accommodate for the time-varying nature of the speech signals. The proposed method is compared to the traditional frequency-domain Wiener filtering, spectral subtraction and wavelet denoising methods using different speech quality metrics. The simulation results reveal the superiority of the proposed Wiener filtering method in the case of Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) as well as colored noise.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahoura, M., & Rouat, J. (2001). Wavelet speech enhancement based on the teager energy operator. IEEE Signal Proc. Letters, 8(1).
Berouti, M., Schwartz, R., & Makhoul, J. (1979). Enhancement of speech corrupted by acoustic noise. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech signal processing (pp. 208–211).
Boll, S. F. (1979). Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ASSP-27, 113–120.
Boll, S. (1990). Suppression of acoustic noise in speech using spectral subtraction. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 27, 113–120.
Deller, J. R., Hansen, J. H. L., & Proakis, J. G. (2000). Discrete-time processing of speech signals (2nd ed.). New York: IEEE Press.
Ephriam, Y., & Van Trees, H. L. (1993). A signal subspace approach for speech enhancement. In Proc. international conference on acoustic, speech and signal processing, Detroit, MI, USA, May 1993 (Vol. II, pp. 355–358).
Ghanbari, Y., & Karami, M. (2004). Spectral subtraction in the wavelet domain for speech enhancement. International Journal of Software & Information Technology (IJSIT), 1, 26–30.
Ghanbari, Y., Karami, M., & Amelifard, B. (2004). Improved multi band spectral subtraction method for speech enhancement. In Proc. 6th IASTED internat. conf. on signal image process, USA (pp. 225–230).
Handel, P. (2007). Power spectral density error analysis of spectral subtraction type of speech enhancement method. EURASIP Journal On Advances in Signal Processing, 1–9.
Haykin, S. (1996). Adaptive filter theory. New York: Prentice-Hall. ISBN 0-13-322760-X.
Johnstone, I. M., & Silverman, B. W. (1997). Wavelet threshold estimators for data with correlated noise. Journal of Royal Statistical Society, 59(2), 319–351.
Kusumoto, A., Arai, T., Kinshita, K., & Hodoshima, N. (2005). Modulation Enhancement of speech by a preprocessing algorithm for improving intelligibility in reverberant environments. Speech Communication, 45(2), 101–113.
Lim, J. S., & Oppenheim, A. V. (1978). All-pole modelling of degraded speech. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, ASSP-26.
Lim, J. S., & Oppenheim, A. V. (1979). Enhancement and bandwidth compression of noisy speech. Proceedings of the IEEE, 12, 197–210.
Manikandan, S. (2006). Speech Enhancement based on Wavelet De noising. Academic Open Internet journal ISSN 1311-4360, 17.
Quatieri, T. F. (2002). Discrete-time speech signal processing: principles and practice. New York: Prentice Hall.
Shao, Y., & Chang, C. H. (2005). A versatile speech enhancement system based on perceptual wavelet denoising. In IEEE (pp. 864–867).
Sheikhzadeh, H. (2001). An improved wavelet-based speech enhancement system. Eurospeech.
Vaseghi, S. V. (2000). Advanced digital signal processing and noise reduction (2nd ed.). Chichester: Wiley.
Wu, C. Z., Tai Guo, M., Boxiong, S., & Li, Q. (2000). Studies on a speech signal testing method based on adaptive filtering feedback technology. Signal Processing Proceedings, 1, 543–546.
Ying, J., Li, G., & Wang, Z. (2008). A novel approach to speech signal synthesis. In Audio, language and image processing, July 2008 (pp. 680–685).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abd El-Fattah, M.A., Dessouky, M.I., Abbas, A.M. et al. Speech enhancement with an adaptive Wiener filter. Int J Speech Technol 17, 53–64 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-013-9205-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-013-9205-5