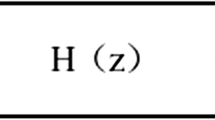Abstract
In this paper, Autoassociative Neural Network (AANN) models are explored for segmentation and indexing the films (movies) using audio features. A two-stage method is proposed for segmenting the film into sequence of scenes, and then indexing them appropriately. In the first stage, music and speech plus music segments of the film are separated, and music segments are labelled as title and fighting scenes based on their position. At the second stage, speech plus music segments are classified into normal, emotional, comedy and song scenes. In this work, Mel frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCCs), zero crossing rate and intensity are used as audio features for segmentation and indexing the films. The proposed segmentation and indexing method is evaluated on manual segmented Hindi films. From the evaluation results, it is observed that title, fighting and song scenes are segmented and indexed without any errors, and most of the errors are observed in discriminating the comedy and normal scenes. Performance of the proposed AANN models used for segmentation and indexing of the films, is also compared with hidden Markov models, Gaussian mixture models and support vector machines.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Li, Y., Narayanan, S., & Kuo, C. C. J. (2003). Movie content analysis indexing and skimming (Vol. 6). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic. Video Mining, Chap. 5.
Yegnanarayana, B., & Kishore, S. P. (2002). AANN an alternative to GMM for pattern recognition. Neural Networks, 15, 459–469.
Haykin, S. (1999). Neural networks: a comprehensive foundation. New Delhi: Pearson Education Aisa, Inc.
Yegnanarayana, B. (1999). Artificial neural networks. New Delhi: Prentice-Hall.
Rao, K. S. (2010). Voice conversion by mapping the speaker-specific features using pitch synchronous approach. Computer Speech & Language, 24(1), 474–494.
Mallidi, S. H. R., Prahallad, K., Gangashetty, S. V., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2010). Significance of pitch synchronous analysis for speaker recognition using AANN models. In INTERSPEECH-2010, Makuhari, Japan, Sept. 2010.
Bajpai, A., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2004). Exploring features for audio clip classification using LP residual and AANN models. In The international conference on intelligent sensing and information processing 2004 (ICISIP 2004), Chennai, India, Jan. 2004 (pp. 305–310).
Yegnanarayana, B., Reddy, K. S., & Kishore, S. P. (2001). Source and system features for speaker recognition using AANN models. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal processing, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA, May 2001 (pp. 409–412).
Mary, L., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2004). Autoassociative neural network models for language identification. In International conference on intelligent sensing and information processing (pp. 317–320). New York: IEEE Press. doi:10.1109/ICISIP.2004.1287674.
Mary, L., Rao, K. S., Gangashetty, S., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2004). Neural network models for capturing duration and intonation knowledge for language and speaker identification. In Int. conf. on cognitive and neural systems (ICCNS), Boston, MA, USA, May 2004.
Rao, K. S. (2011). Role of neural network models for developing speech systems. Sadhana (Springer), 36, 783–836.
Rao, K. S. (2008). Acquisition and incorporation prosody knowledge for speech systems in Indian languages. Ph.D. thesis, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology, Madras, Chennai, India, May 2008.
Mary, L., Rao, K. S., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2005). Neural network classifiers for language identification using syntactic and prosodic features. In 2nd int. conf. intelligent sensing and information processing (ICISIP-2005), Chennai, India, Jan. 2005.
Rao, K. S., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2007). Modeling durations of syllables using neural networks. Computer Speech & Language, 21, 282–295.
Mary, L., Rao, K. S., Gangashetty, S., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2004). Modeling syllable duration in Indian languages using neural networks. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal processing, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, May 2004.
Rao, K. S. (2008). Modeling supra-segmental features of syllables using neural networks. In Speech, audio, image and biomedical signal processing using neural networks (pp. 71–95). Berlin: Springer.
Rao, K. S., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2004). Two-stage duration model for Indian languages using neural networks. In Lecture notes in computer science: Vol. 3316. Neural information processing (pp. 1179–1185). Berlin: Springer.
Reddy, V. R., & Rao, K. S. (2013). Two-stage intonation modeling using feedforward neural networks for syllable based text-to-speech synthesis. Computer Speech & Language, 27(10), 1105–1126.
Koolagudi, S. G., Reddy, R., & Rao, K. S. (2010). Emotion recognition from speech signal using epoch parameters. In IEEE international conference on signal processing and communication (SPCOM), IISc Bangalore, India, July 2010.
Koolagudi, S. G., & Rao, K. S. (2008). Neural network models for capturing prosodic knowledge for emotion recognition. In 12th int. conf. on cognitive and neural systems (ICCNS), Boston, MA, USA, May 2008.
Rao, K. S., & Yegnanarayana, B. (2004). Neural network models for text-to-speech synthesis. In 5th international conference on knowledge based computer systems (KBCS-2004), Hyderabad, India, Dec. 2004 (pp. 520–530).
Rao, K. S., Saroj, V. K., Maity, S., & Koolagudi, S. G. (2011). Recognition of emotions from video using neural network models. Expert Systems with Applications, 38, 13181–13185.
Rao, K. S., Yadav, J., Sarkar, S., Koolagudi, S. G., & Vuppala, A. K. (2012). Neural network based feature transformation for emotion independent speaker identification. International Journal of Speech Technology, 15(3), 335–349.
Rao, K. S., Laskar, R. H., & Koolagudi, S. G. (2007). Voice transformation by mapping the features at syllable level. In Lecture notes in computer science: Vol. 4815. Pattern recognition and machine intelligence (pp. 479–486).
Makhoul, J., Kubala, F., Leek, T., Liu, D., Nguyen, L., Schwartz, R., & Srivastava, A. (2000). Speech and language technologies for audio indexing and retrieval. In Proceedings of the IEEE (Vol. 88, pp. 1338–1353).
Johnson, S., & Woodland, P. C. (2000). A method for direct audio search with applications to indexing and retrieval. In Proc. IEEE int. conf. acoust., speech, signal processing (Vol. 1, pp. 452–455).
Brezeale, D., & Cook, D. J. (2006). Using closed captions and visual features to classify movies by genre. In 7th international workshop on multimedia data mining.
Fischer, S., Lienhart, R., & Effelsberg, W. (1995). Automatic recognition of film genres. In ACM international conference on multimedia (pp. 295–304).
Huang, H.-Y., Shih, W.-S., & Hsu, W.-H. (2008). A film classifier based on low-level visual features. Journal of Multimedia, 3, 26–33.
Oliva, A., & Torralba, A. (2001). Modeling the shape of the scene: A holistic representation of the spatial envelope. International Journal of Computer Vision, 42, 145–175.
Ramachandran, C., Malik, R., Jin, X., Gao, J., Nahrstedt, K., & Han, J. (2009). Videomule: a consensus learning approach to multi-label classification from noisy user-generated videos. In ACM international conference on multimedia.
Rasheed, Z., & Shah, M. (2002). Movie genre classification by exploiting audio-visual features of previews. In International conference on pattern recognition (ICPR).
Rasheed, Z., Sheikh, Y., & Shah, M. (2003). On the use of computable features for film classification. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 15, 52–64.
Roach, M., & Mason, J. (2001). Classification of video genre using audio. In Proc. Eurospeech (Vol. 15, pp. 2693–2696).
van de Sande, K. E. A., Gevers, T., & Snoek, C. G. M. (2008). Evaluation of color descriptors for object and scene recognition. In Proc. IEEE conf. on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR).
Wang, Z., Zhao, M., Song, Y., Kumar, S., & Li, B. (2010). Youtubecat: Learning to categorize wild web videos. In Proc. IEEE conf. on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR).
Wang, Y.-K., & Chang, C.-Y. (2003). Movie scene classification using hidden Markov model. In 16th IPPR conference on computer vision, graphics and image processing (CVGIP 2003), Kinmen, ROC, Aug. 2003 (pp. 196–202).
Yeung, M. M., & Liu, B. L. (1996). Time-constrained clustering for segmentation of video into story unit. In International conference on pattern recognition (pp. 375–380).
Delezoide, B. (2006). Multimedia movie segmentation using low-level and semantic features.
Zhou, H., Hermans, T., Karandikar, A. V., & Rehg, J. M. (2010). Movie genre classification via scene categorization. In ACM international conference on multimedia, Firenze, Italy, Oct. 2010.
Delezoide, B. (2005). Hierarchical film segmentation using audio and visual similarity. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on multimedia and Expo (ICME 05).
Zhai, Y., Rasheed, Z., & Shah, M. (2004). Finite state machines in movie scene classification. In 17th international conference on pattern recognition, Cambridge, UK.
Rabiner, L. R., & Juang, B. H. (1993). Fundamentals of speech recognition. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Quatieri, T. F. (2001). Discrete-time speech signal processing: principles and practice. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Zheng, F., Zhang, G., & Song, Z. (2001). Comparison of different implementations of MFCC. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 16(6), 582–589.
Hogg, R. V., & Ledolter, J. (1987). Engineering statistics. New York: Macmillan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rao, K.S., Nandi, D. & Koolagudi, S.G. Film segmentation and indexing using autoassociative neural networks. Int J Speech Technol 17, 65–74 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-013-9206-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-013-9206-4