Abstract
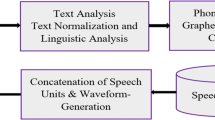
The goal of this paper is to solve the phonetization task of the Arabic text dedicated to text-to-speech synthesis. In this paper, we will describe the steps we followed in order to develop an automatic phonetization system, and the various established rules of phonemic and phonetic transcription. Our text phonetization system is entirely based on a representation according to the Unicode standard, and is divided into two parts. The first part concerns the grapheme-phoneme transcription that combines use of a lexicon of exceptions, and a base of phonemic transcription rules. The second part concerns the generation of allophones by applying phonetic transcription rules to the phonemes obtained from the grapheme-phoneme transcription. The whole system performs an automatic phonetization for Arabic text-to-speech synthesis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-ghamdi, M., Basalamah, M. S., Alsini, M., & Husain, A. (1997). Database of Arabic sounds: Words. In Proceedings of the 15th National Computer Conference, Saudi Arabia (in Arabic).
Al-ghamdi, M., Elshafei, M., & Al-muhtasib, H. (2002). Arabic text-to-speech: Speech units. In Proceeding of the 4th Workshop on Computer and Information Sciences, Dammam (pp. 199–212).
Al-ghamdi, M., Alhamid, A. H., & Aldasuqi, M. M. (2003). Database of Arabic sounds: Sentences. Technical Report, King Abdulaziz City of Science and Technology, Saudi Arabia (in Arabic).
Al-ghamdi, M., Al-muhtaseb, H., & Elshafei, M. (2004). Phonetic rules in Arabic script. King Saud University Journal: Computer Sciences and Information, 16, 1–25.
Al-muhtasib, H., Elshafei, M., & Al-ghamdi, M. (2000). Techniques for high quality arabic speech synthesis. In The third KFUPM workshop on information & computer science (pp. 73–82).
Braga, D., Coelho, L., & Vianna Resende, F. G. (2006). A rule-based grapheme-to-phone converter for TTS systems in European Portuguese. In International Telecommunications Symposium (pp. 328–333).
D’alessandro, C., & Richard, G. (2013). Synthèse de la parole à partir du texte. Techniques de l’Ingénieur, H7288, 1–15.
El-imam, Y. A. (1989). Unrestricted vocabulary Arabic speech synthesis system. IEEE Transactions on Acoustic, Speech and Signal Processing, 12, 1829–1845.
El-imam, Y. A. (2004). Phonetization of Arabic: Rules and algorithms. Computer Speech and Language, 18, 339–373.
Elshafei, M. A. (1991). Toward an Arabic text-to-speech system. The Arabian Journal of Science and Engineering, 16, 339–373.
Elshafei, M., Al-muhtaseb, H., & Al-ghamdi, M. (2002). Techniques for high quality Arabic speech synthesis. Information Sciences, 140, 255–267.
El-bakry, H. M., Rashad, M. Z., & Isma’il, I. R. (2011). Diphone-based concatenative speech synthesis systems for Arabic language. In 10th WSEAS international conference on circuits, systems, electronics, control & signal processing, and the 7th WSEAS international conference on applied and theoretical mechanics (pp. 81–86).
Ghazali, S., Habaili, H., & Zrigui, M. (1990). Correspondance graphème-phonème pour la synthèse de la parole arabe à partir du texte. Tunis: IRSIT Congrès dialogue homme machine.
Harrag, A. (2010). QSDAS: New quranic speech database for Arabic speaker recognition. The Arabian Journal of Science and Engineering, 35, 7–19.
Hamad, M., & Hussain, M. (2011). Arabic text-to-speech synthesizer. In IEEE student conference on research and development, (pp. 409–414).
Imedjdouben, F., & Houacine, A. (2012). Outil de transcription phonétique à partir du texte Arabe. In 11th African conference on research in computer science and applied mathematics (pp. 475–482).
Imedjdouben, F., & Houacine, A. (2013). Automatic phonetization of Arabic text: Modeling approaches and algorithms for advanced computer applications. Studies in Computational Intelligence, 488, 85–94.
Ka-Ho Wong, Wai-Kit Lo, & Meng, H. (2011). Allophonic variations in visual speech synthesis for corrective feedback in Capt. In IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (pp. 5708–5711).
Khalifa O. O., Obaid, M. Z., Naji, A. W., & Daoud J. I. (2011). A rule-based Arabic text-to-speech system based on hybrid synthesis technique. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(6), 342–354.
Rashad, M. Z., El-bakry, H. M., Isma’il, I. R., & Mastorakis, N. (2010). An overview of text-to-speech synthesis techniques. In 4th international conference on communications and information technology, Corfu Island, Greece (pp. 84–89).
Rashad, M. Z., El-bakry, H. M., & Isma’il, I. R. (2010). Diphone speech synthesis system for Arabic using MARY TTS. International Journal of Computer Science & Information Technology (IJCSIT), 2(4), 18–26.
Saidane, T., Zrigui, M., & Ben Ahmed, M. (2004). La Transcription Orthographique-Phonétique de la Langue Arabe. In RÉCITAL, Fès.
Saidane, T., Zrigui, M., & Ben Ahmed, M. (2005). Arabic speech synthesis using a concatenation of polyphones: The results. Lecture notes in computer science: Advances in artificial intelligence, 3501, 406–411.
Stefan-Adrian, T., & Doru-Petru, M. (2009). Rule-based automatic phonetic transcription for the Romanian language. In Computation world: Future computing, service computation, cognitive, adaptive, content, patterns (pp. 682–686).
Tabet, Y., & Boughazi, M. (2011). Speech synthesis techniques. A survey. In 7th international workshop on systems, signal processing and their applications (WOSSPA) (pp. 67–70).
Youssef, A., & Emam, O. (2004). An Arabic TTS System Based on the IBM Trainable Speech Synthesizer. In JEP-TALN, Fès.
Zemirli, Z., Vigouroux, N., & Sellami, M. (1996). SYNTHAR+: un système de pré-traitement de textes arabes en vue de leur synthèse orale sous le système Multivox. In 3th African conference on research in computer science and applied mathematics (pp. 719–729).
Zemirli, Z. (2006). ARAB_TTS: An Arabic text to speech synthesis. In IEEE international conference on computer systems and applications (pp. 976–979).
Zeki, M., Khalifa, O. O., & Naji, A. W. (2010). Development of an Arabic text-to-speech system. In IEEE international conference on computer and communication engineering, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia (pp. 1–5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imedjdouben, F., Houacine, A. Development of an automatic phonetization system for Arabic text-to-speech synthesis. Int J Speech Technol 17, 417–426 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-014-9241-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-014-9241-9