Abstract
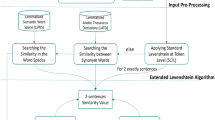
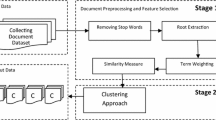
An efficient method is introduced to represent large Arabic texts in comparatively smaller size without losing significant information. The proposed method uses the distributional semantics to build the word-context matrix representing the distribution of words across contexts and to transform the text into a vector space model (VSM) representation based on word semantic similarity. The linguistic features of the Arabic language, in addition to the semantic information extracted from different lexical-semantic resources such as Arabic WordNet and named entities’ gazetteers are used to improve the text representation and to create word clusters of similar and related words. Distributional similarity measures have been used to capture the words’ semantic similarity and to create clusters of similar words. The conducted experiments have shown that the proposed method significantly reduces the size of text representation by about 27 % compared with the stem-based VSM and by about 50 % compared with the traditional bag-of-words model. Their results have shown that the amount of dimension reduction depends on the size and shape of the windows of analysis as well as on the content of the text.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Almaany. (2014). Dictionary and glossary. http://www.almaany.com/.
Awajan, A. (2007). Arabic text preprocessing for the natural language processing applications. Arab Gulf Journal of Scientific Research, 25(4), 179–189.
Awajan, A. (2015). Semantic vector space model for reducing arabic text dimensionality. In Proceedings of the 5th international conference on digital information and communication technology and its applications, Lebanon, (pp. 129–135). April 29–May 1, 2015.
Baker, K. (2013). Singular value decomposition tutorial. Note for NLP Seminar. 1–24. Accessed December 2013, from www.ling.ohio-state.edu/~kbaker/pubs/Singular_Value_Decomposition_Tutorial.pdf.
Beesley, K. R. (1998). Consonant spreading in Arabic stems. In COLING-ACL’98, vol 1, pp 117–123, Montreal, Quebec, Canada, August 10–14.
Biemann, C. (2006). Chinese whispers—An efficient graph clustering algorithm and its application to natural language processing problems. Workshop on TextGraphs, at HLT-NAACL 2006, pp. 73–80
Boudlal, A., Lakhouaja, A., Mazroui, A., Meziane, A., Ould Abdallahi, O. B. M., & Shoul, M. (2010). Alkhalil Morpho Sys: A morphosyntactic analysis system for Arabic texts. In International Arab conference on information technology. http://www.itpapers.info/acit10/Papers/f653.
Bullinaria, J. A., & Levy, J. P. (2012). Extracting semantic representations from word co-occurrence statistics: Stop-lists, stemming and SVD. Behavior Research Methods, 44, 890–907.
Duwairi, R., Al-Refai, M. N., & Khasawneh, N. (2009). Feature reduction techniques for Arabic text categorization. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 60(11), 2347–2352.
Elkateb, S., Black, W., Rodríguez, H., Alkhalifa, M., Vossen, P., Pease, A., & Fellbaum, C. (2006). Building a WordNet for Arabic. In Proceedings of the fifth international conference on language resources and evaluation (LREC 2006). Genoa, Italy, May 22–28, 2006.
Froud, H., Lachkar, A., & Ouatik, S. A. (2012). A comparative study of root-based and stem-based approaches for measuring similarity between Arabic words for Arabic text mining applications. Advanced Computing: An International Journal (ACIJ), 3(6).
Green, S., & Manning, C. D. (2010). Better Arabic parsing: Baselines, evaluations, and analysis. In COLING, Beijing (pp. 394–402).
Habash, N. (2010). Introduction to Arabic natural language processing. San Rafael: Morgan & Claypool Publishers.
Hagiwara, M. (2008). A supervised learning approach to automatic synonym identification based on distributional features. In Proceedings of the ACL-08, Columbus, June 2008 (pp. 1–6).
Harrag, F., El-Qawasmah, E., & Al-Salman, A. M. (2010). Comparing dimension reduction techniques for Arabic text classification using BPNN algorithm. In IEEE first international conference on integrated intelligent computing, pp. 6–11.
Harris, Z. (1954). Distributional structure. Word, 10(23), 146–162.
Hasnah, A. M., & Al-Ja’am, J. M. (2002). Thesaurus-based query disambiguation method for cross-language information retrieval. International Journal Intelligent Computing and Information Sciences, 2(2), 58–68.
Heintz, I. (2010). Arabic language modeling with stem-derived morphemes for automatic speech recognition. Ph.D. thesis, Graduate School of The Ohio State University.
Hmeidi, I., Kanaan, G., & Evens, M. (1997). Design and implementation of automatic indexing for information retrieval with arabic documents. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 48(10), 867–881.
Kirchhoff, K., Vergyri, D., Duh, K., Bilmes, J., & Stolcke, A. (2006). Morphology-based language modeling for conversational Arabic speech recognition. Computer Speech & Language, 20(4), 589–608.
Martins, C. A., Monard, M. C., & Matsubara, E. T. (2003). Reducing the dimensionality of bag-of-words text representation used by learning algorithms. In Proceedings of 3rd IASTED international conference on artificial intelligence and applications (AIA2003), Benalmádena, Espanha (pp. 228–233). Calgary: Acta Press.
Mihalcea, R., & Tarau, P. (2004). TextRank: Brining order into texts. In Proceedings of EMNLP 2004. Association for Computational Linguistics, Barcelona, Spain (pp. 404–411).
Parkinson, D. B. (2005). Using Arabic synonyms. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Saad, M. K., & Ashour, W. (2010). OSAC: Open Source Arabic Corpus, the 6th International Symposium on Electrical and Electronics Engineering and Computer Science, European University of Lefke, Cyprus, from http://sourceforge.net/projects/ar-text-mining/files/ArabicCorpora.
Salton, G., & McGill, M. J. (1986). Introduction to modern information retrieval. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. Inc.
Salton, G., Wong, A., & Yang, C. S. (1975). A vector space model for automatic indexing. Communication of the ACM, 18(11), 613–620.
Shaalan, K. (2014). A survey of Arabic named entity recognition and classification. Computational Linguistics, 40(2), 469–510. doi:10.1162/COLIa00178.
Turney, P. D., & Pantel, P. (2010). From frequency to meaning: Vector space models of semantics. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 37, 141–188.
Van Rijsbergen, C. J. (1979). Information retrieval (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Computer Laboratory, University of Cambridge.
Xu, J., Fraser, A., & Weischedel, R. (2002). Empirical studies in strategies for Arabic retrieval. In SIGIR’02, Proceedings of the 25th annual international ACMSIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval, Tampere, Finland (pp. 269–274). August 11–15, 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Awajan, A. Semantic similarity based approach for reducing Arabic texts dimensionality. Int J Speech Technol 19, 191–201 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-015-9284-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-015-9284-6