Abstract
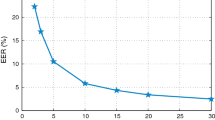
The performance of state-of-the-art speaker verification in uncontrolled environment is affected by different variabilities. Short duration variability is very common in these scenarios and causes the speaker verification performance to decrease quickly while the duration of verification utterances decreases. Linear discriminant analysis (LDA) is the most common session variability compensation algorithm, nevertheless it presents some shortcomings when trained with insufficient data. In this paper we introduce two methods for session variability compensation to deal with short-length utterances on i-vector space. The first method proposes to incorporate the short duration variability information in the within-class variance estimation process. The second proposes to compensate the session and short duration variabilities in two different spaces with LDA algorithms (2S-LDA). First, we analyzed the behavior of the within and between class scatters in the first proposed method. Then, both proposed methods are evaluated on telephone session from NIST SRE-08 for different duration of the evaluation utterances: full (average 2.5 min), 20, 15, 10 and 5 s. The 2S-LDA method obtains good results on different short-length utterances conditions in the evaluations, with a EER relative average improvement of 1.58%, compared to the best baseline (WCCN[LDA]). Finally, we applied the 2S-LDA method in speaker verification under reverberant environment, using different reverberant conditions from Reverb challenge 2013, obtaining an improvement of 8.96 and 23% under matched and mismatched reverberant conditions, respectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Notes
The standard speaker verification method based on LDA session compensation and PLDA model as classifier.
The term “insufficient” refers to the fact that each speaker utterances in the data set does not contains all the variability conditions of interest.
The UBM refers to a universal background model of the population.
References
Dehak, N., Kenny, P. J., Dehak, R., Dumouchel, P., & Ouellet, P. (2011). Front-end factor analysis for speaker verification. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 19(4), 788–798.
Garcia-Romero, D., Zhou, X., & Espy-Wilson, C. Y. (2012). Multicondition training of Gaussian PLDA models in i-vector space for noise and reverberation robust speaker recognition. In Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 4257–4260.
Gonzalez-Rodriguez, J. (2014). Evaluating automatic speaker recognition systems: An overview of the NIST speaker recognition evaluations (1996–2014). Loquens, 1(1), 007.
Hasan, T., Saeidi, R., Hansen, J. H., & van Leeuwen, D. A. (2013). Duration mismatch compensation for i-vector based speaker recognition systems. In Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 7663–7667.
Hautamäki V., Cheng Y. C., Rajan P., & Lee C. H. (2013). Minimax i-vector extractor for short duration speaker verification. In Proceedings of the 14th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (ISCA), pp. 3708–3712.
Kanagasundaram, A., Vogt, R., Dean, D. B., Sridharan, S., & Mason, M. W. (2011). I-vector based speaker recognition on short utterances. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (ISCA), pp. 2341–2344.
Kanagasundaram, A., Vogt, R. J., Dean, D. B., & Sridharan, S. (2012). PLDA based speaker recognition on short utterances. In The Speaker and Language Recognition Workshop (Odyssey). ISCA.
Kanagasundaram, A., Dean, D., Gonzlez Domnguez, J., Sridharan, S., Ramos, D., & Gonzalez-Rodriguez, J. (2013). Improving short utterance based i-vector speaker recognition using source and utterance-duration normalization techniques. In Proceedings of the 14th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (ISCA), pp. 2465–2469.
Kanagasundaram, A., Dean, D., Sridharan, S., & Fookes, C. (2016). Improving short utterance plda speaker verification using suv modelling and utterance partitioning approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.04965.
Kanagasundaram, A., Dean, D., Sridharan, S., Ghaemmaghami, H., & Fookes, C. (2017). A study on the effects of using short utterance length development data in the design of gplda speaker verification systems. International Journal of Speech Technology. doi:10.1007/s10772-017-9402-8.
Kenny, P. (2005). Joint factor analysis of speaker and session variability: Theory and algorithms. CRIM, Montreal (Report) CRIM-06/08-13.
Kenny, P. (2010). Bayesian speaker verification with heavy tailed priors. In Proceedings of The Speaker and Language Recognition Workshop (Odyssey), pp. 14.
Kenny, P., Boulianne, G., & Dumouchel, P. (2005). Eigenvoice modeling with sparse training data. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 13(3), 345–354.
Kenny, P., Stafylakis, T., Ouellet, P., Alam, M. J., & Dumouchel, P. (2013). PLDA for speaker verification with utterances of arbitrary duration. In Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 7649–7653
Kenny, P., Stafylakis, T., Ouellet, P., & Alam, M. J. (2014). JFA-based front ends for speaker recognition. In Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 1705–1709.
Kinoshita, K., Delcroix, M., Yoshioka, T., Nakatani, T., Sehr, A., Kellermann, W., & Maas, R. (2013). The REVERB challenge: A common evaluation framework for dereverberation and recognition of reverberant speech. In Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA), pp. 1–4.
Mandasari, M. I., McLaren, M., & van Leeuwen, D. A. (2011). Evaluation of i-vector speaker recognition systems for forensic application. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), pp. 21–24.
Mandasari, M. I., Saeidi, R., McLaren, M., & van Leeuwen, D. A. (2013). Quality measure functions for calibration of speaker recognition systems in various duration conditions. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 21(11), 2425–2438.
Mandasari, M. I., Saeidi, R., & van Leeuwen, D. A. (2015). Quality measures based calibration with duration and noise dependency for speaker recognition. Speech Communication, 72, 126–137.
McLaren, M., & van Leeuwen, D. (2011, May). Improved speaker recognition when using i-vectors from multiple speech sources. In Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 5460–5463.
McLaren, M., & Van Leeuwen, D. (2011). Source-normalised-and-weighted LDA for robust speaker recognition using i-vectors. In Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 5456–5459.
McLaren, M., & Van Leeuwen, D. (2012). Source-normalized LDA for robust speaker recognition using i-vectors from multiple speech sources. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 20(3), 755–766.
Merhav, N., & Lee, C. H. (1993). A minimax classification approach with application to robust speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 1(1), 90–100.
Prince, S. J., & Elder, J. H. (2007). Probabilistic linear discriminant analysis for inferences about identity. In Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1–8.
Ribas D, Vincent E, & Calvo JR (2015). Full multicondition training for robust i-vector based speaker recognition. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), pp. 1057–1061.
Sarkar, A. K., Matrouf, D., Bousquet, P. M., & Bonastre, J. F. (2012). Study of the effect of i-vector modeling on short and mismatch utterance duration for speaker verification. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (Interspeech), pp. 2662–2665.
Scheffer, N., Ferrer, L., Lawson, A., Lei, Y., & McLaren, M. (2013). Recent developments in voice biometrics: Robustness and high accuracy. In Technologies for Homeland Security (HST), pp. 447–452.
Sohn, J., Kim, N. S., & Sung, W. (1999). A statistical model-based voice activity detection. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 6(1), 1–3.
Stafylakis, T., Kenny, P., Ouellet, P., Perez, J., Kockmann, M., & Dumouchel, P. (2013). Text-dependent speaker recognition using PLDA with uncertainty propagation. Matrix, 500, 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reyes-Díaz, F.J., Hernández-Sierra, G. & Calvo de Lara, J.R. Two-space variability compensation technique for speaker verification in short length and reverberant environments. Int J Speech Technol 20, 475–485 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-017-9414-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-017-9414-4