Abstract
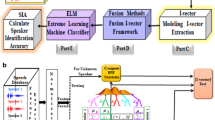
Whispered speech speaker identification system is one of the most demanding efforts in automatic speaker recognition applications. Due to the profound variations between neutral and whispered speech in acoustic characteristics, the performance of conventional speaker identification systems applied on neutral speech degrades drastically when compared to whisper speech. This work presents a novel speaker identification system using whispered speech based on an innovative learning algorithm which is named as extreme learning machine (ELM). The features used in this proposed system are Instantaneous frequency with probability density models. Parametric and nonparametric probability density estimation with ELM was compared with the hybrid parametric and nonparametric probability density estimation with Extreme Learning Machine (HPNP-ELM) for instantaneous frequency modeling. The experimental result shows the significant performance improvement of the proposed whisper speech speaker identification system.








Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Campbell, W. M., Campbell, J. P., Reynolds, D. A., Singer, E., & Torres-Carrasquillo, P. A. (2006). Support vector machines for speaker and language recognition. Computer Speech & Language, 20(2), 210–229.
Campbell, W. M., Sturim, D. E., & Reynolds, D. A. (2006). Support vector machines using GMM supervectors for speaker verification. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 13(5), 308–311.
Fan, X., & Hansen, J. H. (2011). Speaker identification within whispered speech audio streams. IEEE transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 19(5), 1408–1421.
Gu, X., & Zhao, H. (2010). Whispered speech speaker identification based on SVM and FA. In Audio Language and Image Processing (ICALIP), 2010 International Conference on (pp. 757–760). IEEE.
Haim, P., Joseph, F., & Ian, J. (2006). A study of Gaussian mixture models ofcolor and texture features for image classification and segmentation. Pattern Recognition, 39(4), 695–706, 2006.
Huang, G. B., Wang, D., Lan, Y. (2011). Extreme learning machine: A survey. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2, 107–122.
Huang, G. B., Zhu, Q. Y., & Siew, C. K. (2006). Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing, 70(1), 489–501.
Ito, T., Takeda, K., & Itakura, F. (2005). Analysis and recognition of whispered speech. Speech Communication, 45(2), 139–152.
Jain, K., Ross, A., & Prabhakar, S. (2004). An introduction to biometric recognition. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 14(1), 4–20.
Jin, Q., Jou, S.-C. S., & Schultz, T. (2007). Whispering speaker identification. In Multimedia and Expo, 2007 IEEE International Conference on, pp. 1027–1030.
John, H. L. (2007). Analysis and classification of speech Mode: Whispered through shouted. 8th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association, Interspeech.
Jovičić, S. T. (1998). Formant feature differences between whispered and voiced sustained vowels. Acta Acustica United with Acustica, 84(4), 739–743.
Jovičić, S. T., & Šarić, Z. (2008). Acoustic analysis of consonants in whispered speech. Journal of Voice, 22(3), 263–274.
Li, Q. (2001). A detection approach to search-space reduction for HMM state alignment in speaker verification. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 9(5), 569–578.
Mak, M. W., & Kung, S. Y. (2000). Estimation of elliptical basis function parameters by the EM algorithm with application to speaker verification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 11(4), 961–969.
Morris, R. W., & Clements, M. A. (2002). Reconstruction of speech from whispers. Medical Engineering & Physics, 24(7), 515–520.
Oyang, Y. J., Ou, Y. Y., Hwang, S. C., Chenl, C. Y., & Chang, D. T. H. (2005). Data classification with a relaxed model of variable kernel density estimation. In Proc. IEEE Int. Joint Conf. Neural Netw, vol. 5, pp. 2831–2836.
Pellom, L., & Hansen, J. H. L. (1998). An efficient scoring algorithm for Gaussian mixture model based speaker identification. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 5(11) 281–284.
Poignant, J., Besacier, L., & Quenot, G. (2014). Unsupervised speaker identification in TV broadcast based on written names. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 23, 57–68.
Sadjadi, S. O., & Hansen, J. H. L. (2014). Blind spectral weighting for robust speaker identification under reverberation mismatch. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 22(5), 937–945.
Wang, J. C., Chin, Y. H., Hsieh, W. C., Lin, C. H., Chen, Y. R., & Siahaan, E. (2015). Speaker identification with whispered speech for the access control system. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 12(4), 1191–1199.
Wang, J. C., Yang, C. H., Wang, J. F., & Lee, H. P. (2007). Robust speaker identification and verification.” IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine, 2(2), 52–59.
Xu, J., & Zhao, H. (2012). Speaker identification with whispered speech using unvoiced-consonant phonemes. In Proc. Int. Conf. Image Anal. Signal Process, pp. 9–11.
Zhang, C., & Hansen, J. H. (2007). Analysis and classification of speech mode: Whispered through shouted. In Interspeech (Vol. 7, pp. 2289–2292).
Zhao, Y., Wang, & Wang, D. (2014). Robust speaker identification in noisy and reverberant conditions. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 22(4), 836–845.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sangeetha, J., Jayasankar, T. A novel whispered speaker identification system based on extreme learning machine. Int J Speech Technol 21, 157–165 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-017-9488-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-017-9488-z