Abstract
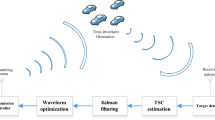
We study a diversity scheme based on waveform design and space-time adaptive processing to improve the detection performance of radar sensor networks in the presence of certain types of interference. To reduce the interference between radar sensors and maximize the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio, we use an orthogonality criterion to design waveforms for radar sensors. Besides, performance of radar sensor networks depends largely on clutter which is extended in both angle and range and is spread in Doppler frequency. By using the space-time adaptive processing, effects of clutter can be suppressed. We also propose a receiver for diversity combining and, as an application example, we investigate the detection performance of radar sensor networks using the proposed diversity scheme. Simulation results for both non-fluctuating targets and fluctuating targets show that the performance of the proposed scheme is superior to that of the single radar with the spatial-temporal diversity only.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Kadambe, Feature Discovery and Sensor Discrimination in a Network of Distributed Radar Sensors for Target Tracking, HRL Laboratories, LLC, 2001.
C. J. Baker and A. L. Hume, Netted radar sensing, IEEE A&E Systems Magazine, February 2002.
R. Fitzgerald, Effects of range-doppler coupling on chirp radar tracking acuracy, IEEE Transaction on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, Vol. 10, pp. 528–532, 1974.
M. R. Bell, Information theory and radar waveform design, IEEE Transaction on Information Theory, Vol. 39, No. 5, pp. 1578–1597, 1993.
C. E. Baum, et al, The singularity expansion method and its application to target identification, Proceedings of the IEEE, Vol. 79, No. 10, 1991.
Q. Liang, Waveform design and diversity in radar sensor networks: theoretical analysis and application to automatic target recognition, Int. Workshop on Wireless Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks, June 2006, New York.
W. L. Melvin, A STAP overview, IEEE A&E Systems Magazine, Vol 19, No. 1, pp. 19–35, 2004
J. Ward, Space-time Adaptive Processing for Airborne Radar, Lincoln Lab Technical Report 1015, December 1994.
J. R. Guerci, Space-time Adaptive Processing for Radar, Artech House, 2003.
M. A. Richards, Fundamentals of Radar Signal Processing, McGraw-Hill, New York, 2005.
P. Swerling, Probability of detection for fluctuating targets, IRE Transaction on Information Theory, Vol IT-6, pp. 269–308, 1960.
B. R. Mahafza, Radar Systems Analysis and Design, Chapman & Hall, 2005.
R. S. Adve et al., Practical joint domain localized adaptive processing in homogeneous and non-homogeneous environments: part I—homogeneous environments, IEE Part F: Proceedings on Radar, Sonar and Navigation, October 1999.
H. D. Ly and Q. Liang, Spatial-temporal-frequency diversity in radar sensor networks, IEEE Military Communications Conference, October 2006, Washington DC.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Office of Naval Research (ONR) Young Investigator Award under Grant N00014-03-1-0466
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ly, H.D., Liang, Q. Diversity in Radar Sensor Networks: Theoretical Analysis and Application to Target Detection. Int J Wireless Inf Networks 16, 209–216 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10776-009-0097-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10776-009-0097-x