Abstract
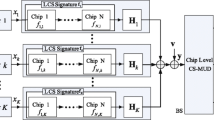
In this paper, we identify issues and possible solutions in the key area of large-scale antenna systems, also know as Massive Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) systems. Additionally, we propose the use of Massive MIMO technology as a means to tackle the uplink mixed-service communication problem. Under the assumption of an available physical narrowband shared channel (PNSCH), the capacity of the MTC network and, in turn, that of the whole system, can be increased by grouping Machine-Type Communication (MTC) devices into clusters and letting each cluster share the same time-frequency physical resource blocks. We study the feasibility of applying sub-optimal linear detection to the problem of detecting a large number of MTC devices sharing the same time-frequency resources at the uplink of a base station (BS) equipped with a large number of antennas, M. In our study, we derive the achievable lower-bound rates for the studied sub-optimal linear detectors and show that the transmitted power of each MTC device can be reduced as M increases, which is a very important result for power-constrained MTC devices running on batteries. Our simulation results suggest that, as M is made progressively larger, the performance of sub-optimal linear detection methods approach the matched filter bound, also known as perfect interference-cancellation bound.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
ITU-R, Recommendation ITU-R M.2083, IMT Vision—framework and overall objectives of the future development of IMT for 2020 and beyond, September 2015.
Huawei Technologies CO., LTD, 5G Network Architecture—a high-level perspective, White Paper, Online. https://www.huawei.com/en/industry-insights/outlook/mobile-broadband/insights-reports/5g-network-architecture, 2016.
4G Americas, 4G Americas’ recommendations on 5G requirements and solutions, Online. http://www.4gamericas.org/en/ resources/white-papers/, October 2014.
G. Fettweis and S. Alamouti, 5G: personal mobile internet beyond what cellular did to telephony, IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol. 52, No. 2, pp. 140–145, 2014.
G. Wunder, et al., 5GNOW: non-orthogonal asynchronous waveforms for future mobile applications, IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol. 52, No. 2, pp. 97–105, 2014.
D. Boswarthick, O. Elloumi and O. Hersent, M2M Communications: A Systems Approach, WileyHoboken, 2012.
A. Elmangoush, H. Coskun, S. Wahle, N. Blum and T. Magedanz, Promoting M2M application development for smart city, 29th meeting of the Wireless World Research Forum (WWRF), October 2012.
J. M. Corchado, J. Bajo, D. I. Tapia and A. Abraham, Using heterogeneous wireless sensor networks in a telemonitoring system for healthcare, IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, Vol. 14, No. 2, pp. 234–240, 2010.
P. Papadimitratos, A. de La Fortelle, K. Evensen, R. Brignolo and S. Cosenza, Vehicular communication systems: enabling technologies, applications, and future outlook on intelligent transportation, IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol. 11, No. 1, pp. 84–95, 2009.
K. Moslehi and R. Kumar, A reliability perspective of the smart grid, IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid, Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 57–64, 2010.
Elias Kyriakides and Marios Polycarpou, Intelligent Monitoring Control and Security of Critical Infrastructure Systems, vol. 1st, SpringerBerlin, 2015.
C. S. Pattichis, E. Kyriacou, S. Voskarides, M. S. Pattichis and R. Istepanian, Wireless telemedicine systems: an overview, IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, Vol. 44, No. 2, pp. 143–153, 2002.
Anita Majerowicz and Susan Tracy, Telemedicine: bridging gaps in healthcare delivery, Journal of AHIMA, Vol. 81, No. 5, pp. 52–53, 2010.
G. Araniti, C. Campolo, M. Condoluci, A. Iera and A. Molinaro, LTE for vehicular networking: a survey, IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol. 51, No. 5, pp. 148–157, 2013.
T. ElBatt, S. K. Goel, G. Holland, H. Krishnan, and J. Parikh, Cooperative collision warning using dedicated short range wireless communications, International Workshop on Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (VANET), pp. 1–9, September 2006.
C. Ide, F. Kurtz and C. Wietfeld, Cluster-based vehicular data collection for efficient LTE machine-type communication, IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC), September 2013.
F. da Costa, Rethinking the Internet of Things: A Scalable Approach to Connecting Everything, vol. 1st, ApressNew York, 2014.
B. C. Villaverde, et al., Service discovery protocols for constrained machine-to-machine communications, IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, Vol. 16, No. 1, pp. 41–60, 2014.
G. Wunder, M. Kasparick, and P. Jung., Spline waveforms and interference analysis for 5G random access with short message support, arXiv:1501.02917, Online. http://arxiv.org/pdf/1501.02917.pdf, January 2015.
G. Wunder, P. Jung, and C. Wang, Compressive random access for Post-LTE systems, IEEE ICC - workshop on massive uncoordinated access protocols, pp. 539–544, June 2014.
J. G. Andrews, et al., What will 5G be?, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, Vol. 32, No. 6, pp. 1065–1082, 2014.
Felipe A. P. deFigueiredo, et al., A spectrum sharing framework for intelligent next generation wireless networks, IEEE Access, Vol. 6, pp. 60704–60735, 2018.
T. L. Marzetta, Noncooperative cellular wireless with unlimited numbers of base station antennas, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, Vol. 9, No. 11, pp. 3590–3600, 2010.
E. G. Larsson, F. Tufvesson, O. Edfors and T. L. Marzetta, Massive MIMO for next generation wireless systems, IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol. 52, No. 2, pp. 186–195, 2014.
Emil Bjornson, Erik G. Larsson and Thomas L. Marzetta, Massive MIMO: ten myths and one critical question, IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol. 54, No. 2, pp. 114–123, 2016.
Emil Bjornson, Jakob Hoydis and Luca Sanguinetti, Massive MIMO networks: spectral, energy, and hardware efficiency, Foundations and Trends in Signal Processing, Vol. 11, No. 3–4, pp. 154–655, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1561/2000000093.
F. A. P. de Figueiredo, F. A. C. M. Cardoso, R. R. Lopes and J. P. Miranda, On the application of massive MU-MIMO in the uplink of machine type communication systems, International workshop on telecommunications (IWT), June 2015.
J. P. Miranda, A. Farhang, N. Marchetti, F. A. P. de Figueiredo, F. A. C. M. Cardoso, and F. Figueiredo, On massive MIMO and its applications to machine type communications and FBMC-based networks, EAI Endorsed Transactions on Ubiquitous Environments, vol. 2, no. 5, July 2015.
Felipe A. P. de Figueiredo, Fabbryccio A. C. M. Cardoso, Ingrid Moerman and Gustavo Fraidenraich, On the application of massive MIMO systems to machine type communications, IEEE Access, Vol. 7, No. 12, pp. 2589–2611, 2018.
Andres Laya, Luis Alonso and Jesus Alonso-Zarate, Is the random access channel of LTE and LTE—A suitable for M2M communications?, A Survey of Alternatives, IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, Vol. 16, No. 1, pp. 4–16, 2014.
Stefania Sesia, Issam Toufik and Matthew Baker, LTE—The UMTS Long Term Evolution: From Theory to Practice, WileyHoboken, 2009. ISBN:9780470697160.
S.-Y. Lien, K.-C. Chen and Y. Lin, Toward ubiquitous massive accesses in 3GPP machine-to-machine communications, IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol. 49, No. 4, pp. 66–74, 2011.
M.-Y. Cheng, G.-Y. Lin, H.-Y. Wei and A.-C. Hsu, Overload control for machine-type-communications in LTE-advanced system, IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol. 50, No. 6, pp. 38–45, 2012.
M. Gerasimenko et al., Energy and delay analysis of LTE-advanced RACH performance under MTC overload, IEEE Globecom Workshops, pp. 1632–1637, December 2012.
U. Phuyal, A. Koc, M.-H. Fong, and R. Vannithamby, Controlling access overload and signaling congestion in M2M networks, Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, pp. 591–595, November 2012.
J. R. Barry, E. A. Lee and D. G. Messerschmitt, Digital Communication, vol. 3rd, SpringerBerlin, 2004.
Shepard, C. et al., Argos: practical many-antenna base stations, International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom), pp. 53–64, August 2012.
R. Janaswamy, Effect of element mutual coupling on the capacity of fixed length linear arrays, IEEE Antennas Wireless Propagation Letters, Vol. 1, No. 1, pp. 157–160, 2002.
J. W. Wallace and M. A. Jensen, Mutual coupling in MIMO wireless systems: a rigorous network theory analysis, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, Vol. 3, No. 4, pp. 1317–1325, 2004.
B. K. Lau, et al., Impact of matching network on bandwidth of compact antenna arrays, IEEE Transactions on Antennas Propagation, Vol. 54, No. 11, pp. 3225–3258, 2006.
A. Sibille, C. Oestges and A. Zanella, MIMO: From Theory to Implementation, Academic PressCambridge, 2010.
X. Artiga, B. Devillers and J. Perruisseau-Carrier, On the selection of radiating elements for compact indoor massive-multiple input multiple output base stations, IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, Vol. 8, No. 1, pp. 1–9, 2014.
A. L. Moustakas, et al., Communication through a diffusive medium: coherence and capacity, Science, Vol. 287, pp. 287–290, 2000.
Gao, X., Tufvesson, F. and Edfors, O., Massive MIMO channels—measurements and models, Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, November 2013.
S. Wu, C.-X. Wang, Y. Yang, W. Wang, and X. Gao, Performance comparison of massive MIMO channel models, IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), July 2016.
Zheng, K. Ou, S. and Yin, X., Massive MIMO channel models: a survey, International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, vol. 2014, 10 pages, June 2014.
Stephan Jaeckel, Leszek Raschkowski, Kai Borner and Lars Thiele, QuaDRiGa: a 3-D multi-cell channel model with time evolution for enabling virtual field trials, IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, Vol. 62, No. 6, pp. 3242–3256, 2014.
F. Rusek, et al., Scaling up MIMO: opportunities and challenges with very large arrays, IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, Vol. 30, No. 1, pp. 40–60, 2013.
Z. Jiang, et al., Achievable rates of FDD massive MIMO systems with spatial channel correlation, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, Vol. 14, No. 5, pp. 2868–2882, 2015.
J. Jose, et al., Pilot contamination and precoding in Multi-Cell TDD systems, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, Vol. 10, No. 8, pp. 2640–2651, 2011.
Kaltenberger, F. et al., Relative channel reciprocity calibration in MIMO/TDD systems, Future Network and Mobile Summit, June 2010.
R. Rogalin et al., Hardware-impairment compensation for enabling distributed large-scale MIMO, Information Theory and Applications Workshop (ITA), February 2013.
R. Rogalin, et al., Scalable synchronization and reciprocity calibration for distributed multiuser MIMO, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, Vol. 13, No. 4, pp. 1815–1831, 2014.
H. Q. Ngo and E. G. Larsson, EVD-based channel estimations for multicell multiuser MIMO with very large antenna arrays, IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), March 2012.
A. Ashikhmin and T. L. Marzetta, Pilot contamination precoding in multi-cell large scale antenna systems, IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (ISIT), July 2012.
H. Yin, et al., A coordinated approach to channel estimation in large-scale multiple-antenna systems, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, Vol. 31, No. 2, pp. 264–273, 2013.
R. Mueller, M. Vehkaperae and L. Cottatellucci, Blind Pilot Decontamination, IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, Vol. 8, No. 5, October 2014.
O. Elijah, C. Y. Leow, T. A. Rahman, S. Nunoo and S. Z. Iliya, A comprehensive survey of pilot contamination in massive MIMO-5G system, IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, Vol. 18, No. 2, pp. 905–923, 2016.
F. A. P. de Figueiredo et. al., Channel estimation for massive MIMO TDD systems assuming pilot contamination and flat fading, EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, vol. 2018, no. 14, January 2018.
R. C. de Lamare, Massive MIMO systems: signal processing challenges and research trends, URSI Radio Science Bulletin, 2013.
K. Zu, R. C. de Lamare and M. Haardt, Generalized design of low-complexity block diagonalization type precoding algorithms for multiuser MIMO systems, IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. 61, No. 10, pp. 4232–4242, 2013.
G. Caire and S. Shamai, On the achievable throughput of a multiantenna Gaussian broadcast channel, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, Vol. 49, No. 7, pp. 1691–1706, 2003.
C. Windpassinger, et al., A performance study of MIMO detectors, IIEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, Vol. 5, No. 8, pp. 2004–2008, 2006.
C. B. Peel, et al., A vector-perturbation technique for near-capacity multiantenna communication, part I: Channel inversion and regularization, IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. 53, No. 1, pp. 195–202, 2005.
Hien Quoc Ngo, Massive MIMO: Fundamentals and System Designs, Linkoping UniversitySweden, 2015.
S. Verdu, Multiuser Detection, vol. 1st, Cambridge University PressCambridge, 1998.
Y.-C. Liang, E. Y. Cheu, L. Bai and G. Pan, On the relationship between MMSE-SIC and BI-GDFE receivers for large multiple-input multiple-output channels, IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, Vol. 56, No. 8, pp. 3627–3637, 2008.
H. Zhao, H. Long and W. Wang, Tabu search detection for MIMO systems, IEEE PIMRC, 2007. pp. 1–5.
Y. Sun, A family of likelihood ascent search multiuser detectors: an upper bound of bit error rate and a lower bound of asymptotic multiuser efficiency, IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. 57, No. 6, pp. 1743–1752, 2009.
J. Jaldén and B. Ottersten, On the complexity of sphere decoding in digital communications, IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, Vol. 53, No. 4, pp. 1474–1484, 2005.
L. Barbero and J. Thompson, Fixing the complexity of the sphere decoder for MIMO detection, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, Vol. 7, No. 6, pp. 2131–2142, 2008.
A. Paulraj, R. Nabar and D. Gore, Introduction to Space-Time Wireless Communications, Cambridge University PressCambridge, 2003.
D. Tse and P. Viswanath, Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Cambridge University PressCambridge, 2005.
Monowar Hasan, Ekram Hossain and Dusit Niyato, Random access for machine-to-machine communication in LTE-advanced networks: issues and approaches, IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol. 51, No. 6, pp. 86–93, 2013.
M. S. Ali, E. Hossain and D. I. Kim, LTE/LTE-A random access for massive machine-type communications in smart cities, IEEE Communications Magazine, Vol. 55, No. 1, pp. 76–83, 2017.
H. S. Jang, S. M. Kim, K. S. Ko, J. Cha and D. K. Sung, Spatial group based random access for M2M communications, IEEE Communications Letters, Vol. 18, No. 6, pp. 961–964, 2014.
S. K. Sharma, and X. Wang, Towards massive machine type communications in ultra-dense cellular iot networks: current issues and machine learning-assisted solutions, arXiv:1808.02924, 2018.
Felipe A. P. de Figueiredo, et al., Multi-stage based cross-correlation peak detection for LTE random access preambles, Revista Telecomunicações, Vol. 15, pp. 1–7, 2013.
Thomas L. Marzetta, Erik G. Larsson and Hong Yang, Hien Quoc Ngo, Fundamentals of Massive MIMO, vol. 1st, Cambridge University PressCambridge, 2016.
Shendi Wang, John S. Thompson and Peter M. Grant, Closed-form expressions for ICI/ISI in filtered OFDM systems for asynchronous 5G uplink, IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. 65, No. 11, pp. 4886–4898, 2017.
J. Abdoli, M. Jia, and J. Ma, Filtered OFDM: a new waveform for future wireless systems, IEEE International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), July 2015.
H. Q. Ngo, E. G. Larsson and T. L. Marzetta, Energy and spectral efficiency of very large multiuser MIMO systems, IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. 61, No. 4, pp. 1436–1449, 2013.
A. Ashikhmin, T. L. Marzetta, L. Li, Interference reduction in multi-cell massive MIMO systems I: large scale fading precoding and decoding, arXiv preprint arXiv:1411.4182, November 2014.
Theodore S. Rappaport, Wireless communications: principles and practice, Prentice HallUpper Saddle River, 2002.
Z. Chen, and E. Bjornson, Channel hardening and favorable propagation in cell-free massive MIMO with stochastic geometry, arXiv:1710.00395, June 2018.
H. Q. Ngo, Erik G. Larsson, and Thomas L. Marzetta, Aspects of favorable propagation in massive MIMO, European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), pp. 76–80, September 2014.
H. Q. Ngo and E. Larsson, No downlink pilots are needed in TDD Massive MIMO, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, Vol. 16, No. 5, pp. 2921–2935, 2017.
M. Matthaiou, M. R. McKay, P. J. Smith and J. A. Nossek, On the condition number distribution of complex wishart matrices, IEEE Transactions on Communications, Vol. 58, No. 6, pp. 1705–1717, 2010.
X. Gao, O. Edfors, F. Rusek and F. Tufvesson, Massive MIMO performance evaluation based on measured propagation data, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, Vol. 14, No. 7, pp. 3899–3911, 2015.
J. Hoydis, C. Hoek, T. Wild, and S. ten Brink, Channel measurements for large antenna arrays, International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems (ISWCS), pp. 811–815, August 2012.
A. O. Martinez, E. D. Carvalho, and J. O. Nielsen, Towards very large aperture massive MIMO: a measurement based study, Proceedings of IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference (GLOBECOM), pp. 281–286, December 2014.
A. O. Martinez, E. De Carvalho, J. O. Nielsen, Massive MIMO properties based on measured channels: channel hardening, user decorrelation and channel sparsity, Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers (ACSSC), November 2016.
P. Viswanath and D. Tse, Sum capacity of the vector gaussian broadcast channel and uplink-downlink duality, IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, Vol. 49, No. 8, pp. 1912–1921, 2003.
E. G. Larsson and H. V. Poor, Joint beamforming and broadcasting in massive MIMO, IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, Vol. 15, No. 4, pp. 3058–3070, 2016.
S. R. Saunders and A. Aragon-Zavala, Antennas and Propagation for Wireless Communication Systems, vol. 2nd, WileyChichester, 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Figueiredo, F.A.P., Cardoso, F.A.C.M., Miranda, J.P. et al. Large-Scale Antenna Systems and Massive Machine Type Communications. Int J Wireless Inf Networks 27, 317–339 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10776-020-00487-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10776-020-00487-3