Abstract
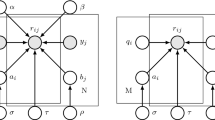
Collaborative filtering is a general technique for exploiting the preference patterns of a group of users to predict the utility of items for a particular user. Three different components need to be modeled in a collaborative filtering problem: users, items, and ratings. Previous research on applying probabilistic models to collaborative filtering has shown promising results. However, there is a lack of systematic studies of different ways to model each of the three components and their interactions. In this paper, we conduct a broad and systematic study on different mixture models for collaborative filtering. We discuss general issues related to using a mixture model for collaborative filtering, and propose three properties that a graphical model is expected to satisfy. Using these properties, we thoroughly examine five different mixture models, including Bayesian Clustering (BC), Aspect Model (AM), Flexible Mixture Model (FMM), Joint Mixture Model (JMM), and the Decoupled Model (DM). We compare these models both analytically and experimentally. Experiments over two datasets of movie ratings under different configurations show that in general, whether a model satisfies the proposed properties tends to be correlated with its performance. In particular, the Decoupled Model, which satisfies all the three desired properties, outperforms the other mixture models as well as many other existing approaches for collaborative filtering. Our study shows that graphical models are powerful tools for modeling collaborative filtering, but careful design is necessary to achieve good performance.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Breese JS, Heckerman D and Kadie C (1998) Empirical analysis of predictive algorithms for collaborative filtering. In the Proceeding of the Fourteenth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence
Cohen W, Shapire R and Singer Y (1998) Learning to order things. In: Advances in Neural Processing Systems 10. MIT Press, Denver, CO, 1997
Connor M and Herlocker J (2001) Clustering items for collaborative filtering. In the Proceedings of SIGIR-2001 Workshop on Recommender Systems, New Orleans, LA
Dempster AP, Laird NM and Rubin DB (1977) Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, B39:1–38
Fisher D, Hildrum K, Hong J, Newman M and Vuduc R (2000) SWAMI: A framework for collaborative filtering algorithm development and evaluation. In the Proceedings of the 23rd Annual International Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR)
Freund Y, Iyer R, Shapire R and Singer Y (1998) An efficient boosting algorithm for combining preferences. In Proceedings of ICML 1998
Ha V and Haddawy P (1998) Toward case-based preference elicitation: Similarity measures on preference structures. In: Proceedings of UAI 1998
Herlocker JL, Konstan JA, Brochers A and Riedl J (1999) An algorithm framework for performing collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the 22nd Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR)
Hofmann T and Puzicha J (1999) Latent class models for collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence 1999
Hofmann T and Puzicha J (1998) Statistical models for co-occurrence data (Technical report). Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Memo 1625, M.I.T
Hofmann T (2003) Gaussian latent semantic models for collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference
Jin R, Si L and Zhai CX (2003) Preference-based graphical models for collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the Nineteenth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI)
Melville P, Mooney RJ and Nagarajan R (2002) Content-boosted collaborative filtering for improved recommendations. In the Proceedings of the Eighteenth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI)
Pennock DM, Horvitz E, Lawrence S and Giles CL (2000) Collaborative filtering by personality diagnosis: A hybrid memory- and model-based approach. In the Proceeding of the Sixteenth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence
Popescul A Ungar LH Pennock DM and Lawrence S (2001) Probabilistic models for unified collaborative and content-based recommendation in sparse-data environments. In: Proceeding of the Seventeenth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence
Resnick P, Iacovou N, Suchak M, Bergstrom P and Riedl J (1994) Grouplens: An open architecture for collaborative filtering of netnews. In Proceeding of the ACM 1994 Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work
Ross DA and Zemel RS (2002) Multiple-cause vector quantization. In NIPS-15: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 15
Si L and Jin R (2003) Product space mixture model for collaborative filtering. In: Proceedings of the Twentieth International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML)
Ueda N and Nakano R (1998) Deterministic annealing EM algorithm. Neural Networks, 11(2):271–282
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, R., Si, L. & Zhai, C. A study of mixture models for collaborative filtering. Inf Retrieval 9, 357–382 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10791-006-4651-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10791-006-4651-1