Abstract
Transparency, participation, and collaboration are the core pillars of open government. For the systematic integration of citizens and other stakeholders into the policy and public value creation process, their opinions, wishes, and complaints first need to be received. In the future, including user-generated content from social media will become a main channel for the enrichment of this information base for public administrative bodies and commercial firms. However, the sheer speed of growth of this constantly updated data pool makes manual work infeasible. The automated gathering, combination, analysis, and visualization of user-generated content from various sources and multiple languages is therefore imperative.
In this study, we present a design science research approach to develop a general framework (‘MarketMiner’) to handle large amounts of foreign-language user-generated content. As a first empirical application, we implement the framework in the automotive industry by analyzing Chinese automotive forums for the benefit of English-speaking users. At the same time, the ideas, methods, and insights are transferred to the public sector context, especially in light of the current challenges of a high number of political refugees from Arabic countries entering into the European Union.
The results are promising in that MarketMiner can dramatically improve the utilization of multi-language, multi-source social media content. The modular set-up of the artifact allows an easy transfer to additional areas of application.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Formats include, i.a., semi-structured textual content (XML data from RSS feeds), unstructured textual content (text data from forums, online groups, or social networking sites), and unstructured visual content (photo and video images from social multimedia sites).
As of November 30, 2015, the internet is used by about 873 million English-speaking and about 705 million Chinese-speaking users
Text REtrieval [sic] Conference, http://trec.nist.gov/
Conference and Labs of the Evaluation Forum, formerly known as Cross-Language Evaluation Forum, http://www.clef-initiative.eu/
NII Testbeds and Community for Information access Research, http://research.nii.ac.jp/ntcir/index-en.html
In their empirically derived taxonomy, Nicolai and Seidl distinguish three forms of practical relevance, i.e., instrumental relevance, conceptual relevance, and legitimative relevance. Instrumental relevance is comprised of schemes, technological rules/recipes and forecasts.
Once the tool had been developed, these scenarios were evaluated by these social media analytics experts (see section 7).
The system was also benchmarked quantitatively on a test set of 800 sentences that were annotated forfeature, evaluation, and emotion phrases and for relations between them. Details can be found in Lipenkova (2015).
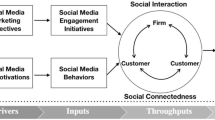
Hilgers and Ihl (2010) mention citizen ideation and innovation, collaborative administration and collaborative democracy as potential forms of open government.
See http://seeclickfix.com for an example from the US, or https://www.fixmystreet.com/ for the UK.
References
Abbas, S., & Ojo, A. (2013). Towards a Linked Geospatial Data Infrastructure. In D. Hutchison, T. Kanade, J. Kittler, J. M. Kleinberg, F. Mattern, J. C. Mitchell, et al. (Eds.), .), Technology-Enabled Innovation for Democracy, Government and Governance (Vol. 8061, pp. 196–210, Lecture Notes in Computer Science). Berlin: Springer.
Abney, S. P. (1991). Parsing by Chunks. In R. C. Berwick, S. P. Abney, & C. Tenny (Eds.), Principle-Based Parsing: Computation and Psycholinguistics (pp. 257–278, Studies in Linguistics and Philosophy, Vol. 44). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Abraham, R., Aier, S., & Winter, R. (2014). Fail Early, Fail Often: Towards Coherent Feedback Loops in Design Science Research Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Information Systems. Auckland, New Zealand.
Abrahams, A. S., Jiao, J., Fan, W., Wang, G., Alan, & Zhang, Z. (2013). What's buzzing in the blizzard of buzz? Automotive component isolation in social media postings. Decision Support Systems, 55(4), 871–882.
Abusalah, M., Tait, J., & Oakes, M. (2005). Literature review of cross-language information retrieval. World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology, 2005(4), 175–177.
Ackoff, R. (1989). From data to wisdom. Journal of Applied Systems Analysis, 16, 3–9.
Ahmed, F., & Nurnberger, A. (2012). Literature Review of Interactive Cross Language Information Retrieval Tools. International Arab Journal of Information Technology, 9(5), 479–486.
Alavi, M., & Leidner, D. E. (2001). Review: knowledge management and knowledge management systems: conceptual foundations and research issues. MIS Quarterly, 25(1), 107–136.
Alter, S. (2004). A work system view of DSS in its fourth decade. Decision Support Systems, 38(3), 319–327.
Anderson-Lehman, R., Watson, H. J., Wixom, B. H., & Hoffer, J. A. (2004). Continental Airlines flies high with real-time business intelligence. MIS Quarterly Executive, 3(4), 1–30.
Appleford, S., Bottum, J. R., & Thatcher, J. B. (2014). Understanding the social web. ACM SIGMIS Database, 45(1), 29–37. doi:10.1145/2591056.2591059.
Arnott, D. (2004). Decision Support Systems Evolution: Framework, Case Study and Research Agenda. European Journal of Information Systems, 13(4), 247–259. doi:10.1057/palgrave.ejis.3000509.
Arnott, D. (2010). Senior executive information behaviors and decision support. Journal of Decision Systems, 19(4), 465–480. doi:10.3166/jds.19.165-480.
Avrahami, T. T., Yau, L., Si, L., & Callan, J. (2006). The FedLemur project: federated search in the real world. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 57(3), 347–358. doi:10.1002/asi.20283.
Barbosa, A. F., Pozzebon, M., & Diniz, E. H. (2013). Rethinking E-government performance assessment from a citizen perspective. Public Administration, 744–762. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9299.2012.02095.x.
Baur, A. W., Breitsprecher, M., & Bick, M. (2014a). Catching Fire: Start-Ups in the Text Analytics Software Industry. In Proceedings of the 20th Americas Conference on Information Systems. Savannah, Georgia.
Baur, A. W., Genova, A. C., Bühler, J., & Bick, M. (2014b). Customer is King? A Framework to Shift from Cost- to Value-Based Pricing in Software as a Service: The Case of Business Intelligence Software. In Proceedings of the 13th IFIP WG 6.11 Conference on e-Business, e-Services, and e-Society. Sanya.
Becker, H., Naaman, M., & Gravano, L. (2010). Learning similarity metrics for event identification in social media. In B. D. Davison (Ed.) (pp. 291–300). New York: ACM.
Bera, P., Burton-Jones, A., & Wand, Y. (2011). Guidelines for designing visual ontologies to support knowledge identification. MIS Quarterly, 35(4), 883.
Berry, A. J., & Otley, D. (2004). Case-Based Research in Accounting. In C. Humphrey & B. Lee (Eds.), The real life guide to accounting research: A behind-the-scenes view of using qualitative research methods. (1st ed., pp. 231–256). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Berthon, P. R., Pitt, L. F., Plangger, K., & Shapiro, D. (2012). Marketing meets Web 2.0, social media, and creative consumers: Implications for international marketing strategy. Business Horizons, 55(3), 261–271. doi:10.1016/j.bushor.2012.01.007.
Bick, M., Hetmank, L., Kruse, P., Maier, R., Pawlowski, J., Peinl, R., et al. (2012). Manifesto for a Standard on Meaningful Representations of Knowledge in Social Knowledge Management Environments. In D. C. Mattfeld & S. Robra-Bissantz (Eds.), Tagungsband Multikonferenz Wirtschaftsinformatik (pp. 1–17). Braunschweig.
Bryman, A. (2012). Social Research Methods (4th ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Campbell, D. A., Lambright, K. T., & Wells, C. J. (2014). Looking for friends, fans, and followers?: social media use in public and nonprofit human services. Public Administration Review, 74(5), 655–663. doi:10.1111/puar.12261.
Chambers, J. M. (1983). Graphical methods for data analysis. Belmont: Wadsworth Intern. Group.
Chang, R. M., Kauffman, R. J., & Kwon, Y. (2014a). Understanding the paradigm shift to computational social science in the presence of big data. Decision Support Systems, 63(July), 67–80. doi:10.1016/j.dss.2013.08.008.
Chang, W.-L., Diaz, A. N., & Hung, P. C. K. (2014b). Estimating trust value: a social network perspective. Information Systems Frontiers, 1–20. doi:10.1007/s10796-014-9519-0.
Charalabidis, Y., Janssen, M., & Krcmar, H. (2015). Introduction to the Big, Open, and Linked Data (BOLD), Analytics, and Interoperability Infrastructures in Government Minitrack. In Proceedings of the 48th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (p. 2074). Kauai, HI.
Chen, J., & Bao, Y. (2009). Cross–language search: The case of Google Language Tools. First Monday, 14(3). doi:10.5210/fm.v14i3.2335
Chen, Y.-C., & Chu, P.-Y. (2012). Electronic governance and cross-boundary collaboration: Innovations and advancing tools. Hershey: IGI Global.
Chen, M., Ebert, D., Hagen, H., Laramee, R. S., van Liere, R., Ma, K.-L., et al. (2009). Data, information, and knowledge in visualization. IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications, 29(1), 12–19. doi:10.1109/MCG.2009.6.
Chen, H., Chiang, R. H. L., & Storey, V. C. (2012). Business intelligence and analytics: from big data to big impact. MIS Quarterly, 36(4), 1165–1188.
Chen, J. V., Yen, D. C., Pornpriphet, W., & Widjaja, A. E. (2015). E-commerce web site loyalty: a cross cultural comparison. Information Systems Frontiers, 17(6), 1283–1299. doi:10.1007/s10796-014-9499-0.
Chesbrough, H. W. (2003a). The era of open innovation. MIT Sloan Management Review, 44(3), 35–41.
Chesbrough, H. W. (2003b). Open innovation: The new imperative for creating and profiting from technology. Boston: Harvard Business School Publication Corp..
Choudhury, M. D., Counts, S., & Czerwinski, M. (2011). Identifying relevant social media content: leveraging information diversity and user cognition. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Conference on Hypertext and Hypermedia (pp. 161–170). New York, NY: ACM.
Chung, W., & Zeng, D. (2015). Social-media-based public policy informatics: Sentiment and network analyses of U.S. Immigration and border security. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 67(7), 1588–1606. doi:10.1002/asi.23449.
Clark, T. D. J., Jones, M. C., & Armstrong, C. P. (2007). The dynamic structure of management support systems: theory development, research focus, and direction. MIS Quarterly, 31(3), 579–615.
Conboy, K. (2009). Agility from first principles: reconstructing the concept of agility in information systems development. Information Systems Research, 20(3), 329–354.
Conboy, K., Fitzgerald, G., & Mathiassen, L. (2012). Qualitative methods research in information systems: motivations, themes, and contributions. European Journal of Information Systems, 21(2), 113–118.
Cook, M., Harrison, T. M., Zhang, J., Puron-Cid, G., & Gil-Garcia, J. R. (2015). Using public value thinking for government IT planning and decision making: A case study. Information Polity, 20(2,3), 183–197. doi:10.3233/IP-150359.
Dang, Y., Zhang, Y., Hu, P. J.-H., Brown, S. A., & Chen, H. (2011). Knowledge mapping for rapidly evolving domains: a design science approach. Decision Support Systems, 50(2), 415–427. doi:10.1016/j.dss.2010.10.003
Dang, Y., Zhang, Y., Hu, P. J.-H., Brown, S. A., Ku, Y., Wang, J.-H., et al. (2014). An integrated framework for analyzing multilingual content in web 2.0 social media. Decision Support Systems, 61(0), 126–135. doi:10.1016/j.dss.2014.02.004.
Davis, G. B. (2005). Advising and Supervising. In D. E. Avison & J. Pries-Heje (Eds.), Research in Information Systems: A Handbook for Research Supervisors and Their Students (pp. 3–34). Amsterdam: Elsevier/Butterworth-Heinemann.
Dellarocas, C. (2003). The digitization of word of mouth: promise and challenges of online feedback mechanisms. Management Science, 49(10), 1407–1424.
Di Gangi, P. M., Wasko, M. M., & Hooker, R. E. (2010). Getting customers’ ideas to work for you: learning from Dell how to succeed with online user innovation communities. MIS Quarterly Executive, 9(4), 163–178.
DiNucci, D. (1999). Fragmented Future. Print, 53(4), 32–35.
Doan, A., Ramakrishnan, R., & Halevy, A. Y. (2011). Crowdsourcing systems on the world-wide web. Communications of the ACM, 54(4), 86–96. doi:10.1145/1924421.1924442.
Eastin, M. S., Daugherty, T., & Burns, N. M. (2011). Handbook of research on digital media and advertising: User generated content consumption. Hershey: Information Science Reference.
Eisenhardt, K. M. (1989). Building theories from case study research. Academy of Management Review, 14(4), 532–550.
Eisenhardt, K. M., & Graebner, M. E. (2007). Theory building from cases: opportunities and challenges. Academy of Management Journal, 50(1), 25–32.
Ekman, P. (1992). An argument for basic emotions. Cognition & Emotion, 6(3), 169–200. doi:10.1080/02699939208411068.
Eppler, M. J., & Platts, K. W. (2009). Visual strategizing: the systematic use of visualization in the strategic-planning process. Long Range Planning, 42(1), 42–74. doi:10.1016/j.lrp.2008.11.005.
Ertek, G., Tokdemir, G., Sevinç, M., & Tunç, M. M. (2015). New knowledge in strategic management through visually mining semantic networks. Information Systems Frontiers, 1–21. doi:10.1007/s10796-015-9591-0.
Estevez, E., Fillottrani, P., Janowski, T., & Ojo, A. (2012). Government Information Sharing. In Y.-C. Chen & P.-Y. Chu (Eds.), Electronic Governance and Cross-Boundary Collaboration (pp. 23–55). Hershey: IGI Global.
Etzelstorfer, S., Gegenhuber, T., & Hilgers, D. (2016). Opening up Government: Citizen Innovation and new modes of collaboration in Austria. In R. Egger, I. Gula, & D. Walcher (Eds.), Open Tourism: Open Innovation, Crowdsourcing and Collaborative Consumption Challenging the Tourism Industry (pp. 1–17). Berlin: Springer.
Fan, L., Zhang, Y., Dang, Y., & Chen, H. (2013). Analyzing sentiments in Web 2.0 social media data in Chinese: experiments on business and marketing related Chinese Web forums. Information Technology and Management, 14(3), 231–242. doi:10.1007/s10799-013-0160-2.
Fang, H., Zhang, J., Bao, Y., & Zhu, Q. (2013). Towards effective online review systems in the Chinese context: a cross-cultural empirical study. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 12(3), 208–220. doi:10.1016/j.elerap.2013.03.001.
Few, S. (2006). Information Dashboard Design. North Sebastopol: O’Reilly.
Fliedl, G., Kop, C., & Vöhringer, J. (2010). Guideline Based Evaluation and Verbalization of OWL Class and Property Labels. Data & Knowledge Engineering, 69(4), 331–342. doi:10.1016/j.datak.2009.08.004.
Gao, G., McCullough, J. S., Agarwal, R., & Jha, A. K. (2010). Are doctors created equal? An investigation of online ratings by patients. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Information Systems and Economics (WISE) (pp. 1–6). St. Louis, MO.
Gelman, I. A., & Wu, N. (2011). Combining Structured and Unstructured Information Sources for a Study of Data Quality: A Case Study of Zillow.com. In Proceedings of the 44th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (pp. 1–12). Kauai, HI.
Glass, R. L. (2000). On design. Journal of Systems and Software, 52(1), 1–2. doi:10.1016/S0164-1212(99)00127-2.
Gregor, S., & Hevner, A. R. (2013). Positioning and presenting design science research for maximum impact. MIS Quarterly, 37(2), 337–355.
Hagen, L., Harrison, T. M., Uzuner, Ö., Fake, T., Lamanna, D., & Kotfila, C. (2015). Introducing textual analysis tools for policy informatics. In K. Mossberger, N. Helbig, J. Zhang, & Y. Kim (Eds.), Proceedings of the 16th Annual International Conference on Digital Government Research (pp. 10–19). Phoenix, AZ.
Hand, E. (2010). Citizen Science: People power. Nature, 466(7307), 685–687. doi:10.1038/466685a.
Hevner, A. R., & Chatterjee, S. (2010). Design research in information systems: Theory and practice. New York: Springer.
Hevner, A. R., March, S. T., Park, J., & Ram, S. (2004). Design science in information systems research. MIS Quarterly, 28(1), 75–105.
Hilgers, D., & Ihl, C. (2010). Citizensourcing – Applying the Concept of Open Innovation to the Public Sector. International Journal of Public Participation (IJP2), 4(1), 67–88.
Hoffman, P. E., & Grinstein, G. G. (2002). A survey of visualizations for high dimensional data mining. In U. M. Fayyad, G. G. Grinstein, & A. Wierse (Eds.), Information visualization in data mining and knowledge discovery. (pp. 47–82). San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann.
Homburg, C. (2015). Marketingmanagement: Strategie, Instrumente, Umsetzung, Unternehmensführung (5th ed.). Wiesbaden: Springer.
Hu, W., Almansoori, A., Kannan, P. K., Azarm, S., & Wang, Z. (2012). Corporate dashboards for integrated business and engineering decisions in oil refineries: an agent-based approach. Decision Support Systems, 52(3), 729–741. doi:10.1016/j.dss.2011.11.019.
Huang, S., Ward, M. O., & Rundensteiner, E. A. (2005). Exploration of Dimensionality Reduction for Text Visualization. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Coordinated and Multiple Views in Exploratory Visualization (pp. 63–74). Los Alamitos, CA.
Janssen, M., Estevez, E., & Janowski, T. (2014). Interoperability in Big, Open, and Linked Data - Organizational Maturity, Capabilities, and Data Portfolios. IEEE Computer, 47(10), 44–49. doi:10.1109/MC.2014.290.
Janssen, M., Mäntymäki, M., Hidders, J., Klievink, B., Lamersdorf, W., van Loenen, B., et al. (Eds.) (2015a). Open and Big Data Management and Innovation (LNCS). Cham: Springer.
Janssen, M., Matheus, R., & Zuiderwijk, A. (2015b). Big and Open Linked Data (BOLD) to Create Smart Cities and Citizens: Insights from Smart Energy and Mobility Cases. In E. Tambouris, M. Janssen, H. J. Scholl, M. A. Wimmer, K. Tarabanis, M. Gascó, et al. (Eds.), Electronic Government (Vol. 9248, pp. 79–90, LNCS). Cham: Springer.
Joachims, T. (1998). Text Categorization with Support Vector Machines: Learning with Many Relevant Features. In Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Machine Learning (pp. 137–142). London, UK: Springer.
Jones, G. J. F. (2011). Integrating social media with existing knowledge and information for crisis response. In Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Social Web Search and Mining (pp. 1–2). Beijing.
Kaplan, A. M., & Haenlein, M. (2010). Users of the world, unite! The challenges and opportunities of Social Media. Business Horizons, 53(1), 59–68. doi:10.1016/j.bushor.2009.09.003.
Karpf, D. (2009). Blogosphere research: a mixed-methods approach to rapidly changing systems. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 24(5), 67–70.
Kawamura, R. (2010). Social media's impact on BI starts with web data services. http://kapowsoftware.com/blog/index.php/social-media-impact-on-bi-starts-with-web-data-services.
Keim, D. A. (2002). Information visualization and visual data mining. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 8(1), 1–8. doi:10.1109/2945.981847.
Keller, K. L. (2014). MSI 2014–2016 Research Priorities. http://www.msi.org/uploads/files/MSI_RP14-16.pdf. Accessed 19 December 2015.
Kornai, A. (2013). Digital language death. PloS One, 8(10), 1–11. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077056.
Krishnaraju, V., Mathew, S. K., & Sugumaran, V. (2016). Web personalization for user acceptance of technology: an empirical investigation of E-government services. Information Systems Frontiers, 18(3), 579–595. doi:10.1007/s10796-015-9550-9.
Kuechler, W., & Vaishnavi, V. (2012). A framework for theory development in design science research: Multiple perspectives. Journal of the Association of Information Systems, 13(6), 395–423.
Kvale, S., & Brinkmann, S. (2015). InterViews: Learning the craft of qualitative research interviewing. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Lau, R. Y. K., Liao, S. Y., Kwok, R. C.-W., Xu, K., Xia, Y., & Li, Y. (2011). Text mining and probabilistic language modeling for online review spam detection. ACM Transactions on Management Information Systems, 2(4), 1–30. doi:10.1145/2070710.2070716.
Lee, A. S., & Baskerville, R. L. (2003). Generalizing generalizability in information systems research. Information Systems Research, 14(3), 221–243.
Lee, T. Y., & Bradlow, E. T. (2011). Automated marketing research using online customer reviews. Journal of Marketing Research (JMR), 48(5), 881–894.
Lee, H., & Choi, B. (2003). Knowledge management enablers, processes, and organizational performance: an integrative view and empirical examination. Journal of Management Information Systems, 20(1), 179–228.
Lee, G., & Kwak, Y. H. (2012). An open government maturity model for social media-based public engagement. Government Information Quarterly, 29(4), 492–503. doi:10.1016/j.giq.2012.06.001.
Leukel, J., Müller, M., & Sugumaran, V. (2014). The State of Design Science Research within the BISE Community: An Empirical Investigation. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Information Systems. Auckland, New Zealand.
Li, N., & Wu, D. D. (2010). Using text mining and sentiment analysis for online forums hotspot detection and forecast. Decision Support Systems, 48(2), 354–368. doi:10.1016/j.dss.2009.09.003.
Lipenkova, J. (2015). A system for fine-grained aspect-based sentiment analysis of Chinese. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Beijing.
Lusch, R. F., Liu, Y., & Chen, Y. (2010). The phase transition of markets and organizations: the new intelligence and entrepreneurial frontier. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 25(1), 71–75.
March, S. T., & Smith, G. F. (1995). Design and natural science research on information technology. Decision Support Systems, 15(4), 251–266. doi:10.1016/0167-9236(94)00041-2.
March, S. T., & Storey, V. C. (2008). Design science in the information systems discipline: an introduction to the special issue on design science research. MIS Quarterly, 32(4), 725–730.
Marland, A., Lewis, J. P., & Flanagan, T. (2016). Governance in the Age of Digital Media and Branding. Governance. doi:10.1111/gove.12194.
Marshall, B., McDonald, D., Chen, H., & Chung, W. (2004). EBizPort: collecting and analyzing business intelligence information. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 55(10), 873–891. doi:10.1002/asi.20037.
Matheus, R., & Janssen, M. (2015). Transparency Dimensions of Big and Open Linked Data. In M. Janssen, M. Mäntymäki, J. Hidders, B. Klievink, W. Lamersdorf, B. van Loenen, et al. (Eds.), Open and Big Data Management and Innovation (Vol. 9373, pp. 236–246, LNCS). Cham: Springer.
Mergel, I. (2013). A framework for interpreting social media interactions in the public sector. Government Information Quarterly, 30(4), 327–334. doi:10.1016/j.giq.2013.05.015.
Miles, M. B., Huberman, A. M., & Saldaña, J. (2013). Qualitative data analysis: A methods sourcebook. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Miniwatts Marketing Group. (2016). Number of Internet Users by Language: Internet World Stats. http://www.internetworldstats.com/stats7.htm. Accessed 13 March 2016.
Moody, D. L., & Shanks, G. G. (2003). Improving the quality of data models: empirical validation of a quality management framework. Information Systems, 28(6), 619–650. doi:10.1016/S0306-4379(02)00043-1.
Muñoz, L. A., & Bolívar, M. P. R. (2015). Theoretical Support for Social Media Research A Scientometric Analysis. In E. Tambouris, M. Janssen, H. J. Scholl, M. A. Wimmer, K. Tarabanis, M. Gascó, et al. (Eds.), Electronic Government (Vol. 9248, pp. 59–75, LNCS). Cham: Springer.
Neff, A. A., Hamel, F., Herz, T. P., Uebernickel, F., Brenner, W., & vom Brocke, J. (2014). Developing a maturity model for service systems in heavy equipment manufacturing enterprises. Information & Management, 51(7), 895–911. doi:10.1016/j.im.2014.05.001.
Netzer, O., Feldman, R., Goldenberg, J., & Fresko, M. (2012). Mine your own business: market-structure surveillance through text mining. Marketing Science, 31(3), 521–543. doi:10.1287/mksc.1120.0713.
Nicolai, A., & Seidl, D. (2010). That's Relevant! Different forms of practical relevance in management science. Organization Studies, 31(9–10), 1257–1285. doi:10.1177/0170840610374401.
Noesselt, N. (2014). Microblogs and the adaptation of the Chinese party-State's governance strategy. Governance, 27(3), 449–468. doi:10.1111/gove.12045.
Nunamaker, J. F., & Briggs, R. O. (2011). Toward a broader vision for information systems. ACM Transactions on Management Information Systems, 2(4), 1–12. doi:10.1145/2070710.2070711.
Nunamaker, J. F., Chen, M., & Purdin, T. D. M. (1990). Systems development in information systems research. Journal of Management Information Systems, 7(3), 89–106. doi:10.2307/40397957.
OECD (2010). Denmark: Efficient e-Government for Smarter Public Service Delivery, OECD Publishing, Paris. DOI:10.1787/9789264087118-en
O’Reilly, T. (2005). What is Web 2.0? Design Patterns and Business Models for the Next Generation of Software. http://www.oreilly.com/pub/a/web2/archive/what-is-web-20.html. Accessed 14 November 2015.
Offermann, P., Levina, O., Schönherr, M., & Bub, U. (2009). Outline of a design science research process. In Vijay K. Vaishnavi & Sandeep Purao (Eds.), Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Design Science Research in Information Systems and Technology (pp. 1–11). Philadelphia, PA.
Österle, H., Becker, J., Frank, U., Hess, T., Karagiannis, D., Krcmar, H., et al. (2011). Memorandum on design-oriented information systems research. EJIS, 20(1), 7–10. doi:10.1057/ejis.2010.55.
Paris, C., & Wan, S. (2011). Listening to the community: social media monitoring tasks for improving government services. In D. Tan, S. Amershi, B. Begole, W. A. Kellogg, & M. Tungare (Eds.), Vancouver, Canada (p. 2095). doi:10.1145/1979742.1979878
Peffers, K. E., Tuunanen, T., Rothenberger, M. A., & Chatterjee, S. (2007). A design science research methodology for information systems research. Journal of Management Information Systems, 24(3), 45–77.
Qin, J., Zhou, Y., Chau, M., & Chen, H. (2006). Multilingual web retrieval: an experiment in English–Chinese business intelligence. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 57(5), 671–683. doi:10.1002/asi.20329.
Recker, J. C., & Rosemann, M. (2010). A measurement instrument for process modeling research: development, test and procedural model. Scandinavian Journal of Information Systems, 22(2), 3–30.
Roberts, N. C. (2011). Tracking and disrupting dark networks: challenges of data collection and analysis. Information Systems Frontiers, 13(1), 5–19. doi:10.1007/s10796-010-9271-z.
Roitman, H., Barkai, G., Konopnicki, D., & Soffer, A. (2014). Measuring the Effectiveness of Multi-channel Marketing Campaigns Using Online Chatter. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on World Wide Web (pp. 143–146). Seoul, Republic of Korea.
Rouibah, K., & Ould-ali, S. (2002). PUZZLE: a concept and prototype for linking business intelligence to business strategy. The Journal of Strategic Information Systems, 11(2), 133–152. doi:10.1016/S0963-8687(02)00005-7.
Santiago-Rivera, D., & Shanks, G. (2015). A dashboard to support management of business analytics capabilities. Journal of Decision Systems, 24(1), 73–86. doi:10.1080/12460125.2015.994335.
Sashi, C. M. (2012). Customer engagement, buyer-seller relationships, and social media. Management Decision, 50(2), 253–272. doi:10.1108/00251741211203551.
Schedler, K., & Proeller, I. (2011). New public management (5th ed., UTB, 2132 : Public management, Betriebswirtschaft). Bern: Haupt.
Schmidt, M., & Hollensen, S. (2006). Marketing Research: An international approach. Harlow: Prentice Hall/Financial Times.
Schultze, U., & Leidner, D. E. (2002). Studying knowledge Management in Information Systems Research: discourses and theoretical assumptions. MIS Quarterly, 26(3), 213–242.
Schumaker, R. P. (2011). From data to wisdom: the progression of computational learning in text mining. Communications of the IIMA, 11(1), 39–53.
Scott Morton, M. S. (1984). The State of the Art of Research in Management Support Systems. In F. W. McFarlan (Ed.), The Information Research Challenge (pp. 13–41). Boston: Harvard University Press.
Sha, S., Huang, T., & Gabardi, E. (2013). Upward Mobility: The Future of China’s Premium Car Market. http://www.mckinsey.com/insights/asia-pacific/getting_to_know_chinas_premium-car_market. Accessed 14 November 2015.
Shareef, M. A., Kumar, V., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Kumar, U. (2016). Service delivery through mobile-government (mGov): driving factors and cultural impacts. Information Systems Frontiers, 18(2), 315–332. doi:10.1007/s10796-014-9533-2.
Sherchan, W., Nepal, S., & Paris, C. (2013). A survey of trust in social networks. ACM Computing Surveys, 45(4), 1–33. doi:10.1145/2501654.2501661.
Shneiderman, B. (1996). The eyes have it: a task by data type taxonomy for information visualizations. In Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE Symposium on Visual Languages (pp. 336–343). Boulder, CO.
Simon, H. A. (1996). The sciences of the artificial (3rd ed.). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Sonnenberg, C., & vom Brocke, J. (2012a). Evaluation Patterns for Design Science Research Artefacts. In M. Helfert & B. Donnellan (Eds.), Practical Aspects of Design Science (Vol. 286, pp. 71–83, Communications in Computer and Information Science). Berlin: Springer.
Sonnenberg, C., & vom Brocke, J. (2012b). Evaluations in the Science of the Artificial - Reconsidering the Build-Evaluate Pattern in Design Science Research. In K. Peffers, M. Rothenberger, & B. Kuechler (Eds.), Design Science Research in Information Systems. (pp. 381–397). Las Vegas: Springer.
Spence, R. (2001). Information visualization. Harlow: Addison-Wesley.
Stevens, C. H. (2013). Many-to many communication. Charleston: Nabu Press.
Stieglitz, S., & Dang-Xuan, L. (2013). Social media and political communication: a social media analytics framework. Social Network Analysis and Mining, 3(4), 1277–1291. doi:10.1007/s13278-012-0079-3.
Stindt, D., Nuss, C., Bensch, S., Dirr, M., & Tuma, A. (2014). An Environmental Management Information System for Closing Knowledge Gaps in Corporate Sustainable Decision-Making. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Information Systems. Auckland, New Zealand.
Straub, D., & Ang, S. (2011). Editor's Comments: Rigor and relevance in IS research: redefining the debate and a call for future research. MIS Quarterly, 35(1), iii–ixi.
Talvensaari, T., Juhola, M., Laurikkala, J., & Järvelin, K. (2007). Corpus-based cross-language information retrieval in retrieval of highly relevant documents. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, 58(3), 322–334. doi:10.1002/asi.20495.
Tambouris, E., Janssen, M., Scholl, H. J., Wimmer, M. A., Tarabanis, K., Gascó, M., et al. (Eds.) (2015). Electronic Government (LNCS). Cham: Springer.
Thomas, J. C. (2003). The New Face of Government: Citizen-Initiated Contacts in the Era of E-Government. Journal of Public Administration Research and Theory, 13(1), 83–102.
Timsina, P., Liu, J., & El-Gayar, O. (2016). Advanced analytics for the automation of medical systematic reviews. Information Systems Frontiers, 18(2), 237–252. doi:10.1007/s10796-015-9589-7.
Torres, L., Pina, V., & Acerete, B. (2006). E-governance developments in European Union cities: reshaping Government's relationship with citizens. Governance, 19(2), 277–302.
Tremblay, M. C., Hevner, A. R., & Berndt, D. J. (2010). Focus groups for artifact refinement & evaluation in design research. Communications of the Association for Information Systems, 26(27), 599–618.
van Aken, J. E. (2004). Management Research Based on the Paradigm of the Design Sciences: The Quest for Field-Tested & Grounded Technological Rules. Journal of Management Studies, 41(2), 219–246.
Vickery, G., & Wunsch-Vincent, S. (2007). Participative Web and user-created content: Web 2.0, wikis and social networking. Paris: Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
von Hippel, E. (2005). Democratizing Innovation. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Vulić, I., Smet, W., de Tang, J., & Moens, M.-F. (2015). Probabilistic topic modeling in multilingual settings: an overview of its methodology and applications. Information Processing & Management, 51(1), 111–147. doi:10.1016/j.ipm.2014.08.003.
Walls, J. G., Widmeyer, G. R., & El Sawy, O. A. (1992). Building an information system design theory for vigilant EIS. Information Systems Research, 3(1), 36–59.
Ware, C. (2000). Information Visualization. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann.
Watson, H. J., & Frolick, M. N. (1993). Determining information requirements for an EIS. MIS Quarterly, 17(3), 255–269.
Wattal, S., Schuff, D., Mandviwalla, M., & Williams, C. B. (2010). Web 2.0 and politics: The 2008 U.S. presidential election and an e-politics research agenda. MIS Quarterly, 34(4), 669–688.
Webster, J., & Watson, R. T. (2002). Analyzing the past to prepare for the future: writing a literature review. MIS Quarterly, 26(2), 13–23.
Winograd, T. (1996). Bringing design to software (ACM press books). Reading: Addison-Wesley.
Winograd, T. (1998). The Design of Interaction. In P. J. Denning & R. M. Metcalfe (Eds.), Beyond calculation: The next fifty years of computing (pp. 149–162). New York: Copernicus.
Wise, J. A. (1999). The ecological approach to text visualization. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 50(13), 1224–1233.
Wise, S., Paton, R. A., & Gegenhuber, T. (2012). Value co-creation through collective intelligence in the public sector. Vine - The journal of information and knowledge management systems, 42(2), 251–276. doi:10.1108/03055721211227273.
Yang, H., & Callan, J. (2009). OntoCop: constructing ontologies for public comments. IEEE Intelligent Systems, 24(5), 70–75.
Yang, H.-L., & Chao, A. F. Y. (2014). Sentiment analysis for Chinese reviews of movies in multi-genre based on morpheme-based features and collocations. Information Systems Frontiers. doi:10.1007/s10796-014-9498-1.
Yin, R. K. (2003). Case study research: Design and methods (3rd ed.). Beverly Hills: Sage.
Yin, P., Wang, H., & Guo, K. (2013). Feature–opinion pair identification of product reviews in Chinese: a domain ontology modeling method. New Review of Hypermedia and Multimedia, 19(1), 3–24. doi:10.1080/13614568.2013.766266.
Zeng, D., Wei, D., Chau, M., & Wang, F. (2011). Domain-specific Chinese word segmentation using suffix tree and mutual information. Information Systems Frontiers, 13(1), 115–125. doi:10.1007/s10796-010-9278-5.
Zhan, J., Loh, H. T., & Liu, Y. (2009). Gather customer concerns from online product reviews – A text summarization approach. Expert Systems with Applications, 36(2, Part 1), 2107–2115. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2007.12.039.
Zhou, Y., Qin, J., Chen, H., & Nunamaker, J. F. (2005). Multilingual Web Retrieval: An Experiment on a Multilingual Business Intelligence Portal. In 38th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences. Big Island, HI.
Zikopoulos, P., Eaton, C., De Roos, D., Deutsch, T., & Lapis, G. (2012). Understanding big data: Analytics for Enterprise class Hadoop and streaming data. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Zuiderwijk, A. (2015). Open data infrastructures: The design of an infrastructure to enhance the coordination of open data use. Delft: Delft University of Technology.
Zuiderwijk, A., Janssen, M., Zhang, J., Puron-Cid, G., & Gil-Garcia, J. R. (2015). Towards decision support for disclosing data: Closed or open data? Information Polity, 20(2,3), 103–117. doi:10.3233/IP-150358.
Zwass, V. (2010). Co-creation: toward a taxonomy and an integrated research perspective. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 15(1), 11–48.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baur, A.W. Harnessing the social web to enhance insights into people’s opinions in business, government and public administration. Inf Syst Front 19, 231–251 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-016-9681-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-016-9681-7