Abstract
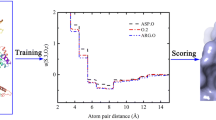
Learning strategies can be used to improve the efficiency of virtual screening of very large databases. In these strategies new compounds to be screened are selected on the basis of the results obtained in previous stages, even if truly good ligands have not yet been identified. This approach requires that the scoring function used correctly predicts the energy and geometry of suboptimal complexes, i.e. weak complexes that are not the final solution of the screening but help direct the search toward the most productive regions of chemical space. We show that a small modification in the treatment of the solvation of polar atoms corrects the tendency of the original Autodock 3.0 scoring function to bury ligand polar atoms away from solvent, even if no complementary groups are present in the target and improves the performance of Autodock 3.0 and 4.0 in reproducing the experimental docking energies of weak complexes, resembling the suboptimal complexes encountered in the intermediate stages of virtual screening.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walters WP, Sthal MT, Murcko MA (1998) Drug Discov Today 3:160. doi:10.1016/S1359-6446(97)01163-X
Seifert MHJ, Wolf K, Vitt D (2003) BIOSILICO 1:143. doi:10.1016/S1478-5382(03)02359-X
Lengauer T, Lemmen C, Rarey M, Zimmermann M (2004) Drug Discov Today 9:27. doi:10.1016/S1359-6446(04)02939-3
Mestres J (2002) Biochem Soc Trans 30:797. doi:10.1042/BST0300797
Jones G (1998) Encyclopedia of computational chemistry: genetic and evolutionary algorithms. Wiley Publisher, Chichester
Vidal D, Thormann M, Pons M (2006) J Chem Inf Model 46:836. doi:10.1021/ci050458q
Barbosa F, Horvath D (2004) Curr Top Med Chem 4:589. doi:10.2174/1568026043451186
Shanmugasundaram V, Maggiora GM, Lajiness MS (2005) J Med Chem 48:240. doi:10.1021/jm0493515
Warmuth MK, Liao J, Rätsch G, Mathieson M, Putta S, Lemmen C (2003) J Chem Inf Comput Sci 43:667. doi:10.1021/ci025620t
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday SR, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK et al (1998) J Comput Chem 19:1639. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(19981115)19:14<1639::AID-JCC10>3.0.CO;2-B
Sousa SF, Fernandes PA, Ramos MJ (2006) Proteins 65:15. doi:10.1002/prot.21082
Vidal D, Thormann M, Pons M (2005) J Chem Inf Model 45:386. doi:10.1021/ci0496797
Thormann M, Pons M (2001) J Comput Chem 22:1971. doi:10.1002/jcc.1146
Hetényi C, Paragi G, Maran U, Timár Z, Karelson M, Penke B (2006) J Am Chem Soc 128:1233. doi:10.1021/ja055804z
Huey R, Morris GM, Olson AJ, Goodsell DS (2007) J Comput Chem 28:1145. doi:10.1002/jcc.20634
Stouten PFW, Frömmel C, Nakamura H, Sander C (1993) Mol Simul 10:97. doi:10.1080/08927029308022161
Block P, Sotriffer CA, Dramburg I, Klebe G (2006) Nucleic Acids Res 34:D522. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj039
Liu T, Lin Y, Wen X, Jorissen RN, Gilson MK (2007) Nucleic Acids Res 35:D198. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl999
AffinDB is freely accessible at http://www.agklebe.de/affinity. Accessed Jan 2005
Barbault F, Zhang L, Fan BT (2006) Chemom Intell Lab Syst 82:269. doi:10.1016/j.chemolab.2005.05.014
ChemAxon Ltd Budapest, Hungary. http://www.chemaxon.com. Accessed Jan 2005
Gerber PR MOLOC—a molecular design software suite. http://www.moloc.ch. Accessed Jan 2005
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by funds from the Spanish Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia-FEDER BIO2004-5436 and BIO2007-63458 and the Generalitat de Catalunya. DV and GC gratefully acknowledge predoctoral grants from the Spanish Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cincilla, G., Vidal, D. & Pons, M. An improved scoring function for suboptimal polar ligand complexes. J Comput Aided Mol Des 23, 143–152 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-008-9246-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-008-9246-z