Abstract
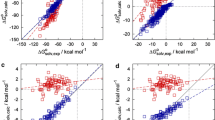
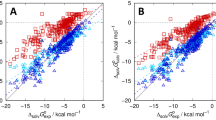
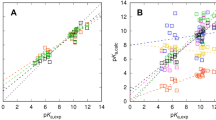
The “embedded cluster reference interaction site model” (EC-RISM) integral equation theory is applied to the problem of predicting aqueous pKa values for drug-like molecules based on an ensemble of tautomers. EC-RISM is based on self-consistent calculations of a solute’s electronic structure and the distribution function of surrounding water. Following-up on the workflow developed after the SAMPL5 challenge on cyclohexane-water distribution coefficients we extended and improved the methodology by taking into account exact electrostatic solute–solvent interactions taken from the wave function in solution. As before, the model is calibrated against Gibbs energies of hydration from the “Minnesota Solvation Database” and a public dataset of acidity constants of organic acids and bases by adjusting in total 4 parameters, among which only 3 are relevant for predicting pKa values. While the best-performing training model yields a root-mean-square error (RMSE) of 1 pK unit, the corresponding test set prediction on the full SAMPL6 dataset of macroscopic pKa values using the same level of theory exhibits slightly larger error (1.7 pK units) than the best test set model submitted (1.7 pK units for corresponding training set vs. test set performance of 1.6). Post-submission analysis revealed a number of physical optimization options regarding the numerical treatment of electrostatic interactions and conformational sampling. While the experimental test set data revealed after submission was not used for reparametrizing the methodology, the best physically optimized models consequentially result in RMSEs of 1.5 if only improved electrostatic interactions are considered and of 1.1 if, in addition, conformational sampling accounts for quantum-chemically derived rankings. We conclude that these numbers are probably near the ultimate accuracy achievable with the simple 3-parameter model using a single or the two best-ranking conformations per tautomer or microstate. Finally, relations of the present macrostate approach to microstate pKa results are discussed and some illustrative results for microstate populations are presented.




Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
http://www.drugdesigndata.org/about/sampl6. Accessed 29 May 2018
Geballe MT, Skillman AG, Nicholls A, Guthrie JP, Taylor PJ (2010) J Comput-Aid Mol Des 24:259–279
Bannan CC, Burley KH, Chiu M, Shirts MR, Gilson MK, Mobley DL (2016) J Comput-Aid Mol Des 30:927–944
Kast SM, Heil J, Güssregen S, Schmidt KF (2010) J Comput-Aid Mol Des 24:343–353
Tielker N, Tomazic D, Heil J, Kloss T, Ehrhart S, Güssregen S, Schmidt KF, Kast SM (2016) J Comput-Aid Mol Des 30:1035–1044
Kloss T, Heil J, Kast SM (2008) J Phys Chem B 112:4337–4343
Beglov D, Roux B (1997) J Phys Chem 101:7821–7826
Kovalenko A, Hirata F (1998) Chem Phys Lett 290:237–244
Sato H (2013) Phys Chem Chem Phys 15:7450–7465
Kast SM, Kloss T (2008) J Chem Phys 129:236101
Heil J, Kast SM (2015) J Chem Phys 142:114107
Heil J, Tomazic D, Egbers S, Kast SM (2014) J Mol Model 20:2161
Frach R, Kast SM (2014) J Phys Chem A 118:11620–11628
Hoffgaard F, Heil J, Kast SM (2013) J Chem Theory Comput 9:4718–4726
Frach R, Kibies P, Böttcher S, Pongratz T, Strohfeldt S, Kurrmann S, Koehler J, Hofmann M, Kremer W, Kalbitzer HR, Reiser O, Horinek D, Kast SM (2016) Angew Chem Int Ed 55:8757–8760
Frach R, Heil J, Kast SM (2016) Mol Phys 114:2461–2476
Hölzl C, Kibies P, Imoto S, Frach R, Suladze S, Winter R, Marx D, Horinek D, Kast SM (2016) J Chem Phys 144:144104
Imoto S, Kibies P, Rosin C, Winter R, Kast SM, Marx D (2016) Angew Chem Int Ed 55:9534–9538
Ratkova EL, Palmer DS, Fedorov MV (2015) Chem Rev 115:6312–6356
Sergiievskyi V, Jeanmairet G, Levesque M, Borgis D (2015) J Chem Phys 143:184116
Misin M, Fedorov MV, Palmer DS (2016) J Phys Chem B 120:975–983
Klicić JJ, Friesner RA, Liu SY, Guida WC (2002) J Phys Chem A 106:1327–1335
Klamt A. Eckert F, Diedenhofen M, Beck ME (2003) J Phys Chem A 107:9380–9386
Eckert F, Klamt A (2005) J Comput Chem 27:11–19
Marenich AV, Kelly CP, Thompson JD, Hawkins GD, Chambers CC, Giesen DK, Winget P, Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG (2012) Minnesoate solvation database—version 2012. University of Minnesota, Minneapolis
Kelly CP, Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG (2005) J Chem Theory Comput 1:1133–1152
Marenich AV, Olson RM, Kelly CP, Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG (2007) J Chem Theory Comput 3:2011–2033
Marenich AV, Cramer CJ, Truhlar DG (2009) J Phys Chem B 113:6378–6396
Heil J (2016) PhD dissertation. https://eldorado.tu-dortmund.de/handle/2003/35930
Imai T, Kinoshita M, Hirata F (2000) J Chem Phys 112:9469–9478
Imai T (2007) Cond Matter Phys 10:343–361
Frisch MJ et al (2009) Gaussian 09, Rev E.01. Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford
Hawkins PCD, Skillman AG, Warren GL, Ellingson BA, Stahl MT, OMEGA 2.6.7: OpenEye Scientific Software, Santa Fe
3D Structure Generator CORINA Classic, version 4.1.0, Molecular Networks GmbH, Nuremberg, Germany
Small-Molecule Drug Discovery Suite 2017-2 (2017) Schrödinger, LLC, New York
Wang J, Wolf RM, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA, Case DA (2004) J Comput Chem 25:1157–1174
Chirlian LE, Francl MM (1987) J Comput Chem 8:894–905
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Cluster of Excellence RESOLV (EXC 1069) and the Research Unit FOR 1979, funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. We also thank the IT and Media Center (ITMC) of the TU Dortmund for computational support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tielker, N., Eberlein, L., Güssregen, S. et al. The SAMPL6 challenge on predicting aqueous pKa values from EC-RISM theory. J Comput Aided Mol Des 32, 1151–1163 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-018-0140-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10822-018-0140-z