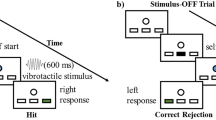
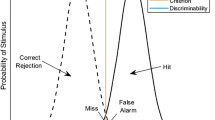
Abstract
We present a stochastic learning model that combines the essential elements of Hebbian and Rescorla-Wagner theories for operant conditioning. The model was used to predict the behavioral data of rats performing a vibrotactile yes/no detection task. Probabilistic nature of learning was implemented by trial-by-trial variability in the random distributions of associative strengths between the sensory and the response representations. By using measures derived from log-likelihoods (corrected Akaike and Bayesian information criteria), the proposed model and its subtypes were compared with each other, and with previous models in the literature, including reinforcement learning model with softmax rule and drift diffusion model. The main difference between these models was the level of stochasticity which was implemented as associative variation or response selection. The proposed model with subject-dependent variance coefficient (SVC) and with trial-dependent variance coefficient (TVC) resulted in better trial-by-trial fits to experimental data than the other tested models based on information criteria. Additionally, surrogate data were simulated with estimated parameters and the performance of the models were compared based on psychophysical measures (A’: non-parametric sensitivity index, hits and false alarms on receiver operating characteristics). Especially the TVC model could produce psychophysical measures closer to those of the experimental data than the alternative models. The presented approach is novel for linking psychophysical response measures with learning in a yes/no detection task, and may be used in neural engineering applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adibi, M., & Arabzadeh, E. (2011). A comparison of neuronal and behavioral detection and discrimination performances in rat whisker system. Journal of Neurophysiology, 105(1), 356–365. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00794.2010.
Augier, E., Flanigan, M., Dulman, R. S., Pincus, A., Schank, J. R., Rice, K. C., Kejun, C., Heilig, M., & Tapocik, J. D. (2014). Wistar rats acquire and maintain self-administration of 20% ethanol without water deprivation, saccharin/sucrose fading, or extended access training. Psychopharmacology, 231(23), 4561–4568. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3605-3.
Berg, J. A., Dammann 3rd, J. F., Tenore, F. V., Tabot, G. A., Boback, J. L., Manfredi, L. R., et al. (2013). Behavioral demonstration of a somatosensory neuroprosthesis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 21(3), 500–507. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2013.2244616.
Beygi, M., Mutlu, Ş., & Güçlü, B. (2016). A microfabricated strain gauge array on polymer substrate for tactile neuroprostheses in rats. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering, 26(8), 084006.
Chapin, J. K., Moxon, K. A., Markowitz, R. S., & Nicolelis, M. A. (1999). Real-time control of a robot arm using simultaneously recorded neurons in the motor cortex. Nature Neuroscience, 2(7), 664–670. https://doi.org/10.1038/10223.
Cohen, J. C., Makous, J. C., & Bolanowski, S. J. (1999). Under which conditions do the skin and probe decouple during sinusoidal vibrations? Experimental Brain Research, 129(2), 211–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002210050891.
Daw, N. D. (2011). Trial-by-trial data analysis using computational models. In M. R. Delgado, E. A. Phelps, & T. W. Robbins (Eds.), Decision making, affect, and learning: Attention and performance XXIII. New York: Oxford University Press.
Daw, N. D., Gershman, S. J., Seymour, B., Dayan, P., & Dolan, R. J. (2011). Model-based influences on humans' choices and striatal prediction errors. Neuron, 69(6), 1204–1215.
Dayan, P., & Balleine, B. W. (2002). Reward, motivation, and reinforcement learning. Neuron, 36(2), 285–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00963-7.
Dayan, P., & Yu, A. J. (2003). Uncertainty and learning. IETE Journal of Research, 49(2–3), 171–181. https://doi.org/10.1080/03772063.2003.11416335.
De Leonibus, E., Costantini, V. J., Massaro, A., Mandolesi, G., Vanni, V., Luvisetto, S., et al. (2011). Cognitive and neural determinants of response strategy in the dual-solution plus-maze task. Learning & Memory, 18(4), 241–244. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.2074311.
Devecioğlu, İ., & Güçlü, B. (2013). Asymmetric response properties of rapidly adapting mechanoreceptive fibers in the rat glabrous skin. Somatosensory & Motor Research, 30(1), 16–29. https://doi.org/10.3109/08990220.2012.732128.
Devecioğlu, İ., & Güçlü, B. (2015). A novel vibrotactile system for stimulating the glabrous skin of awake freely behaving rats during operant conditioning. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 242, 41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.01.004.
Devecioğlu, İ., & Güçlü, B. A preliminary model for operant conditioning of rats in a detection task. In 20th National Biomedical Engineering Meeting (BIYOMUT), 2016 (pp. 1–6). doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/BIYOMUT.2016.7849381.
Dragoi, V. (1997). A dynamic theory of acquisition and extinction in operant learning. Neural Networks, 10(2), 201–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0893-6080(96)00067-6.
Dragoi, V., & Staddon, J. (1999). The dynamics of operant conditioning. Psychological Review, 106(1), 20–61.
Emiliano, P. C., Vivanco, M. J., & De Menezes, F. S. (2014). Information criteria: How do they behave in different models? Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 69, 141–153.
Flesher, S. N., Collinger, J. L., Foldes, S. T., Weiss, J. M., Downey, J. E., Tyler-Kabara, E. C., et al. (2016). Intracortical microstimulation of human somatosensory cortex. Sci Transl Med, aaf8083, doi:https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf8083.
Fremaux, N., & Gerstner, W. (2015). Neuromodulated spike-timing-dependent plasticity, and theory of three-factor learning rules. Front Neural Circuits, 9, 85. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2015.00085.
Fulvio, J. M., Green, C. S., & Schrater, P. R. (2014). Task-specific response strategy selection on the basis of recent training experience. PLoS Computational Biology, 10(1), e1003425. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003425.
Garrud, P., Goodall, G., & Mackintosh, N. (1981). Overshadowing of a stimulus–reinforcer association by an instrumental response. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 33(2), 123–135.
Gescheider, G. A. (1997). Psychophysics: The Fundamentals: Taylor & Francis.
Graczyk, E. L., Schiefer, M. A., Saal, H. P., Delhaye, B. P., Bensmaia, S. J., & Tyler, D. J. (2016). The neural basis of perceived intensity in natural and artificial touch. Sci Transl Med, 8(362), 362ra142. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf5187.
Grossberg, S. (1969). Embedding fields: A theory of learning with physiological implications. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 6(2), 209–239.
Grossberg, S. (1971). On the dynamics of operant conditioning. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 33(2), 225–255.
Grossberg, S., & Levine, D. S. (1987). Neural dynamics of attentionally modulated Pavlovian conditioning: Blocking, interstimulus interval, and secondary reinforcement. Applied Optics, 26(23), 5015–5030.
Güçlü, B. (2007). Deviation from Weber's law in the non-Pacinian I tactile channel: A psychophysical and simulation study of intensity discrimination. Neural Computation, 19(10), 2638–2664. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.2007.19.10.2638.
Güçlü, B., & Bolanowski, S. J. (2004a). Probability of stimulus detection in a model population of rapidly adapting fibers. Neural Computation, 16(1), 39–58. https://doi.org/10.1162/08997660460733985.
Güçlü, B., & Bolanowski, S. J. (2004b). Tristate Markov model for the firing statistics of rapidly-adapting mechanoreceptive fibers. Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 17(2), 107–126. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JCNS.0000037680.56375.85.
Güçlü, B., & Bolanowski, S. J. (2005). Vibrotactile thresholds of the non-Pacinian I channel: II. Predicting the effects of contactor location on the phalanx. Somatosensory & Motor Research, 22(1–2), 57–68. https://doi.org/10.1080/08990220512331387971.
Güçlü, B., & Dinçer, S. M. (2013). Neural coding in the non-Pacinian I tactile channel: A psychophysical and simulation study of magnitude estimation. Somatosensory & Motor Research, 30(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.3109/08990220.2012.732127.
Güçlü, B., Gescheider, G. A., Bolanowski, S. J., & Istefanopulos, Y. (2005). Population-response model for vibrotactile spatial summation. Somatosensory & Motor Research, 22(4), 239–253. https://doi.org/10.1080/08990220500262075.
Hall, G., Channell, S., & Pearce, J. M. (1981). The effects of a signal for free or for earned reward: Implications for the role of response-reinforcer associations in instrumental performance. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 33(2), 95–107.
Hebb, D. O. (1932). Conditioned and unconditioned reflexes and inhibition. McGill University,
Hebb, D. O. (1949). The organization of behavior: A neuropsychological theory: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Holcman, D., & Tsodyks, M. (2006). The emergence of up and down states in cortical networks. PLoS Computational Biology, 2(3), e23. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0020023.
Horner, A. E., Heath, C. J., Hvoslef-Eide, M., Kent, B. A., Kim, C. H., Nilsson, S. R., et al. (2013). The touchscreen operant platform for testing learning and memory in rats and mice. Nature Protocols, 8(10), 1961–1984. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2013.122.
Karakuş, İ., Şahin, H., Atasoy, A., Kaplanoğlu, E., Özkan, M., & Güçlü, B. Evaluation of Sensory Feedback from a Robotic Hand: A Preliminary Study. In International Conference on Human Haptic Sensing and Touch Enabled Computer Applications, 2018 (pp. 452–463): Springer. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-93399-3_39.
Kingdom, F. A. A., & Prins, N. (2016). Model Comparisons. In F. A. A. Kingdom & N. Prins (Eds.), Psychophysics (Second ed., pp. 247–307). San Diego: Academic Press.
Klopf, A. H. (1988). A neuronal model of classical conditioning. Psychobiology, 16(2), 85–125.
Kocatürk, M., Gülçür, H. Ö., & Canbeyli, R. Chronic recordings from rat motor cortex for developing neural prostheses. In 15th National Biomedical Engineering Meeting (BIYOMUT), 21–24 April 2010 2010 (pp. 1–5). doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/BIYOMUT.2010.5479802.
Kuchiiwa, S., & Kuchiiwa, T. (2014). A novel semi-automated apparatus for measurement of aggressive biting behavior in mice. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 228, 27–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.02.017.
Lawson, R., & Watson, L. S. J. (1963). Learning in the rat (rattus norvegicus) under positive vs. negative reinforcement with incentive conditions controlled. Ohio Journal of Science, 63(2), 87–91.
Levine, D. S. (2000). Introduction to neural and cognitive modeling: Psychology press.
Lew, S. E., Wedemeyer, C., & Zanutto, B. S. (2001). Role of unconditioned stimulus prediction in the operant learning: A neural network model. IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 1, 331–336.
Li, J., Wang, Z. J., Palmer, S. J., & McKeown, M. J. (2008). Dynamic Bayesian network modeling of fMRI: A comparison of group-analysis methods. Neuroimage, 41(2), 398–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.01.068.
London, B. M., Jordan, L. R., Jackson, C. R., & Miller, L. E. (2008). Electrical stimulation of the proprioceptive cortex (area 3a) used to instruct a behaving monkey. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 16(1), 32–36. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnsre.2007.907544.
Maass, W., & Zador, A. M. (1999). Dynamic stochastic synapses as computational units. Neural Computation, 11(4), 903–917.
Machens, C. K., Romo, R., & Brody, C. D. (2005). Flexible control of mutual inhibition: A neural model of two-interval discrimination. Science, 307(5712), 1121–1124. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1104171.
Markram, H., Muller, E., Ramaswamy, S., Reimann, M. W., Abdellah, M., Sanchez, C. A., Ailamaki, A., Alonso-Nanclares, L., Antille, N., Arsever, S., Kahou, G. A. A., Berger, T. K., Bilgili, A., Buncic, N., Chalimourda, A., Chindemi, G., Courcol, J. D., Delalondre, F., Delattre, V., Druckmann, S., Dumusc, R., Dynes, J., Eilemann, S., Gal, E., Gevaert, M. E., Ghobril, J. P., Gidon, A., Graham, J. W., Gupta, A., Haenel, V., Hay, E., Heinis, T., Hernando, J. B., Hines, M., Kanari, L., Keller, D., Kenyon, J., Khazen, G., Kim, Y., King, J. G., Kisvarday, Z., Kumbhar, P., Lasserre, S., le Bé, J. V., Magalhães, B. R. C., Merchán-Pérez, A., Meystre, J., Morrice, B. R., Muller, J., Muñoz-Céspedes, A., Muralidhar, S., Muthurasa, K., Nachbaur, D., Newton, T. H., Nolte, M., Ovcharenko, A., Palacios, J., Pastor, L., Perin, R., Ranjan, R., Riachi, I., Rodríguez, J. R., Riquelme, J. L., Rössert, C., Sfyrakis, K., Shi, Y., Shillcock, J. C., Silberberg, G., Silva, R., Tauheed, F., Telefont, M., Toledo-Rodriguez, M., Tränkler, T., van Geit, W., Díaz, J. V., Walker, R., Wang, Y., Zaninetta, S. M., DeFelipe, J., Hill, S. L., Segev, I., & Schürmann, F. (2015). Reconstruction and simulation of neocortical microcircuitry. Cell, 163(2), 456–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.09.029.
McLaren, I., Kaye, H., & Mackintosh, N. (1989). An associative theory of the representation of stimuli: Applications to perceptual learning and latent inhibition. In R. Morris (Ed.), Parallel distributed processing - Implications for psychology and neurobiology. Oxford: OUP.
McLaren, I., & Mackintosh, N. (2000). An elemental model of associative learning: I. latent inhibition and perceptual learning. Animal Learning & Behavior, 28(3), 211–246.
Miller, R. R., Barnet, R. C., & Grahame, N. J. (1995). Assessment of the Rescorla-Wagner model. Psychological Bulletin, 117(3), 363–386.
Navarro, D. J., & Fuss, I. G. (2009). Fast and accurate calculations for first-passage times in wiener diffusion models. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 53(4), 222–230.
O'Doherty, J. E., Dayan, P., Friston, K., Critchley, H., & Dolan, R. J. (2003). Temporal difference models and reward-related learning in the human brain. Neuron, 38(2), 329–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0896-6273(03)00169-7.
O'Doherty, J. E., Lebedev, M. A., Hanson, T. L., Fitzsimmons, N. A., & Nicolelis, M. A. (2009). A brain-machine interface instructed by direct intracortical microstimulation. Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience, 3, 20. https://doi.org/10.3389/neuro.07.020.2009.
Ortiz-Catalan, M., Håkansson, B., & Brånemark, R. (2014). An osseointegrated human-machine gateway for long-term sensory feedback and motor control of artificial limbs. Sci Transl Med, 6(257), 257re256–257re256. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3008933.
Öztürk, S., Devecioğlu, İ., Beygi, M., Atasoy, A., Mutlu, Ş., Özkan, M., et al. (2017). Demonstration of a sensory neuroprosthesis on behaving rats. Anatomy: An International Journal of Experimental and Clinical Anatomy, 11(Suppl. 1), P-035.
Öztürk, S., Vardar, B., & Güçlü, B. (2018). Sorting spikes from S1 cortex for prediction of behavioral events in neuroprostheses. Anatomy: An International Journal of Experimental and Clinical Anatomy, 12(Suppl. 1), P-023.
Pedersen, M. L., Frank, M. J., & Biele, G. (2017). The drift diffusion model as the choice rule in reinforcement learning. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 24(4), 1234–1251.
Rajan, R., Clement, J. P., & Bhalla, U. S. (2006). Rats smell in stereo. Science, 311(5761), 666–670. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1122096.
Raspopovic, S., Capogrosso, M., Petrini, F. M., Bonizzato, M., Rigosa, J., Di Pino, G., et al. (2014). Restoring natural sensory feedback in real-time bidirectional hand prostheses. Sci Transl Med, 6(222), 222ra219. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3006820.
Raymond, J. L., Baxter, D. A., Buonomano, D. V., & Byrne, J. H. (1992). A learning rule based on empirically-derived activity-dependent neuromodulation supports operant conditioning in a small network. Neural Networks, 5(5), 789–803.
Rescorla, R. A., & Wagner, A. W. (1972). A theory of Pavlovian conditioning: Variations in the effectiveness of reinforcement and nonreinforcement. In a. H. Black, & W. F. Prokasy (Eds.), Classical Conditioning II: Current Research and Theory (pp. 64-99): Appleton-century-crofts.
Roelfsema, P. R., van Ooyen, A., & Watanabe, T. (2010). Perceptual learning rules based on reinforcers and attention. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14(2), 64–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2009.11.005.
Schachtman, T. R., & Reilly, S. (2011). Things you always wanted to know about conditioning but were afraid to ask. Associative Learning and Conditioning Theory: Human and Non-Human Applications, 1.
Skinner, B. (1932). On the rate of formation of a conditioned reflex. The Journal of General Psychology, 7(2), 274–286.
Steyvers, M. (2011). MATJAGS 1.3: A Matlab interface for JAGS.
Tabot, G. A., Dammann, J. F., Berg, J. A., Tenore, F. V., Boback, J. L., Vogelstein, R. J., & Bensmaia, S. J. (2013). Restoring the sense of touch with a prosthetic hand through a brain interface. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 110(45), 18279–18284. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1221113110.
Talwar, S. K., & Gerstein, G. L. (1999). A signal detection analysis of auditory-frequency discrimination in the rat. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 105, 1784–1800.
Tesauro, G. (1986). Simple neural models of classical conditioning. Biological Cybernetics, 55(2–3), 187–200.
Wabersich, D., & Vandekerckhove, J. (2014). Extending JAGS: A tutorial on adding custom distributions to JAGS (with a diffusion model example). Behavior Research Methods, 46(1), 15–28.
Walker, J. L., Walker, B. M., Fuentes, F. M., & Rector, D. M. (2011). Rat psychomotor vigilance task with fast response times using a conditioned lick behavior. Behavioural Brain Research, 216(1), 229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2010.07.041.
Wiest, M. C., Thomson, E., Pantoja, J., & Nicolelis, M. A. (2010). Changes in S1 neural responses during tactile discrimination learning. Journal of Neurophysiology, 104(1), 300–312. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00194.2010.
Windisch, K. A., Kosobud, A. E., & Czachowski, C. L. (2014). Intravenous alcohol self-administration in the P rat. Alcohol, 48(5), 419–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alcohol.2013.12.007.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by TÜBİTAK Grant 117F481 within European Union’s FLAG-ERA JTC 2017 project GRAFIN and Boğaziçi University BAP no: 17XP2 given to Dr. Güçlü. We thank Bige Vardar and Sevgi Öztürk for their help in the experiments and comments on the Discussion section.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
"Action Editor: P. Dayan"
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original version of this article was revised because of some typographical errors in equations (5), (6), (7), (8), and (12).
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 6465 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Devecioğlu, İ., Güçlü, B. Psychophysical detection and learning in freely behaving rats: a probabilistic dynamical model for operant conditioning. J Comput Neurosci 48, 333–353 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-020-00751-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10827-020-00751-8