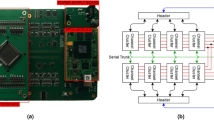
Abstract
High pin count packaging and 3D IC technology make testing such advanced ICs more and more difficult and expensive. The HOY wireless test platform provides an alternative and cost-effective test solution to address the poor accessibility and high test cost issues. The key idea is implementing a low-cost and short-distance wireless transceiver on chip so that all test instructions and data can be transmitted without physical access. Due to the limited wireless bandwidth, all modules in the device under test (DUT) are preferred to have some built-in self-test (BIST) features. Prior works successfully demonstrated that DUTs with memory and digital circuits can be tested on the low-cost wireless test platform. However, there is no example to show if it is also possible to test the DUT embedded with analog circuits on the HOY test platform. This paper demonstrates the first system-level integration including hardware and software for testing a fully-integrated BIST ADC on the HOY wireless test platform. The DUT chip fabricated in 0.18-μm CMOS consists of a second-order Σ–Δ ADC under test (AUT) and the BIST circuitry. The AUT design employs the decorrelating design-for-digital-testability (D3T) scheme to make itself digitally testable. The BIST design is based on the modified controlled sine wave fitting (CSWF) method. The required BIST circuits are purely digital and as small as 9.9k gates. The gate count of the HOY test wrapper is less than 1k. Experimental results obtained by the HOY wireless test platform show that the AUT achieves a dynamic range of 85.1 dB and a peak SNDR of 78.6 dB. The wireless test results show good agreement with those acquired by conventional analog tests.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alampally S, Venkatesh RT, Shanmugasundaram P, Parekhji RA, Agrawal VD (2011) An efficient test data reduction technique through dynamic pattern mixing across multiple fault models. In: Proc. IEEE VLSI test symp. (VTS), pp 285–290
Al-Yamani AA, McCluskey EJ (2010) Test set compression through alternation between deterministic and pseudorandom test patterns. J Electron Test (JETTA) 26(5):513–521
Burns M, Roberts G.W. (2001) An introduction to mixed-signal IC test and measurement. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Bushnell ML, Agrawal VD (2000) Essentials of electronics testing for digital, memory & mixed-signal VLSI circuits. Kluwer Academic, Norwell
Chi C-C, Lo C-Y, Ko T-W, Wu C-W (2009) Test integration for SOC supporting very low-cost tester. In: IEEE Asian test symp. (ATS), pp 287–292
Chouba N, Bouzaida L (2010) A BIST architecture for Sigma Delta ADC testing based on embedded NOEB self-test and CORDIC algorithm. In: Proc. IEEE int. conf. design and technology of integrated systems in nanoscale era (DTIS), pp 1–7
Hong H-C (2004) Design-for-digital-testability 30 MHz second-order Sigma–Delta modulator. In: Proc. IEEE custom integrated circuits conf. (CICC), pp 211–214
Hong H-C (2007) A design-for-digital-testability circuit structure for Σ–Δ modulators. IEEE Trans VLSI Syst 15(12):1341–1350
Hong H-C (2007) A fully-settled linear behavior plus noise model for evaluating the digital stimuli of the design-for-digital-testability Σ–Δ modulators. J Electron Test (JETTA) 23(6):527–538
Hong H-C, Liang S-C (2009) A decorrelating design-for-digital-testability scheme for Σ–Δ modulators. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I, Reg Pap 56(1):60–73
Hong H-C, Su F-Y, Hung S-F (2010) A fully integrated built-in self-test Σ–Δ ADC based on the modified controlled sine-wave fitting procedure. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 59(9):2334–2344
Hsing Y-T, Denq L-M, Chen C-H, Wu C-W (2010) Economic analysis of the HOY wireless test methodology. IEEE Des Test Comput 27(3):20–30
Huang X-L, Kang P-Y, Yu Y-C, Huang J-L (2011) Histogram-based calibration of capacitor mismatch and comparator offset for 1-bit/stage pipelined ADCs. J Electron Test (JETTA) 27(4):441–453
Hung S-F, Hong H-C (2011) Design of a design-for-digital-testability third-order Σ–Δ modulator. In: Proc. IEEE 17th international mixed-signals, sensors and systems test workshop, pp 110–113
Hung S-F, Hong H-C, Liang S-C (2009) A low-cost output response analyzer for the built-in-self-test Σ–Δ modulator based on the controlled sine wave fitting method. In: IEEE Asian test symp. (ATS), pp 385–388
Kochte MA, Zoellin CG, Wunderlich H-J (2010) Efficient concurrent self-test with partially specified patterns. J Electron Test (JETTA) 26(5):581–594
Li C-F, Lee C-Y, et al (2011) A low-cost wireless interface with no external antenna and crystal oscillator for cm-range contactless testing. In: Proc. IEEE/ACM design automation conf. (DAC), pp 771–776
Liou J-J, Huang C-T, Wu C-W, Tien C-C, Wang C-H, Ma H-P, Chen Y-Y, Hsu Y-C, Deng L-M, Chiu C-J, Li Y-W, Chang C-M (2007) A prototype of a wireless-based test system. In: IEEE int. SOC conf. (SOCC), pp 225–228
Lu AK, Roberts GW (1994) A high-quality analog oscillator using oversampling D/A conversion techniques. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Analog Digit Signal Process 41(7):437–444
Mattes H, Sattler S, Dworski C (2004) Controlled sine wave fitting for ADC test. In: Proc. IEEE int. test conf. (ITC), pp 963–971
Mehta US, Dasgupta KS, Devashrayee NM (2010) Modified selective Huffman coding for optimization of test data compression, test application time and area overhead. J Electron Test (JETTA) 26(6):679–688
Mullane B, O’Brien V, MacNamee C, Fleischmann T (2009) A prototype platform for system-on-chip ADC test and measurement. In: IEEE int. SOC conf. (SOCC), pp 169–172
Rolindez L, Mir S, Bounceur A, Carbonero J-L (2006) A BIST scheme for SNDR testing of Σ–Δ ADCs using sine-wave fitting. J Electron Test (JETTA) 22(4–6):325–335
Rolindez L, Mir S, Carbonero J-L, Goguet D, Chouba N (2007) A stereo audio Σ–Δ ADC architecture with embedded SNDR self-test. In: Proc. IEEE int. test conf. (ITC), pp 1–10
Santin E, Oliveira L, Nowacki B, Goes J (2010) Fully integrated and reconfigurable architecture for coherent self-testing of IQ ADCs. In: Proc. IEEE int. symp. circuits and systems (ISCAS), pp 1927–1930
Ting H-W, Chang S-J, Huang S-L (2011) A design of linearity built-in self-test for current-steering DAC. J Electron Test (JETTA) 27(1):85–94
Toner MF, Roberts GW (1995) A BIST scheme for a SNR, gain tracking, and frequency response test of a Sigma–Delta ADC. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst II Analog Digit Signal Process 42(1):1–15
Vinnakota B (1998) Analog and mixed-signal test. Prentice-Hall, Englewoods Cliffs
Wang Z, Karpovsky M, Kulikowski KJ (2010) Design of memories with concurrent error detection and correction by nonlinear sec-ded codes. J Electron Test (JETTA) 26(5):559–580
Wu C-W, Huang C-T, Huang S-Y, Huang P-C, Chang T-Y, Hsing Y-T (2006) The HOY tester—can IC testing go wireless? In: Proc. IEEE int. symp. VLSI design, automation and test, pp 1–4
Yang C-Y, Chen Y-Y, Chen S-Y, Liou J-J (2010) Automatic test wrapper synthesis for a wireless ATE Platform. IEEE Des Test Comput 27(3):31–41
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Science Council, Taiwan, under Grant 97-2221-E-009-169-MY3, and in part by the Ministry of Economic Affairs, Taiwan, under Grant 97-EC-17-A-01-S1-002. The authors thank the Chip Implementation Center, Taiwan for fabricating the test chips, and Prof. J.-J. Liou, Prof. C.-T. Huang, and their research teams of National Tsing-Hwa University, Taiwan, for their software support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: D. Keezer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hung, SF., Hong, HC. Experimental Results of Testing a BIST Σ–Δ ADC on the HOY Wireless Test Platform. J Electron Test 28, 571–584 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-012-5302-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-012-5302-7