Abstract
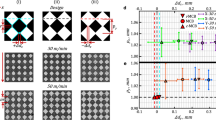
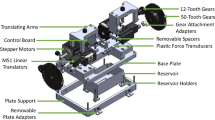
Recent advances in the field of stereolithography based manufacturing, have led to a number of 3D-printed sensor and actuator devices, as a cost-effective and low fabrication complexity alternative to micro-electro-mechanical counterparts. Yet the reliability of such 3D-printed dynamic structures have yet to be explored. Here we perform reliability tests and analysis of a selected 3D-printed actuator, namely an electromechanical scanner. The scanner is targeted towards scanning incoming light onto the target, which is particularly useful for barcoding, display, and opto-medical tissue imaging applications. We monitor the deviations in the fundamental mechanical resonance, scan-line, and the quality factor on a number of scanners having different device thicknesses, for a total duration of 5 days (corresponding to 20–80 million cycles, depending on the device operating frequency). A total of 9 scanning devices, having 10 mm × 10 mm die size were tested, with a highlight on device-device variability, as well as the effect of device thickness itself. An average standard deviation of < ~%10 (with respect to the mean) was observed for all tested parameters among scanners of the same type (an indicator device to device variability), while an average standard deviation of less than about 10 percent (with respect to the mean) was observed for all parameters for the duration of the entire test (as an indicator of device reliability), for a total optical scan angle of 5 degrees.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Connally JA, Brown SB (1992) Slow crack growth in single-crystal silicon. Science 256(5063):1537–1539
Heinrich SM, Boudjiet MT, Thuau D, Poulin P, Ayela C, Dufour I (2014) Development of analytical models of T- and U-shaped cantilever-based MEMS devices for sensing and energy harvesting applications. In: IEEE SENSORS 2014 Proceedings pp. 1648–1651
Hod Lipson MK (2013) Fabricated the new world of 3D printing. John Wiley & Sons, Inc,1st Ed, no 1, pp 1–5
Holmström STS, Baran U, Urey H (2014) MEMS laser scanners: a review. J Microelectromech Syst 23(2):259–275
Hoy CL, Durr NJ, Ben-Yakar A (2011) Fast-updating and nonrepeating Lissajous image reconstruction method for capturing increased dynamic information. Appl Opt 50(16):2376–2382
Huang Y, Sai Sarathi Vasan A, Doraiswami R, Osterman M, Pecht M (2012) MEMS reliability review. IEEE Trans Device Mater Reliab 12(2):482–493
Ishiguro Y, Poupyrev I (2014) 3D printed interactive speakers. Proc 32nd Annu ACM Conf Hum factors Comput Syst - CHI ‘14, pp. 1733–1742
Lulec SZ, Sagiroglu C, Mostafazadeh A, Ermek E, Timurdogan E, Leblebici Y, and Urey H (2012) Simultaneous self-sustained actuation and parallel readout with MEMS cantilever sensor array. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Int Conf Micro Electro Mech Syst (MEMS) pp. 644–647
MacDonald E, Wicker R (2016) Multiprocess 3D printing for increasing component functionality. Science 353(6307):aaf2093
Peele BN, Wallin TJ, Zhao H, Shepherd RF (2015) 3D printing antagonistic systems of artificial muscle using projection stereolithography. Bioinspir Biomim 10(5):55003
Qiu Z and Piyawattanametha W (2015) MEMS-based medical Endomicroscopes. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron 21(4)
Sakai M, Tabata O (2007) Reliability of MEMS testing of materials and devices
Savas J, Khayatzadeh R, Civitci F, Gokdel YD, Ferhanoglu O (2018) Towards fully 3D-printed miniaturized confocal imager. Opt Eng 57(4):41402
Senturia SD (2001) Microsyst Design 49(0)
Shemelya C, Cedillos F, Aguilera E, Maestas E, Ramos J, Espalin D, Muse D, Wicker R, MacDonald E (2013) 3D printed capacitive sensors. In: IEEE SENSORS 2013 - proceedings
Stratasys (2014) “PolyJet Materials Data Sheet.” [Online]. Available: http://usglobalimages.stratasys.com/
Urey H, Holmstrom S, Yalcinkaya AD (2008) Electromagnetically actuated FR4 scanners. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 20(1):30–32
Willis K, Brockmeyer E, Hudson S, Poupyrev I (2012) Printed optics: 3D printing of embedded optical elements for interactive devices. Proc 25th Annu ACM Symp User interface Softw Technol - UIST ‘12, pp. 589–598
Wu S-Y, Yang C, Hsu W, Lin L (2015) 3D-printed microelectronics for integrated circuitry and passive wireless sensors. Microsyst Nanoeng 1:15013
Yelten MB, Franzon PD, Steer MB (2011) Surrogate-model-based analysis of analog circuits -part I: variability analysis. IEEE Trans Device Mater Reliab 11(3):458–465
Young WC, Budynas RG Roark’s formulas for stress and strain. Library (Lond) 7:2002, 832 no 7th Edition
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank Ahmet Turan Talas from Boğaziçi University Life Sciences Center for his support in manufacturing all 3D printed parts.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: M. Barragan and K. Huang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mert Gönültaş, B., Savaş, J., Khayatzadeh, R. et al. Reliability Testing of 3D-Printed Electromechanical Scanning Devices. J Electron Test 34, 363–370 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-018-5722-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10836-018-5722-0