Abstract
Frequent subgraph mining algorithms are widely used in various areas for information analysis. As yet, a handful of algorithms have been proposed and defined in the literature. While several experimental studies were reported, these experiments lack critical information which are important for selecting an implementation of an algorithm for a specific case of use. In this paper, we report on experiments that we carried out on available implementations of complete search Frequent Subgraph Mining (FSM) algorithms. These experiments are conducted in order to choose a suitable FSM solution (i.e., implementation). We identified 32 algorithms in the literature, six of them were selected for our experiments, through a filtering process relying on a set of criteria. Thirteen working implementations of these 6 algorithms are experimented. In this paper, we provide details of the experiments in terms of performance metrics and input variation effect. We propose a preliminary selection of the most efficient FSM solutions for end users, based on the most tested centralized graph-transaction datasets of the literature.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
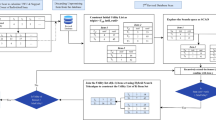
Complete search in centralized graph transaction databases.
CAIR home page: www.irit.fr/CAIR.
Copyright is with the authors. Published in the Proceedings of the BDA 2016 Conference: bda2016.ensma.fr/program.html.
Supergraphs are the graphs containing g.
A simple graph is “an un-weighted and undirected graph with no loops and no multiple links between any two distinct nodes” (Gibbons 1985)
studies with keyword ’Frequent Subgraph Mining’
The list of algorithms is based on our search of FSM studies until March 2016
From public references or by contacting authors
1 request and 2 reminders have been sent to authors.
Original ParMol github.com/yangyi0318/MyParMol/tree/master/ParMol
Please refer to liris.cnrs.fr/rihab.ayed/ESFSM.pdf for more details.
We collected the references of datasets from FSM papers or by contacting authors that used them (March 2016)
Please refer to perso.liris.cnrs.fr/rihab.ayed/DFSM.pdf for dataset links.
For more details, please refer to perso.liris.cnrs.fr/rihab.ayed/DFSM.pdf
We tested the effect of our modifications on performance.
For all results, see liris.cnrs.fr/rihab.ayed/DFSM.pdf
Please note that the number of frequent subgraphs evolves inversely to the support (MST): this is due to the anti-monotone property of the support (Grahne et al. 2000).
Authors tried to explain this difference in their tests.
Please refer to liris.cnrs.fr/rihab.ayed/ESFSM.pdf for more detailed results of gSpan solutions.
Please refer to liris.cnrs.fr/rihab.ayed/ESFSM.pdf for more detailed results of Gaston solutions.
We verified that failure at low support values is due to a lack of memory (by resorting to a machine with 128 GB of memory).
Please refer to liris.cnrs.fr/rihab.ayed/ESFSM.pdf for more details.
No abortion at the beginning of the execution.
Please refer to liris.cnrs.fr/rihab.ayed/DFSM.pdf for all results of Gaston ParMol
The repository can be accessed by contacting us
CAIR home page: https://www.irit.fr/CAIR/fr/.
References
Acosta-Mendoza, N., Gago-Alonso, A., Medina-Pagola, J.E. (2012). Frequent approximate subgraphs as features for graph-based image classification. Knowledge-Based Systems, 27, 381–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2011.12.002.
Adamchik, V. (2019). Graph theory. www.cs.cmu.edu/~adamchik/21-127/lectures/graphs_1_print.pdf. [Online: Accessed 20 Jul 2019].
Aggarwal, C.C., Wang, H., et al. (2010). Managing and mining graph data Vol. 40. Berlin: Springer.
Agrawal, R., Imieliński, T., Swami, A. (1993). Mining association rules between sets of items in large databases. In Proceedings of the 1993 ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data, SIGMOD ’93. https://doi.org/10.1145/170035.170072 (pp. 207–216). New York: ACM.
Al Hasan, M., Chaoji, V., Salem, S., Besson, J., Zaki, M.J. (2007). ORIGAMI: mining representative orthogonal graph patterns. In Seventh IEEE international conference on data mining (ICDM 2007). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2007.45 (pp. 153–162).
Al Hasan, M., Chaoji, V., Salem, S., Parimi, N., Zaki, M.J. (2005). Dmtl: a generic data mining template library. Library-Centric Software Design (LCSD’05), 53.
Aridhi, S., d’Orazio, L., Maddouri, M., Mephu Nguifo, E. (2015). Density-based data partitioning strategy to approximate large-scale subgraph mining. Information Systems, 48, 213–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.is.2013.08.005.
Aridhi, S., d’Orazio, L., Maddouri, M., Nguifo, E. (2014). Un partitionnement basé sur la densité de graphe pour approcher la fouille distribuée de sous-graphes fréquents. Technique et Science Informatiques, 33(9-10), 711–737. https://doi.org/10.3166/tsi.33.711-737.
Ayed, R., Hacid, M., Haque, R., Jemai, A. (2018). An intra-algorithm comparison study of complete search FSM implementations in centralized graph transaction databases. In Foundations of intelligent systems - 24th international symposium, ISMIS 2018, Limassol, Cyprus, October 29-31, 2018, Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01851-1_8 (pp. 78–88).
Borgelt, C. (2018). Eclat/lcm - frequent item set mining. http://www.borgelt.net/eclat.html. [Online; Accessed 25 Aug 2018].
Borgelt, C. (2016). Moss - molecular substructure miner. http://www.borgelt.net/moss.html. [Online; Accessed 30 May 2016].
Borgelt, C., & Berthold, M.R. (2002). Mining molecular fragments: finding relevant substructures of molecules. In 2002 IEEE international conference on data mining, 2002. ICDM 2003. Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2002.1183885(pp. 51–58).
Buehrer, G., Parthasarathy, S., Nguyen, A., Kim, D., Chen, Y.K., Dubey, P. (2005). Parallel graph mining on shared memory architectures. Technical Report.
Chen, Q. (2018). gspan with python. https://github.com/betterenvi/gSpan. [Online; Accessed 25 Aug 2018].
Cho, Y.R. (2018). Csi 4352, introduction to data mining. http://web.ecs.baylor.edu/faculty/cho/4352/. [Online; Accessed 25 Aug 2018].
Cohen, M., & Gudes, E. (2004). Diagonally subgraphs pattern mining. In Proceedings of the 9th ACM SIGMOD workshop on research issues in data mining and knowledge discovery, DMKD ’04. https://doi.org/10.1145/1008694.1008702 (pp. 51–58). New York: ACM.
Conduff, C. (2018). Gaston graph mining with python. https://github.com/ColinConduff/FrequentSubgraphMining. [Online; Accessed 25 Aug 2018].
Dehaspe, L., Toivonen, H., King, R.D. (1998). Finding frequent substructures in chemical compounds, (pp. 30–36). New York: AAAI Press.
Desrosiers, C., Galinier, P., Hansen, P., Hertz, A. (2007). Sygma: reducing symmetry in graph mining. Tech. rep., Les Cahiers du GERAD.
Dhifli, W., & Nguifo, E. (2015). Motif discovery in protein 3d-structures using graph mining techniques. Pattern Recognition in Computational Molecular Biology: Techniques and Approaches. Hoboken: Wiley.
Douar, B., Liquiere, M., Latiri, C., Slimani, Y. (2014). LC-mine: a framework for frequent subgraph mining with local consistency techniques. Knowledge and Information Systems, 44(1), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10115-014-0769-4.
Elseidy, M., Abdelhamid, E., Skiadopoulos, S., Kalnis, P. (2014). GraMi: frequent subgraph and pattern mining in a single large graph. Proc. VLDB Endow., 7 (7), 517–528. 10.14778/2732286.2732289.
Fei, H. (2016). Fast frequent subgraph mining (ffsm). https://sourceforge.net/projects/ffsm/. [Online; Accessed 30 May 2016].
Gago-Alonso, A., & Carrasco-Ochoa, J.A. (2010). Full duplicate candidate pruning for frequent connected subgraph mining. Integrated Computer-Aided Engineering, 17 (3), 211–225. https://doi.org/10.3233/ICA-2010-0342.
Gago-Alonso, A., Pagola, J.E.M., Carrasco-Ochoa, J.A., Martínez-Trinidad, J.F. (2008). Mining frequent connected subgraphs reducing the number of candidates. In Daelemans, W., Goethals, B., Morik, K. (Eds.) Machine learning and knowledge discovery in databases, no. 5211 in lecture notes in computer science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-87479-9_42 (pp. 365–376). Berlin: Springer.
Gago-Alonso, A., Puentes-Luberta, A., Carrasco-Ochoa, J.A., Medina-Pagola, J.E., Martínez-Trinidad, J.F. (2010). A new algorithm for mining frequent connected subgraphs based on adjacency matrices. Intelligent Data Analysis, 14(3), 385–403. https://doi.org/10.3233/IDA-2010-0427.
Gao, Z., Shang, L., Jian, Y. (2012). Frequent subgraph mining based on the automorphism mapping. In 2012 2nd international conference on computer science and network technology (ICCSNT). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCSNT.2012.6526208 (pp. 1518–1522).
Gibbons, A. (1985). Algorithmic graph theory. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Grahne, G., Lakshmanan, L.V., Wang, X. (2000). Efficient mining of constrained correlated sets. In 16th international conference on data engineering, 2000. Proceedings (pp. 512–521): IEEE.
Gudes, E., Shimony, S.E., Vanetik, N. (2006). Discovering frequent graph patterns using disjoint paths. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 18(11), 1441–1456. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2006.173.
Han, J., Pei, J., Kamber, M. (2011). Data mining: concepts and techniques. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Han, S., Ng, W.K., Yu, Y. (2007). FSP: frequent substructure pattern mining. In 2007 6th international conference on information, communications signal processing (pp. 1–5), DOI https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICS.2007.4449818, (to appear in print).
Helal, N.A., Soliman, T.H., Karam, O.H. (2007). Analyzing efficient embedding list structures in subgraph mining. In IADIS European conference data mining 2007 (part of MCCSIS 2007) (pp. 129–134).
Hong, M., Zhou, H., Wang, W., Shi, B. (2003). An efficient algorithm of frequent connected subgraph extraction. In Whang, K.Y., Jeon, J., Shim, K., Srivastava, J. (Eds.) Advances in knowledge discovery and data mining, no. 2637 in lecture notes in computer science. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-36175-8_5 (pp. 40–51). Berlin: Springer.
van der Horst, E., & Ijzerman, A.P. (2008). Computational approaches to fragment and substructure discovery and evaluation. Chichester: Wiley.
Huan, J., Wang, W., Prins, J. (2003). Efficient mining of frequent subgraphs in the presence of isomorphism. In Third IEEE international conference on data mining, 2003. ICDM 2003 (pp. 549–552): IEEE.
Inokuchi, A., Washio, T., Motoda, H. (2000). An apriori-based algorithm for mining frequent substructures from graph data. In European conference on principles of data mining and knowledge discovery (pp. 13–23): Springer.
Inokuchi, A., Washio, T., Motoda, H. (2003). Complete mining of frequent patterns from graphs: mining graph data. Machine Learning, 50(3), 321–354. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021726221443.
Inokuchi, A., Washio, T., Motoda, H. (2005). A general framework for mining frequent subgraphs from labeled graphs. Fundamenta Informaticae, 66(1-2), 53–82.
Inokuchi, A., Washio, T., Nishimura, K., Motoda, H. (2002). A fast algorithm for mining frequent connected subgraphs. Tech. rep. IBM.
Jiang, C., Coenen, F., Zito, M. (2013). A survey of frequent subgraph mining algorithms. The Knowledge Engineering Review, 28(01), 75–105. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0269888912000331.
Jin, R., Wang, C., Polshakov, D., Parthasarathy, S., Agrawal, G. (2005). Discovering frequent topological structures from graph datasets. In Proceedings of the eleventh ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery in data mining, KDD ’05. https://doi.org/10.1145/1081870.1081944 (pp. 606–611). New York: ACM.
Ke, Y., & Cheng, J. (2008). Efficient correlation search from graph databases. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 20(12), 1601–1615. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2008.86.
Keyvanpour, M.R., & Azizani, F. (2012). Classification and analysis of frequent subgraphs mining algorithms. ResearchGate, 7(1), 220–227. https://doi.org/10.4304/jsw.7.1.220-227.
Kopliku, A., Pinel-Sauvagnat, K., Boughanem, M. (2014). Aggregated search: a new information retrieval paradigm. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 46(3), 41.
Kramer, S., De Raedt, L., Helma, C. (2001). Molecular feature mining in HIV data. In Proceedings of the seventh ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, KDD ’01 (pp. 136–143). New York: ACM, DOI https://doi.org/10.1145/502512.502533, (to appear in print).
Krishna, V., Suri, N.R., Athithan, G. (2011). A comparative survey of algorithms for frequent subgraph discovery. Current Science, 100(2), 190.
Kuramochi, M., & Karypis, G. (2001). Frequent subgraph discovery. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE international conference on data mining, ICDM ’01 (pp. 313–320). Washington: IEEE Computer Society.
Kuramochi, M., & Karypis, G. (2005). Finding frequent patterns in a large sparse graph. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 11(3), 243–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10618-005-0003-9.
Lee, G., & Yun, U. (2012). An efficient approach for mining frequent sub-graphs with support affinities. In International conference on hybrid information technology (pp. 525–532): Springer.
Li, Y., Lin, Q., Zhong, G., Duan, D., Jin, Y., Bi, W. (2009). A directed labeled graph frequent pattern mining algorithm based on minimum code. In Third international conference on multimedia and ubiquitous engineering, 2009. MUE ’09. https://doi.org/10.1109/MUE.2009.67 (pp. 353–359).
McKay, B.D., & et al. (1981). Practical graph isomorphism. Department of Computer Science, Vanderbilt University Tennessee US.
Meinl, T., Wörlein, M., Urzova, O., Fischer, I., Philippsen, M. (2007). The ParMol Package for Frequent Subgraph Mining Electronic Communications of the EASST 1(0). https://doi.org/10.14279/tuj.eceasst.1.85.
Mendoza, N.A., Carrasco-Ochoa, J.A., Gago-Alonso, A., Martınez-trinidad, J.F., Medina-Pagola, J.E. (2015). Representative frequent approximate subgraph mining in multi-graph collections.
Nadimi-Shahraki, M.H., Taki, M., Naderi, M. (2015). IDFP-TREE: an efficient tree for interactive mining of frequent subgraph patterns. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information Technology, 74(3).
Nguyen, P.C., Washio, T., Ohara, K., Motoda, H. (2004). Using a hash-based method for apriori-based graph mining. In Boulicaut, J.F., Esposito, F., Giannotti, F., Pedreschi, D. (Eds.) Knowledge discovery in databases: PKDD 2004, no. 3202 in lecture notes in computer science. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-30116-5_33 (pp. 349–361). Berlin: Springer.
Nijssen, S. (2016). Gaston - download. http://liacs.leidenuniv.nl/~nijssensgr/gaston/download.html. [Online; Accessed 30 May 2016].
Nijssen, S., & Kok, J. (2001). Faster association rules for multiple relations. In International joint conference on artificial intelligence (pp. 891–896). San Mateo: Morgan Kaufmann.
Nijssen, S., & Kok, J.N. (2004). A quickstart in frequent structure mining can make a difference. In Proceedings of the tenth ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, KDD ’04. https://doi.org/10.1145/1014052.1014134 (pp. 647–652). New York: ACM.
Nijssen, S., & Kok, J.N. (2005). The gaston tool for frequent subgraph mining. Electronic Notes in Theoretical Computer Science, 127(1), 77–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.entcs.2004.12.039.
Nijssen, S., & Kok, J.N. (2006). Frequent subgraph miners: runtime dont say everything. In Proceedings of the international workshop on mining and learning with graphs (MLG 2006) (pp. 173–180).
Nowozin, S. (2019). A fork of Sebastian Nowozin’s and Koji Tsuda’s gboost code. https://github.com/rkwitt/gboost. [Online; Accessed 7 Jul 2019].
Nowozin, S., & Tsuda, K. (2008). Frequent subgraph retrieval in geometric graph databases. In 2008 eighth IEEE international conference on data mining. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2008.38 (pp. 953–958).
Patel, H.J., Prajapati, R., Panchal, M., Patel, M. (2013). A survey of graph pattern mining algorithm and techniques. International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & Management, 2(1), 125–129.
Philippsen, M. (2016). Parsemis - the parallel and sequential mining suite. https://www2.cs.fau.de/EN/research/zold/ParSeMiS/index.html. [Online; Accessed 30 May 2016].
Ray, A., Holder, L.B., Choudhury, S. (2014). Frequent subgraph discovery in large attributed streaming graphs. In Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on big data, streams and heterogeneous source mining: algorithms, systems, programming models and applications - vol. 36, BIGMINE’14, pp. 166–181. JMLR.org. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2999973.2999986.
Rehman, S.U., Asghar, S., Zhuang, Y., Fong, S. (2014). Performance evaluation of frequent subgraph discovery techniques. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2014, e869198. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/869198.
Saha, T.K., & Hasan, M.A. (2014). FS3̂: a sampling based method for top-k frequent subgraph mining. arXiv:1409.1152[cs].
Skonieczny, Ł. (2009). Mining for unconnected frequent graphs with direct subgraph isomorphism tests. In Cyran, K.A., Kozielski, S., Peters, J.F., Stańczyk, U., Wakulicz-Deja, A. (Eds.) Man-machine interactions, no. 59 in advances in intelligent and soft computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00563-3_55 (pp. 523–531). Berlin: Springer.
de Sousa Gomide, R., de Aguiar Ciferri, C.D., Ciferri, R.R., Vieira, M.T.P. (2011). ADI-Minebio: a graph mining algorithm for biomedical data. Journal of Information and Data Management, 2(3), 433.
Vijayalakshmi, N. (2011). FP-GraphMiner - a fast frequent pattern mining algorithm for network graphs. Journal of Graph Algorithms and Applications, 15(6), 753–776. https://doi.org/10.7155/jgaa.00247.
Wang, F., Dong, J., Yuan, B. (2013). Graph-based substructure pattern mining using cuda dynamic parallelism. In International conference on intelligent data engineering and automated learning (pp. 342–349): Springer.
Wang, W., Wang, C., Zhu, Y., Shi, B., Pei, J., Yan, X., Han, J. (2005). GraphMiner: a structural pattern-mining system for large disk-based graph databases and its applications. In Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data, SIGMOD ’05. https://doi.org/10.1145/1066157.1066273 (pp. 879–881). New York: ACM.
Washio, T., & Motoda, H. (2003). State of the art of graph-based data mining. Acm Sigkdd Explorations Newsletter, 5(1), 59–68.
Wörlein, M., Meinl, T., Fischer, I., Philippsen, M. (2005). A quantitative comparison of the subgraph miners MoFa, gSpan, FFSM, and Gaston. In Jorge, A.M., Torgo, L., Brazdil, P., Camacho, R., Gama, J. (Eds.) Knowledge discovery in databases: PKDD 2005, no. 3721 in lecture notes in computer science. https://doi.org/10.1007/11564126_39 (pp. 392–403). Berlin: Springer.
Wu, J., & Chen, L. (2008). A fast frequent subgraph mining algorithm. In Young computer scientists, 2008. ICYCS 2008. The 9th international conference for, pp. 82–87. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICYCS.2008.355.
Yan, X. (2016). Software - gspan: frequent graph mining package. http://www.cs.ucsb.edu/~xyan/software/gSpan.htm. [Online; Accessed 30 May 2016].
Yan, X., Cheng, H., Han, J., Yu, P.S. (2008). Mining significant graph patterns by leap search. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGMOD international conference on management of data, SIGMOD ’08. https://doi.org/10.1145/1376616.1376662 (pp. 433–444). New York: ACM.
Yan, X., & Han, J. (2002). gSpan : graph-based substructure pattern mining. Tech. rep., UIUC UIUCDCS-r-2002-2296.
Yan, X., & Han, J. (2002). gSpan: graph-based substructure pattern mining. In 2002 IEEE international conference on data mining, 2002. ICDM 2003. Proceedings, pp. 721–724. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2002.1184038.
Yan, X., & Han, J. (2003). CloseGraph: mining closed frequent graph patterns. In Proceedings of the ninth ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, KDD ’03. https://doi.org/10.1145/956750.956784 (pp. 286–295). New York: ACM.
Zaki, M.J. (2016). Data mining template library (dmtl). http://www.cs.rpi.edu/~zaki/www-new/pmwiki.php/Software/Software. [Online; Accessed 30 May 2016].
Zeng, Z., Wang, J., Zhou, L., Karypis, G. (2006). Coherent closed quasi-clique discovery from large dense graph databases. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, KDD ’06. https://doi.org/10.1145/1150402.1150506 (pp. 797–802). New York: ACM.
Zhou, K. (2016). gspan algorithm in data mining. https://github.com/Jokeren/DataMining-gSpan. [Online; Accessed 30 May 2016].
Acknowledgements
This work was elaborated as a part of the CAIRFootnote 26 project. Special thanks are addressed to FSM authors and particularly to Xifeng Yan, Thorsten Meinl, Andrés Gago-Alonso, Christian Borgelt, Mohammad Al Hasan and Sabeur Aridhi for sending us software, datasets, providing us with some clarifications, as well as for their availability.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This research is performed within the scope of the CAIR (Contextual and Aggregated Information Retrieval) project that is funded by ANR (Agence Nationale de la Recherche) grant ANR-14-CE23-0006 -www.irit.fr/CAIR
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayed, R., Hacid, MS., Haque, R. et al. An updated dashboard of complete search FSM implementations in centralized graph transaction databases. J Intell Inf Syst 55, 149–182 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10844-019-00579-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10844-019-00579-4