Abstract
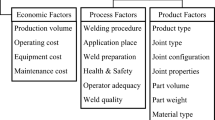
Polishing is widely used as a final processing operation for many products and components. Although the level of automation increases gradually over the years, manual or semi-automatic polishing is still commonly practised. The choice of polishing process parameters is largely based on experience of polishing technicians and involves a lengthy “trial and error” iteration before reaching an acceptable level. This paper proposes to acquire successful projects and build up a case repository of polishing parameters of both products and processes. Case-based reasoning (CBR) is then applied to mimic the experience-based polishing process planning. A problem case is first well-structured and then matched against all cases in the repository. The most similar ones are retrieved for further reasoning for their potentials of being revised and adapted to form an optimal solution. This research combines Fuzzy Set Theory with CBR to address two fundamental problems in polishing process planning. One is that values of product features and process parameters such as polishing force, amount of polishing compounds, polishing wheels, rotating speed, and feed rate cannot be exactly measured and controlled. The other is that influencing relationships between process parameters and polishing quality indicators as measured by surface roughness (Ra) and grossness (Gu) cannot be scientifically established mathematically. A case study is conducted within the collaborating company and the results from the proposed system are generally consistent with the actual decisions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aamodt A., Plaza E. (1994) Case-based reasoning: Foundational issues, methodologies variations, and system approaches. AI Communications 7(1): 39–59
Arezoo B., Ridgway K., Al-Ahmari A.M.A. (2000) Selection of cutting tools and conditions of machining operations using an expert system. Computers in Industry 42(1): 43–58. doi:10.1016/S0166-3615(99)00051-2
Azuaje F., Dubitzky W., Black N., Adamson K. (2000) Discovering relevance knowledge in data: A growing cell structure approach. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics 30(3): 448–460. doi:10.1109/3477.846233
Birnbaum, L., & Collings, G. (1989). Remindings and engineering design themes: A case study in indexing vocabulary. In Proceedings of the second workshop on base-based reasoning, Pensacola Beach, FL, USA.
Boogert R.M., Kals H.J.J., Van F.J.A.M. (1996) Tool paths and cutting technology in computer aided process planning. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 11(3): 186–197. doi:10.1007/BF01351324
Chang P.C., Chen L.Y., Fan C.Y. (2008) A case-based evolutionary model for defect classification of printed circuit board images. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 19(2): 203–214. doi:10.1007/s10845-008-0074-8
Chang P.C., Chen L.Y., Liu C.H. (2006) An evolutionary regulation algorithm for the twin laser measuring system. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 17(5): 545–556. doi:10.1007/s10845-006-0027-z
Chang T.C., Wysk R.A., Wang H.P. (1991) Computer-aided manufacturing. Prentice Hall, New Jersey, USA
David, B. S. (1991). Principles for case representation in a case-based aiding system for lesson planning. In Proceedings of the workshop on case-based reasoning, 8–10 May, Madison Hotel, Washington.
Driankov D., Hellendoorn H., Reinfrank M. (1993) An introduction to fuzzy control. Springer, Berlin, Germany
Dubois, D., Esteva, F., Garcia, P., Godo, L., Lopez de Mantaras, R., & Prade, H. (1997). Fuzzy modelling of case-based reasoning and decision. In Proceeding of case-based reasoning ICCBR’97, Springer Verlag, pp. 599–611.
Dvir, G., Langholz, G., & Schneider, M. (1999). Matching attributes in a fuzzy case based reasoning. In Fuzzy Information Processing Society, 1999, NAFIPS. 18th International conference of the North American (pp. 33–36).
Finnie G., Sun Z. (2003) A logical foundation for the case-based reasoning cycle. International Journal of Intelligent Systems 18(4): 367–382. doi:10.1002/int.10093
Hammond, K. J. (1989). On functionally motivated vocabularies: An apologia. In Proceedings of the second workshop on case-based reasoning, Pensacola Beach, FL, USA.
Haque B.U., Belecheanu R.A., Barson R.J., Pawar K.S. (2000) Towards the application of case based reasoning to decision-making in concurrent product development (concurrent engineering). Knowledge-Based Systems 13(2): 101–112. doi:10.1016/S0950-7051(00)00051-4
Hsu Q.C., Lee R.S. (1991) Geometry-oriented knowledge-based system for preliminary process design of cold-forged parts. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 6(1): 45–61. doi:10.1007/BF02601546
Jaczynski, M., & Trousse, B. (1994). Fuzzy logic for the retrieval step of a case-based reasoner. In Proceeding of the EWCBR’94 (pp. 313–321).
Kolodner J.L. (1991) Improving human decision making through case-based decision aiding. AI Magazine 12(2): 52–68
Kolodner J.L. (1992) An introduction to case-based reasoning. Artificial Intelligence Review 6(1): 3–34. doi:10.1007/BF00155578
Lee D., Lee K.H. (1999) An approach to case-based system for conceptual ship design assistant. Expert Systems with Applications 16(2): 97–104. doi:10.1016/S0957-4174(98)00064-5
Luong L.H.S., Spedding T. (1995) An integrated system for process planning and cost estimation in hole making. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 10(6): 411–415. doi:10.1007/BF01179405
Masao M. (2001) Fuzzy logic for beginners. World Scientific River Edge, USA
Mendes E., Mosley N., Steve Counsell. (2005) Exploring case-based reasoning for web hypermedia project cost estimation. International Journal of Web Engineering Technology 2(1): 117–143. doi:10.1504/IJWET.2005.007467
Mileman T., Knight B., Petridis M., Cowell D., Ewer J. (2002) Case-based retrieval of 3-dimensional shapes for the design of metal castings. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 13(1): 39–45. doi:10.1023/A:1013676928961
Navinchandra, D., Sycara, K. P., & Narasimhan, S. (1991). Behavioral synthesis in CADET: A case-based design tool. In Proceedings of the 7th Conference on Artificial Intelligence Applications, Miami Beach, USA (pp. 217–221).
Schank R. (1982) Dynamic memory: A theory of reminding and learning in computers and people. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Siddique Z., Wilmes L. (2007) An application of design space for assembly process reasoning to utilize current assembly plant resources for new product family members. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 18(1): 171–184. doi:10.1007/s10845-007-0013-0
Simoudis, E., Mendall, A., & Miller, P. (1993). Automated support for developing retrieve-and-propose systems. In Proceedings of artificial intelligence XI conference, Orlando, Florida.
Smith J.S., Cohen P.H., Davis J.W., Irani S.A. (1992) Process plan generation for sheet metal parts using an integrated feature-based expert system approach. International Journal of Production Research 30(5): 1175–1190. doi:10.1080/00207549208942949
Su Q. (2007) Applying case-based reasoning in assembly sequence planning. International Journal of Production Research 45(1): 29–47. doi:10.1080/00207540600632182
Takahashi M., Oono J.I., Saitoh K. (1995) Manufacturing process design by CBR with knowledge ware. IEEE Expert 10(6): 74–80. doi:10.1109/64.483255
Tsai C.Y., Chiu C.C. (2007) A case-based reasoning system for PCB principal process parameter identification. Expert Systems with Applications 32(4): 1183–1193. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2006.02.014
Tsang V.Y.M., Ngai B.K.K., Huang G.Q. et al (2007) Web-based polishing process planning using data-mining techniques. Springer, London, UK
Veerakamolmal P., Gupta S.M. (2002) A case-based reasoning approach for automating disassembly process planning. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. London 13(1): 47–59. doi:10.1023/A:1013629013031
Watson I. (1997) Applying case-based reasoning: Techniques for enterprise systems. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Francisco
Wilson D.R., Martinez T.R. (1997) Improved heterogeneous distance functions. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 6: 1–34
Wu R.-R., Zhang H.-M. (1998) Object-oriented and fuzzy-set-based approach for set-up planning. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 14(6): 406–411. doi:10.1007/BF01304619
Yamazaki K., Kawahara Y., Jeng J.C., Aoyama H. (1995) Autonomous process planning with real-time machining for productive sculptured surface manufacturing based on automatic recognition of geometric features. CIRP Annals—Manufacturing Technology 44(1): 439–444
Yang H., Lu W.F., Lin A.C. (1994) PROCASE: A case-based process planning system for machining of rotational parts. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 5(6): 411–430. doi:10.1007/BF00123660
Yeo S.H., Ngoi B.K.A., Chen H. (1998) Process sequence optimization based on a new cost-tolerance model. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 9(1): 29–37. doi:10.1023/A:1008895224256
Zadeh L.A. (1975) The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning—Part 1. Information Sciences 8: 199–249. doi:10.1016/0020-0255(75)90036-5
Zadeh L.A. (1996) Fuzzy sets, fuzzy logic, and fuzzy systems: Selected papers. World Scientific Publishing Company, NJ, USA
Zhu B., Wang Z., Yang H.C., Zhao Y. (2008) Applying fuzzy multiple attributes decision making for product configuration. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 19(5): 591–598. doi:10.1007/s10845-008-0132-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Huang, G.Q., Ngai, B.K.K. et al. Case-based polishing process planning with Fuzzy Set Theory. J Intell Manuf 21, 831–842 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-009-0259-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-009-0259-9