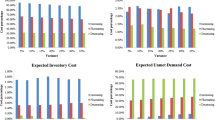
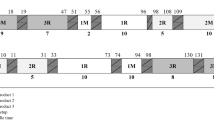
Abstract
This paper considers control wafers replenishment problem in wafer fabrication factories. A dynamic lot-sizing replenishment problem with reentry and downward substitution is examined in a pulling control production environment. The objective is to set the inventory level so as to minimize the total cost of control wafers, where the costs include order cost, purchase cost, setup cost, production cost and holding cost, while maintaining the same level of production throughput. In addition, purchase quantity discounts and precise inventory level are considered in the replenishment model. The control wafers replenishment problem is first constructed as a network, and is then transformed into a mixed integer programming model. Lastly, an efficient heuristic algorithm is proposed for solving large-scale problems. A numerical example is given to illustrate the practicality for empirical investigation. The results demonstrate that the proposed mixed integer programming model and the heuristic algorithm are effective tools for determining the inventory level of control wafers for multi-grades in multi-periods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassok Y., Anupindi R., Akella R. (1997) Single-period multiproduct inventory models with substitution. Operations Research 47: 632–642
Boctor F. F., Laporte G., Renaud J. (2004) Models and algorithms for the dynamic-demand joint replenishment problem. International Journal of Production Research 42(13): 2667–2678
Cárdenas-Barrón L. E. (2010) Adaptive genetic algorithm for lot-sizing problem with self-adjustment operation rate: A discussion. International Journal of Production Economics 123(1): 243–245
Cha B. C., Moon I. K. (2005) The joint replenishment problem with quantity discounts under constant demand. OR Spectrum 27: 569–581
Chang C.-T., Chin C. L., Lin M.-F. (2006) On the single item multi-supplier system with variable lead-time, price-quantity discount, and resource constraints. Applied Mathematics and Computation 182(1): 89–97
Chang C.-T., Lo T. Y. (2009) On the inventory model with continuous and discrete lead time, backorders and lost sales. Applied Mathematical Modelling 33: 2196–2206
Chen K. K., Chang C.-T. (2007) A seasonal demand inventory model with variable lead time and resource constraints. Applied Mathematical Modelling 31: 2433–2445
Chung S. H., Pearn W. L., Kang H. Y. (2005) Control wafers inventory management in the wafer fabrication photolithography area. Production Planning and Control 16: 286–296
Chung C.-S., Hum S.-H., Kirca O. (1996) The coordinated replenishment dynamic lot-sizing problem with quantity discounts. European Journal of Operational Research 94(1): 122–133
Chung C.-S., Hum S.-H., Kirca O. (2000) Optimal procedure for the coordinated replenishment dynamic lot-sizing problem with quantity discounts. Naval Research Logistics 47(8): 686–695
Compaq Visual Fortran programmer’s guide, version 6.6. (2001). Compaq Computer Corporation, Houston, USA.
Denizel M., Süral H. (2006) On alternative mixed integer programming formulations and LP-based heuristics for lot-sizing with setup times. Journal of Operations Research Society 57: 389–399
de Araujo S. A., Arenales M. N., Clark A. R. (2008) Lot sizing and furnace scheduling in small foundries. Computers and Operations Research 35: 916–932
Goren H. G., Tunali S., Jans R. (2010) A review of applications of genetic algorithms in lot sizing. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 21: 575–590
Hop N. V., Tabucanon M. T. (2005) Adaptive genetic algorithm for lot-sizing problem with self-adjustment operation rate. International Journal of Production Economics 98(2): 129–135
Hsu A., Bassok Y. (1999) Random yield and random demand in a production system with downward substitution. Operations Research 47: 277–290
Jans R., Degraeve Z. (2008) Modeling industrial lot sizing problems: A review. International Journal of Production Research 46(6): 1619–1643
Kang H.-Y. (2008) Optimal replenishment policies for deteriorating control wafers inventory. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 35: 736–744
LINGO user’s manual, version 10. (2006). LINGO System Inc., Chicago, USA.
Minner S. (2009) A comparison of simple heuristics for multi-product dynamic demand lot-sizing with limited warehouse capacity. International Journal of Production Economics 118(1): 305–310
Mohammadi M., Ghomi S. M. T. F., Karimi B., Torabi S. A. (2010) Rolling-horizon and fix-and-relax heuristics for the multi-product multi-level capacitated lotsizing problem with sequence-dependent setups. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 21: 501–510
Özelkan E. C., Çakanyildirim M. (2006) Test wafer management for semiconductor manufacturing. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing 19: 241–251
Raa B., Aghezzaf E. H. (2005) A robust dynamic planning strategy for lot-sizing problems with stochastic demands. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 16: 207–213
Rajagopalan S., Swaminathan J. M. (2001) A coordinated production planning model with capacity expansion and inventory management. Management Science 47: 1562–1580
Rezaei J., Davoodi M. (2008) A deterministic, multi-item inventory model with supplier selection and imperfect quality. Applied Mathematical Modelling 32: 2106–2116
Robinson P., Narayanan A., Sahin F. (2009) Coordinated deterministic dynamic demand lot-sizing problem: A review of models and algorithms. Omega 37: 3–15
Stadtler H. (1996) Mixed integer programming model formulations for dynamic multi-item multi-level capacitated lotsizing. European Journal of Operational Research 94: 561–581
Süer G. A., Badurdeen F., Dissanayake N. (2008) Capacitated lot sizing by using multi-chromosome crossover strategy. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing 19: 273–282
Wagner H. M., Whitin T. M. (1958) Dynamic version of the economic lot size model. Management Science 5: 89–96
Wemmerlöv U. (1982) A comparison of discrete, single stage lot-sizing heuristics with special emphasis on rules based on the marginal cost principle. Engineering Costs and Production Economics 7: 45–53
Wu M. C., Chien C. S., Lu K. S. (2005) Downgrade decision for control/dummy wafers in a fab. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 26: 585–590
Yang P. C., Wee H. W., Yu J. C. P. (2007) Collaborative pricing and replenishment policy for hi-tech industry. Journal of Operations Research Society 58: 894–900
Zoller K., Robrade A. (1988) Efficient heuristics for dynamic lot sizing. International Journal of Production Research 26: 249–265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, HY., Lee, A.H.I. & Lai, CM. An integrated replenishment model with quantity discounts, reentry and downward substitution for control wafers. J Intell Manuf 23, 1745–1761 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-010-0479-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-010-0479-z