Abstract
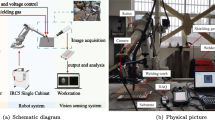
Ability to observe and measure weld pool surfaces in real-time is the foundation for next generation intelligent welding that partially mimics welders’ sensory capability, i.e., acquiring weld status information from the observation of weld pool. To image and measure the mirror-like weld pool surface under the strong arc radiation, a structured light laser pattern, dot matrix, has been projected onto the weld pool surface and its specular reflection is intercepted and imaged by an imaging plane placed with a distance from the arc. The reflection pattern, deformed by the specular liquid weld pool, contains three-dimensional (3D) geometry information of the weld pool. In this paper, a robust recognition procedure has been proposed to identify the reflection pattern in real-time. In particular, an adaptive thresholding algorithm is proposed to distinguish the laser dots in the reflection pattern. Then a reflection pattern recognition algorithm is proposed to determine the row and column number for each reflected laser dot such that reflection pattern can be matched with the projection pattern. The identified reflection pattern can be used to reconstruct the 3D weld pool surface. Experiments with different welding conditions have been conducted to verify the real-time performance of the proposed procedure, including the effectiveness, robustness and time complexity. It has been found that the procedure is capable of identifying the reflection pattern from a captured image in less than 19 ms. The real-time performance meets the most widely used arc welding process for precise welding-gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) that typically requires to be controlled a few times per second.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, R., & Bischof, L. (1994). Seeded region growing. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 16, 641–647.
Ai, X. P., Liu, N. S., Wei, Y. Q., Hu, X., & Wei, X. R. L. S. (2009). Study on image acquisition in 3-d sensor system of arc welding pool surface shape using grating projection. Proceedings of SPIE, 7506, 750628.
Anedenroomer, A. J. R., & den Ouden, G. (1998). Weld pool oscillation as a tool for penetration sensing during pulsed GTA welding. Welding Journal, 77(5), 181–187.
ANSI/ASME Standard 36.19M. American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Std.
Balfour, C., Smith, J., & Al-Shamma, A. (2006). A novel edge feature correlation algorithm for real-time computer vision-based molten weld pool measurements. Welding Journal, 85(1), 1s–8s.
Bao, M., & Ume, I. C. (2006). Real-time weld penetration depth monitoring with laser ultrasonic sensing system. Transactions of the ASME, 28, 280–286.
Chandrasekhar, N., Vasudevan, M., Bhaduri, A. K., & Jayakumar, T. (2013). Intelligent modeling for estimating weld bead width and depth of penetration from infra-red thermal images of the weld pool. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-013-0762-x.
Chavan, M. S., Mastorakis, N., Chavan, M. N., & Gaikwad, M. S. (2011). Implementation of symlet wavelets to removal of gaussian additive noise from speech signal. In NEHIPISIC’11 Proceeding of 10th WSEAS international conference on electronics, hardware, wireless and optical communications, and 10th WSEAS international conference on signal processing, robotics and automation, and 3rd WSEAS international conference on nanotechnology, and 2nd WSEAS international conference on Plasma-fusion-nuclear physics.
Chokkalingham, S., Chandrasekhar, N., & Vasudevan, M. (2012). Predicting the depth of penetration and weld bead width from the infra red thermal image of the weld pool using artificial neural network modeling. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(5), 1995–2001.
Choong, D. Y., & Lee, J. (2004). 3-d measurement of weld pool using biprism stereo vision sensor, Seoul National University. http://joining1.kaist.ac.kr/research/vision.htm.
Daubechies, I. (1992). Ten lectures on wavelets. Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics.
Donoho, D. L., & Johnstone, I. M. (1994). Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage. Biometrika, 81, 425–455.
Du, Q. Y., Chen, S. B., & Lin, T. (2006). Reconstruction of weld pool surface based on shape from shading. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 19(2), 168–171.
Fan, C., Lv, F., & Chen, S. (2009). Visual sensing and penetration control in aluminum alloy pulsed GTA welding. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 42(1), 126–137.
Fukunage, K. (1972). Introduction to statistical pattern recognition. New York: Academic Press.
Gonzalez, R. C., & Woods, R. E. (2007). Digital image processing, 3rd ed. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Graham, G., & Ume, I. (1997). Automated system for laser ultrasonic sensing of weld penetration. Mechatronics, 7(8), 711–721.
Gupta, S., Kaur, L., Chauhan, R., & Saxena, S. (2009). A wavelet based statistical approach for speckle reduction in medical ultrasound images. In Conference on convergent technologies for the Asia-Pacific region.
Kovacevic, R., & Zhang, Y. M. (1996). Sensing free surface of arc weld pool using specular reflection: Principle and analysis. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part B, Journal of Engineering Manufacturing, 210(6), 553–564.
Kovacevic, R., & Zhang, Y. M. (1997). Real-time image processing for monitoring of free weld pool surface. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 119, 161–169.
Lee, J.-S. (1981). Speckle analysis and smoothing of synthetic aperture radar images. Computer Graphics and Image Processing, 17, 24–32.
Li, L. P., Yang, X. Q., Zhang, F. Y., & Lin, T. (2011). Research on surface recover of aluminum alloy PGTAW pool based on SFS. Robotic Welding, Intelligence and Automation, Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering., 88, 307–314.
Liao, T. W. (2004). Fuzzy reasoning based automatic inspection of radiographic welds: Weld recognition. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 15, 69–85.
Ma, H. B., & Wei, S. C. (2010). Binocular vision system for both weld pool and root gap in robot welding process. Sensor Review, 30(2), 116–123.
Ma, X. J., & Zhang, Y. M. (2011). Gas metal arc weld pool surface imaging: Modeling and processing. Welding Journal, 90(5), 85s–94s.
Mnich, C., Al-Bayat, F., Debrunner, C., et al. (2004). In situ weld pool measurement using stereovision. Proceedings of 2004 Japan–USA symposium on flexible automation, ASME, pp. 1–2.
O’Brien, R. (Ed.) (1998). Welding handbook, 8th edn, Vol. 2—Welding Processes. AWS.
Petrou, M., & Petrou, C. (2010). Image processing: The fundamentals. New York: Wiley.
Saeed, G., & Zhang, Y. M. (2003). Mathematical formulation and simulation of specular reflection based measurement system for gas tungsten arc weld pool surface. Measurement Science and Technology, 14(8), 1671–1682.
Shiwa, M., Yamaguchi, A., Sato, M., Murao, S., & Nagai, M. (1999). Acoustic emission waveform analysis from weld defects in steel ring samples. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 121(1), 77–83.
Song, H. S., & Zhang, Y. M. (2007). Three-dimensional reconstruction of specular surface for gas tungsten arc weld pool. Measurement Science and Technology, 18, 3751–3767.
Song, H. S., & Zhang, Y. M. (2007). Image processing for measurement of three-dimensional GTAW weld pool surface. Welding Journal, 86, 323s–330s.
Sorensen, C., & Eagar, T. (1990). Measurement of oscillations in partially penetrated weld pools through spectral analysis. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 112, 463–468.
Steele, J., Mnich, C., Debrunner, C., Vincent, T., & Liu, S. (2005). Development of closed-loop control of robotic welding processes. Industrial Robot: An International Journal, 32(4), 350–355.
Tso, B., & Mather, P. (2009). Classification methods for remotely sensed data (2nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Wang, X., & Li, R. (2013). Intelligent modelling of back-side weld bead geometry using weld pool surface characteristic parameters. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-013-0731-4.
Wang, J. F., Wang, W. Y., & Chen, S. B. (2007). Extraction of welding pool shape using linear approximation. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 28(8), 54–56.
Wang, J., Wang, W., & Chen, S. (2009). Inspection of welding pool height from shading in pulsed GTAW with wire filler. Industrial Robot: An International Journal, 36(3), 270–276.
Wei, Y. Q., Liu, N. S., Hu, X., & Ai, X. (2011). Phase-correction algorithm of deformed grating images in the depth measurement of weld pool surface in gas tungsten arc welding. Optical Engineering, 50(5), 057209(1)–057209(7).
Wikle, H. C., Zee, R. H., & Chin, B. (1999). Sensing system for weld process control. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 89–90, 254–259.
Xiong, J., Zhang, G., Hu, J., & Wu, L. (2012). Bead geometry prediction for robotic GMAW-based rapid manufacturing through a neural network and a second-order regression analysis. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-012-0682-1.
Yan, Z. H., Zhang, G. J., & Wu, L. (2011). Simulation and controlling for weld shape process in p-gmaw based on fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE international conference on mechatronics and automation, pp. 2078–2082.
Zhang, W. J., Zhang, Y. M. (2012). Real-time measurement of the weld pool surface in gtaw process. In: Trends in Welding Research Proceedings of the 9th International Conference.
Zhang, G. J., Yan, Z. H., & Lin, L. (2006). Reconstructing a three-dimensional p-GMAW weld pool shape from a two-dimensional visual image. Measurement Science and Technology, 17(7), 1877–1882.
Zhang, W., Liu, Y., & Zhang, Y. M. (2012). Characterization of three-dimensional weld pool surface in GTAW. Welding Journal, 91(7), 195s–203s.
Zong, X., Laine, A. F., & Geiser, E. A. (1998). Speckle reduction and contrast enhancement of echocardiograms via multiscale nonlinear processing. IEEE Transcations on Medical Imaging, 17, 532–540.
Acknowledgments
This work is funded by the National Science Foundation under Grant CMMI-\(0927707\).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W.J., Zhang, X. & Zhang, Y.M. Robust pattern recognition for measurement of three dimensional weld pool surface in GTAW. J Intell Manuf 26, 659–676 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-013-0825-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-013-0825-z