Abstract
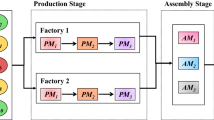
This paper studies the problem of scheduling a multiple-load carrier which is used to deliver parts to line-side buffers of a general assembly (GA) line. In order to maximize the reward of the GA line, both the throughput of the GA line and the material handling distance are considered as scheduling criteria. After formulating the scheduling problem as a reinforcement learning (RL) problem by defining state features, actions and the reward function, we develop a Q(\(\lambda \)) RL algorithm based scheduling approach. To improve performance, forecasted information such as quantities of parts required in a look-ahead horizon is used when we define state features and actions in formulation. Other than applying traditional material handling request generating policy, we use a look-ahead based request generating policy with which material handling requests are generated based not only on current buffer information but also on future part requirement information. Moreover, by utilizing a heuristic dispatching algorithm, the approach is able to handle future requests as well as existing ones. To evaluate the performance of the approach, we conduct simulation experiments to compare the proposed approach with other approaches. Numerical results demonstrate that the policies obtained by the RL approach outperform other approaches.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belmecheri, F., Prins, C., Yalaoui, F., & Amodeo, L. (2013). Particle swarm optimization algorithm for a vehicle routing problem with heterogeneous fleet, mixed backhauls, and time windows. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 24(4), 775–789. doi:10.1007/s10845-012-0627-8.
Berman, S., Schechtman, E., & Edan, Y. (2009). Evaluation of automatic guided vehicle systems. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 25(3), 522–528. doi:10.1016/j.rcim.2008.02.009.
Chen, C., Xi, L., Zhou, B., & Zhou, S. (2011). A multiple-criteria real-time scheduling approach for multiple-load carriers subject to LIFO-loading constraints. International Journal of Production Research, 49(16), 4787–4806. doi:10.1080/00207543.2010.510486.
Chen, C., Zhou, B., & Xi, L.. (2010). A support vector machine based scheduling approach for a material handling system. In: Presented at the natural computation (ICNC), 2010 sixth international conference on (Vol. 7, pp. 3768–3772).
Dang, Q.-V., Nielsen, I., Steger-Jensen, K., & Madsen, O. (2013). Scheduling a single mobile robot for part-feeding tasks of production lines. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-013-0729-y.
de Koster, R.(M.) B. M., Le-Anh, T., & van der Meer, J. R. (2004). Testing and classifying vehicle dispatching rules in three real-world settings. Journal of Operations Management, 22(4), 369–386. doi:10.1016/j.jom.2004.05.006.
Duda, R. O., & Hart, P. E. (1973). Pattern classification and scene analysis. New York: Wiley.
Fowler, J. W., Hogg, G. L., & Philips, D. T. (1992). Control of multiproduct bulk service diffusion/oxidation processes. IIE Transactions, 24(4), 84–96. doi:10.1080/07408179208964236.
Gabel, T., & Riedmiller, M. (2011). Distributed policy search reinforcement learning for job-shop scheduling tasks. International Journal of Production Research, 50(1), 41–61. doi:10.1080/00207543.2011.571443.
Grunow, M., Günther, H.-O., & Lehmann, M. (2004). Dispatching multi-load AGVs in highly automated seaport container terminals. OR Spectrum, 26(2), 211–235. doi:10.1007/s00291-003-0147-1.
Ho, Y.-C., Liu, H.-C., & Yih, Y. (2012). A multiple-attribute method for concurrently solving the pickup-dispatching problem and the load-selection problem of multiple-load AGVs. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 31(3), 288–300. doi:10.1016/j.jmsy.2012.03.002.
Jeon, S., Kim, K., & Kopfer, H. (2011). Routing automated guided vehicles in container terminals through the Q-learning technique. Logistics Research, 3(1), 19–27. doi:10.1007/s12159-010-0042-5.
Joe, Y. Y., Gan, O. P., & Lewis, F. L. (2012). Multi-commodity flow dynamic resource assignment and matrix-based job dispatching for multi-relay transfer in complex material handling systems (MHS). Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 1–17. doi:10.1007/s10845-012-0713-y.
Kim, D. B., & Hwang, H. (2001). A dispatching algorithm for multiple-load AGVS using a fuzzy decision-making method in a iob shop environment. Engineering Optimization, 33(5), 523–547. doi:10.1080/03052150108940932.
Le-Anh, T., & De Koster, M. B. M. (2006). A review of design and control of automated guided vehicle systems. European Journal of Operational Research, 171(1), 1–23. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2005.01.036.
Le-Anh, T., de Koster, R. B. M., & Yu, Y. (2010). Performance evaluation of dynamic scheduling approaches in vehicle-based internal transport systems. International Journal of Production Research, 48(24), 7219–7242. doi:10.1080/00207540903443279.
Li, X., Tao Geng, YuPu Yang, & Xiaoming Xu. (2002). Multiagent AGVs dispatching system using multilevel decisions method. In Presented at the American control conference, 2002. Proceedings of the 2002, IEEE (Vol. 2, pp. 1135–1136 vol. 2). doi:10.1109/ACC.2002.1023172.
Min, H.-S., & Yih, Y. (2003). Selection of dispatching rules on multiple dispatching decision points in real-time scheduling of a semiconductor wafer fabrication system. International Journal of Production Research, 41(16), 3921–3941.
Montazeri, M., & Van Wassenhove, L. N. (1990). Analysis of scheduling rules for an FMS. International journal of production research, 28(4), 785.
Nayyar, P., & Khator, S. K. (1993). Operational control of multi-load vehicles in an automated guided vehicle system. In Proceedings of the 15th annual conference on computers and industrial engineering (pp. 503–506). Blacksburg, Virginia, United States: Pergamon Press, Inc., Retrieved from http://portal.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=186340
Neuts, M. F. (1967). A general class of bulk queues with Poisson input. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 38(3), 759–770.
Occena, L. G., & Yokota, T. (1993). Analysis of the AGV loading capacity in a JIT environment. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 12(1), 24.
Orides, M., Castro, P. A. D., Kato, E. R. R., & Camargo, H. A. (2006). A genetic fuzzy system for defining a reactive dispatching rule for AGVs. In Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 2006. SMC ’06. IEEE international conference on (Vol. 1, pp. 56–61). doi:10.1109/ICSMC.2006.384358.
Ozden, M. (1988). A simulation study of multiple-load-carrying automated guided vehicles in a flexible manufacturing system. International Journal of Production Research, 26(8), 1353–1366. doi:10.1080/00207548808947950.
Peng, J., & Williams, R. J. (1996). Incremental multi-step Q-learning. Machine Learning, 22(1–3), 283–290. doi:10.1023/A:1018076709321.
Potvin, J.-Y., Shen, Y., & Rousseau, J.-M. (1992). Neural networks for automated vehicle dispatching. Computers & Operations Research, 19(3–4), 267–276. doi:10.1016/0305-0548(92)90048-A.
Sarin, S. C., Varadarajan, A., & Wang, L. (2010). A survey of dispatching rules for operational control in wafer fabrication. Production Planning & Control, 22(1), 4–24. doi:10.1080/09537287.2010.490014.
Sinriech, D., & Kotlarski, J. (2002). A dynamic scheduling algorithm for a multiple-load multiple-carrier system. International Journal of Production Research, 40(5), 1065–1080. doi:10.1080/00207540110105662.
Vahdani, B., Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R., Zandieh, M., & Razmi, J. (2012). Vehicle routing scheduling using an enhanced hybrid optimization approach. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(3), 759–774. doi:10.1007/s10845-010-0427-y.
Vis, I. F. A. (2006). Survey of research in the design and control of automated guided vehicle systems. European Journal of Operational Research, 170(3), 677–709. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2004.09.020.
Wang, C.-N., & Chen, L.-C. (2012). The heuristic preemptive dispatching method of material transportation system in 300 mm semiconductor fabrication. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(5), 2047–2056. doi:10.1007/s10845-011-0531-7.
Wang, Y. C., & Usher, J. M. (2005). Application of reinforcement learning for agent-based production scheduling. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 18(1), 73–82. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2004.08.018.
Weng, W. W., & Leachman, R. C. (1993). An improved methodology for real-time production decisions at batch-process work stations. IEEE Transactions on Semiconductor Manufacturing, 6(3), 219–225. doi:10.1109/66.238169.
Zhang, Z., Zheng, L., Hou, F., & Li, N. (2011). Semiconductor final test scheduling with Sarsa(\(\lambda \), k) algorithm. European Journal of Operational Research, 215(2), 446–458. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2011.05.052.
Zhang, Z., Zheng, L., Li, N., Wang, W., Zhong, S., & Hu, K. (2012). Minimizing mean weighted tardiness in unrelated parallel machine scheduling with reinforcement learning. Computers & Operations Research, 39(7), 1315–1324. doi:10.1016/j.cor.2011.07.019.
Acknowledgments
The research is supported by the National Science Foundation of China under Grants No. 51075277, No. 51275558 and No. 61273035.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Xia, B., Zhou, Bh. et al. A reinforcement learning based approach for a multiple-load carrier scheduling problem. J Intell Manuf 26, 1233–1245 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-013-0852-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-013-0852-9