Abstract
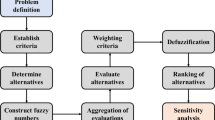
A programmable logic controller (PLC) is a real-time system operated in severe conditions such as high/low temperatures or tough environments with excessive electrical noise. In particular, a PLC is designed to connect and control multiple mechatronic devices such as facility sensors and actuators and thus the issue of selecting/assessing PLC suppliers is critically important to achieve automatic process control and facility monitoring. In reality, various MCDM (multi-criteria decision making) composed of MADM (multi-attribute) and MODM (multi-objective) based schemes are frequently adopted to tackle the problem of supplier selection. Nevertheless, most of them have the following demerits: (1) the causal dependences between main criteria (or associate attributes) are rarely considered (2) a large number of pairwise comparisons are usually required to conduct the evaluation process. Consequently, a novel framework combining fuzzy DEMATEL, fuzzy AHP, with fuzzy Delphi is proposed to overcome the aforementioned shortcomings. Without requiring tedious pairwise comparisons, the importance weights of main criteria (associated attributes) and the performance scores of PLC vendors are systematically fused into the whole evaluation process. Furthermore, an industrial example is demonstrated to assist PLC practitioners in assessing the top three suppliers, such as SIEMENS (31 %), Allen-Bradley (22 %) and Mitsubishi (13 %).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolton, W. (2009). Programmable logic controllers (5th ed.). Newnes.
Chang, K. H., & Cheng, C. H. (2011). Evaluating the risk of failure using the fuzzy OWA and DEMATEL method. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 22, 113–129.
Chen, M. F., Tzeng, G. H., & Ding, C. G. (2008). Combining fuzzy AHP with MDS in identifying the preference similarity of alternatives. Applied Soft Computing, 8, 110–117.
Chua, T. C., & Lin, Y. (2009). An extension to fuzzy MCDM. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 57, 445–454.
Erol, I., William, G., & Ferrell, W. G, Jr. (2003). A methodology for selection problems with multiple conflicting objectives and both qualitative and quantitative criteria. International Journal of Production Economics, 86, 187–199.
Fontela, E., & Garbus, A. (1976). The DEMATEL observer. Battelle Institute, Geneva Research Centre.
Geng, X., Chu, X., Xue, D., & Zhang, Z. (2010). An integrated approach for rating engineering characteristics’ final importance in product-service system development. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 59, 585–594.
Guo, R. S., Chiang, M. H., & Pai, F. Y. (2007). Multi-objectives exception management model for semiconductor back-end environment under turnkey service. Production Planning & Control, 18(3), 203–216.
Ho, W., Xu, X., & Dey, P. K. (2010). Multi-criteria decision making approaches for supplier evaluation and selection: A literature review. European Journal of Operational Research, 202, 16–24.
Hwang, C. L., & Yoon, K. (1981). Multiple attribute decision making-methods and applications: A state of the art survey. Berlin: Springer.
Kumar, M., Vrat, P., & Shankar, R. (2004). A fuzzy goal programming approach for vendor selection problem in a supply chain. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 46, 69–85.
Lin, Y. T., Lin, C. L., Yu, H. C., & Tzeng, G. H. (2010). A novel hybrid MCDM approach for outsourcing vendor selection: A case study for a semiconductor company in Taiwan. Expert Systems with Applications, 37, 4796–4804.
Murry, T. J., Pipino, L. L., & Gigch, J. P. (1985). A pilot study of fuzzy set modification of Delphi. Human Systems Management, 5(1), 76–80.
Rabiee, M. (2012). Programmable logic controllers: Hardware and programming (3rd ed.). Tinley Park, IL: Goodheart-Willcox.
Saaty, T. L. (1980). The analytic hierarchy process. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Shyur, H. J., & Shih, H. S. (2006). A hybrid MCDM model for strategic vendor selection. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 44, 749–761.
Tzeng, G. H., & Huang, J. J. (2013). Multiple attribute decision making: Methods and applications. New York: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis.
Wadhwa, V., & Ravindran, A. R. (2007). Vendor selection in outsourcing. Computers & Operations Research, 34(12), 3725–3737.
Wang, C. H., & Chen, J. N. (2012). Using quality function deployment for collaborative product design and optimal selection of module mix. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 63(4), 1030–1037.
Wu, W. W. (2012). Segmenting critical factors for successful knowledge management implementation using the fuzzy DEMATEL method. Applied Soft Computing, 12(1), 527–535.
Yang, J. L., Chiu, H. N., Tzeng, G. H., & Yeh, R. H. (2008). Vendor selection by integrated fuzzy MCDM techniques with independent and interdependent relationships. Information Sciences, 178(21–1), 4166–4183.
Zhu, B., Wang, Z., Yang, H., Mo, R., & Zhao, Y. (2008). Applying fuzzy multiple attributes decision making for product configuration. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 19(5), 591–598.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank two anonymous referees for their constructive comments on improving the quality of this draft.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, CH., Wu, HS. A novel framework to evaluate programmable logic controllers: a fuzzy MCDM perspective. J Intell Manuf 27, 315–324 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-013-0863-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-013-0863-6