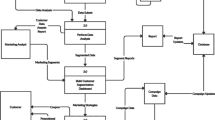
Abstract
To enhance customer retention and customer acquisition, product differentiation, product configuration and product recommendation are of importance to help firms implement segmentation–targeting–positioning strategies. In reality, however, user perceptions of product features are usually vague and diverse by individuals. Consequently, for a manufacturer, learning an efficient way to balance the trade-offs between satisfying customer needs and optimizing product varieties has become much more challenging than before. In order to overcome the aforementioned difficulty, this paper presents a novel framework to assist firms in determining the optimal product varieties of smart glasses with consideration of diverse requirements of three distinct segments (i.e. home entertainment, medical healthcare, and industry service). In particular, correspondence analysis is employed to indicate which product attributes best characterize a specific segment for achieving product differentiation. Then, by means of Grey relational model, the top three priorities with regard to three segments are systematically identified for conducting product configuration. Lastly, Bayes theorem is utilized to assign a potential buyer to his/her most similar segment for accomplishing unsupervised product recommendation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, Y. F., Chen, C. S., & Zhou, H. (2009). Smart phone for mobile commerce. Computers Standards & Interfaces, 31, 740–747.
Chen, C. C., & Chuang, M. C. (2008). Integrating the Kano model into a robust design approach to enhance customer satisfaction with product design. International Journal of Production Economics, 114(2), 667–681.
Deng, J. (1982). Control problems of grey systems. System and Control Letters, 1(5), 288–294.
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. I., & Anderson, R. E. (2009). Multivariate data analysis (7th ed.). New York: Prentice Hall.
Işıklar, G., & Büyüközkan, G. (2007). Using a multi-criteria decision making approach to evaluate mobile phone alternatives. Computers Standards & Interfaces, 29, 265–274.
Johnson, R. A., & Wichern, D. W. (2006). Applied multivariate statistical analysis (8th ed.). New York: Prentice Hall.
Kwong, C. K., Luo, X. G., & Tang, J. F. (2011). A methodology for optimal positioning with engineering constraints consideration. International Journal of Production Economics, 132(1), 93–100.
Lai, H. H., Lin, Y. C., Yeh, C. H., & Wei, C. H. (2006). User-oriented design for the optimal combination on product design. International Journal of Production Economics, 100(1), 253–267.
Lilien, G. L., & Rangaswamy, A. (2003). Marketing engineering—Computer assisted marketing analysis and planning (2nd ed.). New York: Prentice Hall.
Lin, Y. C., Lai, H. H., & Yeh, C. H. (2007). Consumer-oriented product form design based on fuzzy logic: A case study of mobile phones. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 37, 531– 543.
Liu, D. R., & Shih, Y. Y. (2005). Hybrid approaches to product recommendation based on customer lifetime value and purchase preferences. The Journal of systems and Software, 77, 181–191.
Liu, C., Ramirez-Serrano, A., & Yin, G. (2011). Customer-driven product design and evaluation method for collaborative design environments. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 22(5), 751–764.
Luo, X. G., Kwong, C. K., & Tang, J. F. (2010). Determining optimal levels of engineering characteristics in quality function deployment under multi-segment market. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 59(1), 126–135.
Oküdan, G. E., Chiu, M. C., & Kim, T. H. (2013). Perceived feature utility-based product family design: A mobile phone case study. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 24(5), 935–949.
Petiot, J. F., & Grogent, S. (2006). Product design: A vectors field-based approach for preference modeling. Journal of Engineering Design, 17(3), 217–233.
Wang, C. H., & Hsueh, O. Z. (2013). A novel approach to incorporate customer preference and perception into product configuration: A case study on smart pads. Computer Standards & Interfaces, 35(5), 549–556.
Wang, C. H., & Shih, C. W. (2013). Integrating conjoint analysis with quality function deployment to carry out customer-driven concept development for ultrabooks. Computer Standards & Interfaces, 36(1), 89–96.
Wang, C. H., & Wu, C. W. (2014). Combining conjoint analysis with Kano model to optimize product varieties of smart phones: A VIKOR perspective. Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering. doi:10.1080/21681015.2014.918566.
Wang, Y., & Tseng, M. M. (2013a). Customized products recommendation based on probabilistic relevance model. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 24(5), 951–960.
Wang, Y., & Tseng, M. M. (2013b). A Naïve Bayes approach to map customer requirements to product variants. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. doi:10.1007/s10845-013-0806-2.
Yang, Y. S., Shih, C. Y., & Fung, R. F. (2014). Multi-objective optimization of the light guide rod by using the combined Taguchi method and Grey relational approach. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 25(1), 99–107.
Acknowledgments
The author wants to thank two anonymous referees’ for their constructive comments on improving the quality of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, CH. Integrating correspondence analysis with Grey relational model to implement a user-driven STP product strategy for smart glasses. J Intell Manuf 27, 1007–1016 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0931-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0931-6