Abstract
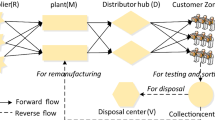
Growing awareness of environmental issues is prompting the development of sustainable supply chain management. Closed-loop supply chains in which used products can be returned for remanufacture are becoming increasingly popular. This paper introduces a two-phase approach to the design of supply chain networks taking into account carbon emission and remanufacturing. In the first phase, a continuous approximation model is used to design the forward supply chain network. The objective is to minimize the total forward network cost by simultaneously determining the number and the service areas of distribution centers (DCs) and the replenishment cycle time for DCs. A nonlinear optimization technique is used to solve the forward supply chain network design problem. In the second phase, a reverse supply chain network is formulated based on the results of the first phase to determine the optimal number and service areas of remanufacturing centers (RCs) and the replenishment cycle time for RCs. Finally, numerical analyses are conducted to show the solution approach and provide some managerial insights.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amezquita, T., Hammond, R., Salazar, M., & Bras, B. (1995). Characterizing the remanufacturability of engineering systems. ASME advances in design automation conference, 1995. American Society of Mechanical Engineersm, US, 82, 271–278.
Baud-Lavigne, B., Agard, B., & Penz, B. (2014). Environmental constraints in joint product and supply chain design optimization. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 76, 16–22. doi:10.1016/j.cie.2014.07.014.
Benjaafar, S., Li, Y., & Daskin, M. (2010). Carbon footprint and the management of supply chains: Insights from simple models. Working paper. University of Minnesota.
Bing, X., Bloemhof-Ruwaard, J. M., & van der Vorst, J. G. A. J. (2014). Sustainable reverse logistics network design for household plastic waste. Flexible Services and Manufacturing Journal, 26, 119–142. doi:10.1007/s10696-012-9149-0.
Chen, J. M., & Chang, C. I. (2012). The co-opetitive strategy of a closed-loop supply chain with remanufacturing. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 48, 387–400. doi:10.1016/j.tre.2011.10.001.
Dasci, A., & Verter, V. (2001). A continuous model for production-distribution system design. European Journal of Operational Research, 129, 287–298. doi:10.1016/S0377-2217(00)00226-5.
Daskin, M. S. (1985). Special Issue Transportation Research: The State of the Art and Research OpportunitiesLogistics: An overview of the state of the art and perspectives on future research. Transportation Research Part A: Genera, 19, 383–398. doi:10.1016/0191-2607(85)90036-6.
Elhedhli, S., & Merrick, R. (2012). Green supply chain network design to reduce carbon emissions. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 17(5), 370–379. doi:10.1016/j.trd.2012.02.002.
Ferrer, G., & Whybark, D. C. (2000). From garbage to goods: Successful remanufacturing systems and skills. Business Horizons, 43, 55–64.
Fleischmann, M., Bloemhof-Ruwaard, J. M., Dekker, R., van der Laan, E., van Nunen, J. A. E. E., & Van Wassenhove, L. N. (1997). Quantitative models for reverse logistics: A review. European Journal of Operational Research, 103, 1–17.
Georgiadis, P., & Athanasiou, E. (2013). Flexible long-term capacity planning in closed-loop supply chains with remanufacturing. European Journal of Operational Research, 225, 44–58. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2012.09.021.
Gray, C., & Charter, M. (2007). Remanufacturing and product design. International Journal of Product Development, 6(3–4), 375–392.
Guide, V. D. R, Jr. (2000). Production planning and control for remanufacturing: Industry practice and research needs. Journal of Operations Management, 18, 467–483. doi:10.1016/S0272-6963(00)00034-6.
Gülsün, B., Bıyık, G., & Özgen, D. (2006). Reverse logistics: A survey. In 10th international research, expert conference TMT 2006. 11–15 September (pp. 569–572). Spain: Barcelona-Lloret de Mar.
Hollnagel, E., Woods, D. D., & Levesson, N. (Eds.). (2006). Resilience engineering: Concepts and precepts. Hampshire: Ashgate.
Hua, G., Cheng, T. C. E., & Wang, S. (2011). Managing carbon footprints in inventory management. International Journal of Production Economics, 132, 178–185. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2011.03.024.
Ijomah, J., & Udu, M. (1998). Effects of various pre-germination treatments on seeds of prosopis Africana (Guill and Perr) and Tamarindus indica (Linn) Global. Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences, 4, 369–374.
Ismail, N., Mandil, G., & Zwolinski, P. (2014). A remanufacturing process library for environmental impact simulations Jnl Remanufactur, 4, 1–14. doi:10.1186/2210-4690-4-2.
Jayaraman, V., Jr.,VDRG, & Srivastava, R. (1999). A closed-loop logistics model for remanufacturing. The Journal of the Operational Research Society, 50, 497–508. doi:10.2307/3009998.
Kenné, J.-P., Dejax, P., & Gharbi, A. (2012). Production planning of a hybrid manufacturing-remanufacturing system under uncertainty within a closed-loop supply chain. International Journal of Production Economics, 135, 81–93. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2010.10.026.
Kim, K., Song, I., Kim, J., & Jeong, B. (2006). Supply planning model for remanufacturing system in reverse logistics environment. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 51, 279–287. doi:10.1016/j.cie.2006.02.008.
Langevin, A., Mbaraga, P., & Campbell, J. F. (1996). Continuous approximation models in freight distribution: An overview. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 30, 163–188. doi:10.1016/0191-2615(95)00035-6.
Larsen, C., & Turkensteen, M. (2014). A vendor managed inventory model using continuous approximations for route length estimates and Markov chain modeling for cost estimates. International Journal of Production Economics, 157, 120–132. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2014.08.001.
Martí, J. M. C., Tancrez, J.-S., & Seifert, R. W. (2015). Carbon footprint and responsiveness trade-offs in supply chain network design. International Journal of Production Economics, 166, 129–142. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2015.04.016.
Miao, Z., Mao, H., Fu, K., & Wang, Y. (2016). Remanufacturing with trade-ins under carbon regulations. Computers and Operations Research. doi:10.1016/j.cor.2016.03.014.
Naber, S. K., de Ree, D. A., Spliet, R., & van den Heuvel, W. (2015). Allocating \(\text{CO}_{2}\) emission to customers on a distribution route. Omega, 54, 191–199. doi:10.1016/j.omega.2015.01.017
Pujari, N. A., Hale, T. S., & Huq, F. (2008). A continuous approximation procedure for determining inventory distribution schemas within supply chains. European Journal of Operational Research, 186, 405–422. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2007.01.030.
Savaskan, R. C., Bhattacharya, S., & Van Wassenhove, L. N. (2004). Closed-loop supply chain models with product remanufacturing. Management Science, 50, 239–252. doi:10.1287/mnsc.1030.0186.
Schulz, T., & Voigt, G. (2014). A flexibly structured lot sizing heuristic for a static remanufacturing system. Omega, 44, 21–31. doi:10.1016/j.omega.2013.09.003.
Simchi-Levi, D., Kaminsky, P., & Simchi-Levi, E. (2008). Designing and managing the supply chain: Concepts, strategies and case studies, 3rd ed, McGraw-Hill, (c2), pp. 27–48.
Sundarakani, B., de Souza, R., Goh, M., Wagner, S. M., & Manikandan, S. (2010). Modeling carbon footprints across the supply chain. International Journal of Production Economics, 128, 43–50. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2010.01.018.
Tsao, Y.-C. (2013). Distribution center network design under trade credits. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 222, 356–364. doi:10.1016/j.amc.2013.07.028.
Tsao, Y.-C., Mangotra, D., Lu, J.-C., & Dong, M. (2012). A continuous approximation approach for the integrated facility-inventory allocation problem. European Journal of Operational Research, 222, 216–228. doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2012.04.033.
Wang, J. W., Ip, W. H., & Zhang, W. J. (2010). An integrated road construction and resource planning approach to the evacuation of victims from single source to multiple destinations. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 11(2), 277–289. doi:10.1109/TITS.2010.2040276.
Xiong, Y., Li, G., Zhou, Y., Fernandes, K., Harrison, R., & Xiong, Z. (2014). Dynamic pricing models for used products in remanufacturing with lost-sales and uncertain quality. International Journal of Production Economics, 147, 678–688. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2013.04.025
Xiong, Y., Zhao, Q., & Zhou, Y. (2016). Manufacturer-remanufacturing vs supplier-remanufacturing in a closed-loop supply chain. International Journal of Production Economics, 176, 21–28. doi:10.1016/j.ijpe.2016.03.001.
Zhang, W. J., Li, Q., & Guo, L. S. (1999). Integrated design of mechanical structure and control algorithm for a programmable four-bar linkage. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 4(4), 354–362. doi:10.1109/3516.809514.
Zhang, W. J., & van Luttervelt, C. A. (2011). Toward a resilient manufacturing system. CIRP Annals, Manufacturing Technology, 60(1), 469–472. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2011.03.041.
Acknowledgements
This paper is supported in part by the Ministry of Science and Technology under Grant MOST 105-2221-E-011-099-MY3 and 104-2221-E-011-171-MY3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsao, YC., Linh, VT., Lu, JC. et al. A supply chain network with product remanufacturing and carbon emission considerations: a two-phase design. J Intell Manuf 29, 693–705 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-017-1296-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-017-1296-4