Abstract
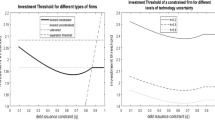
We study an optimal investment policy of a risky project when there exists the possibility that a firm may permanently exit the business under deeply deteriorated market conditions in the future. To capture the riskiness of the investment return rate, a Geometric Brownian motion is adopted to model the firm’s profit stream. Applying the real options framework, this paper aims at characterizing the firm’s optimal investment policy of the risky project under permanent exit option. It is shown that the investment threshold is no longer a monotonic function of the market uncertainty. Specifically, the investment threshold can decrease with market uncertainty for moderate uncertainty. And the investment threshold will eventually increase with market uncertainty if the uncertainty becomes sufficiently high. Extensive numerical experiments are conducted to check the robustness of the theoretic results. Some managerial implications are derived for investment decisions under the exit option.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adkins, R., & Paxson, D. (2016). The effects of an uncertain abandonment value on the investment decision. European Journal of Finance, 21(4), 1–24.
Alvarez, L. H. R. (2003). On the properties of r-excessive mapping for a class of diffusions. Annals of applied probability, 13, 1517–1533.
Alvarez, L. H. R., & Stenbacka, R. (2001). Adoption of uncertain multi-stage technology projects: A real options approach. Journal of Mathematical Economics, 35, 71–97.
Boomsma, T. K., Meade, N., & Fleten, S. E. (2012). Renewable energy investments under different support schemes: A real options approach. European Journal of Operational Research, 220, 225–237.
Christensen, C. M. (2000). The Innovator’s Dilemma. New York: HarperBusiness.
Chronopoulos, M., De Reyck, B., & Siddiqui, A. (2011). Optimal investment under operational flexibility, risk aversion, and uncertainty. European Journal of Operational Research, 213, 221–237.
Dixit, A. (1989). Entry and exit decisions under uncertainty. Journal of political Economy, 97, 620–638.
Dixit, A. (1992). Investment and hysteresis. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 6, 107–132.
Dixit, A. K., & Pindyck, R. S. (1994). Investment under Uncertainty. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Hagspiel, V., Huisman, K. J., Kort, P. M., & Nunes, C. (2016). How to escape a declining market: Capacity investment or Exit? European Journal of Operational Research, 254(1), 40–50.
Hagspiel, V., Huisman, K. J., & Nunes, C. (2015). Optimal technology adoption when the arrival rate of new technologies changes. European Journal of Operational Research, 243(3), 897–911.
Kwon, H. D. (2010). Invest or exit? Optimal decisions in the face of a declining profit stream. Operations Research, 58(3), 638–649.
Lavrutich, M. N. 2016. Capacity choice under uncertainty in a duopoly with endogenous exit. European Journal of Operational Research. Forthcoming
Leland, H. E. (1998). Agency costs, risk management, and capital structure. The Journal of Finance, 53(4), 1213–1243.
Leland, H. E., & Toft, K. B. (1996). Optimal capital structure, endogenous bankruptcy, and the term structure of credit spreads. The Journal of Finance, 51(3), 987–1019.
Li, G., & Rajagopalan, S. (2008). Process improvement, learning, and real options. Production and Operations Management, 17(1), 61–74.
Lin, T. T. (2009). The determinant of production entry and exit model on financing behavior. European Journal of Operational Research, 196, 258–265.
Mella-Barral, P., & Perraudin, W. (1997). Strategic debt service. Journal of Finance, 52(2), 531–556.
Øksendal, B. (2003). Stochastic Differential Equations: An Introduction with Applications. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
Pindyck, R. S. (1988). Irreversible investment, capacity choice, and the value of the firm. American Economic Review, 78(5), 969–985.
Trigeorgis, L. (1993). The nature of option interactions and the valuation of investments with multiple real options. Journal of financial and quantitative analysis, 28(1), 1–20.
Wang, H. (2005). A sequential entry problem with forced exits. Mathematics of Operations Research, 30, 501–520.
Wang, W., Ferguson, M. E., Hu, S., & Souza, G. C. (2013). Dynamic capacity investment with two competing technologies. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, 15(4), 616–629.
Zambujal-Oliveira, J., & Duque, J. (2011). Operational asset replacement strategy: A real options approach. European Journal of Operational Research, 210, 318–325.
Acknowledgements
This work of J. Ni was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 71601159), this work of J. W. Wang was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 71571156) and the open project funded by State Key Laboratory of Synthetical Automation for Process Industries (PAL-N201505), this work of L.K. Chu was supported by the University of Hong Kong Small Project Funding (201409176228), and this work of C. D. Li was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No. 71672074).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Wang, J., Ni, J. et al. The optimal time to make a risky investment under a permanent exit option. J Intell Manuf 30, 2669–2680 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-017-1299-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-017-1299-1