Abstract
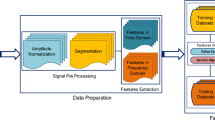
Fault diagnosis plays an essential role in rotating machinery manufacturing systems to reduce their maintenance costs. How to improve diagnosis accuracy remains an open issue. To this end, we develop a novel framework through combined use of multi-domain vibration feature extraction, feature selection and cost-sensitive learning method. First, we extract time-domain, frequency-domain, and time-frequency-domain features to make full use of vibration signals. Second, a feature selection technique is employed to obtain a feature subset with good generalization properties, by simultaneously measuring the relevance and redundancy of features. Third, a cost-sensitive learning method is designed for a classifier to effectively learn the discriminating boundaries, with an extremely imbalanced distribution of fault instances. For illustration, a real-world dataset of rotating machinery collected from an oil refinery in China is utilized. The extensive experiments have demonstrated that our multi-domain feature extraction and feature selection can significantly improve the diagnosis accuracy. Meanwhile, our cost-sensitive learning method consistently outperforms the traditional classifiers such as support vector machine (SVM), gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT), etc., and even better than the classification method calibrated by six popular imbalanced data resampling algorithms, such as the Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE) and the Adaptive Synthetic sampling method (ADASYN), in terms of decreasing missed alarms and reducing the average cost. Owing to its high evaluation scores and low average misclassification cost, cost-sensitive GBDT (CS-GBDT) is preferred for imbalanced fault diagnosis in practice.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrhein, W., Gruber, W., Bauer, W., & Reisinger, M. (2016). Magnetic levitation systems for cost-sensitive applications-some design aspects. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 52(5), 3739–3752.
Ben Ali, J., Saidi, L., Harrath, S., Bechhoefer, E., & Benbouzid, M. (2018). Online automatic diagnosis of wind turbine bearings progressive degradations under real experimental conditions based on unsupervised machine learning. Applied Acoustics, 132, 167–181.
Beygelzimer, A., Dani, V., Hayes, T., Langford, J., & Zadrozny, B. (2005). Error limiting reductions between classification tasks. In Proceedings of the 22nd international conference on machine learning (pp. 49–56).
Castro, C. L., & Braga, A. P. (2013). Novel cost-sensitive approach to improve the multilayer perceptron performance on imbalanced data. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 24(6), 888–899.
Chawla, N. V., Bowyer, K. W., Hall, L. O., & Kegelmeyer, W. P. (2002). SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 16, 321–357.
Ciabattoni, L., Ferracuti, F., Freddi, A., & Monteriú, A. (2018). Statistical spectral analysis for fault diagnosis of rotating machines. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 65(5), 4301–4310.
Correa Bahnsen, A., Aouada, D., & Ottersten, B. (2015). Example-dependent cost-sensitive decision trees. Expert Systems with Applications, 42(19), 6609–6619.
Diebold, F. X., & Mariano, R. S. (1995). Comparing predictive accuracy. Journal of Business and Economic Statistics, 13(3), 253–263.
Ding, C., & Peng, H. (2005). Minmum redundancy feature selection from microarray gene expression data. Journal of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, 3(2), 185–205.
Domingos, P. (1999). MetaCost: A general method for making classifiers cost-sensitive. In Proceedings of the fifth ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (pp. 155–164).
Dou, R., He, Z., & Hsu, C. (2018). Foreword: Smart manufacturing, innovative product and service design to empower industry 4.0. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 125, 514–516.
Gan, M., Wang, C., & Zhu, C. (2018). Fault feature enhancement for rotating machinery based on quality factor analysis and manifold learning. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 29(2), 463–480.
Gardner, J., & Xiong, L. (2009). An integrated framework for de-identifying unstructured medical data. Data & Knowledge Engineering, 68(12), 1441–1451.
Georgoulas, G., Loutas, T., Stylios, C. D., & Kostopoulos, V. (2013). Bearing fault detection based on hybrid ensemble detector and empirical mode decomposition. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 41(1–2), 510–525.
Haibo, H., Yang, B., Garcia, E. A., & Shutao, L. (2008). ADASYN: Adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning. In Proceedings of the fifth ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining (pp. 155–164).
Han, H., Wang, W., & Mao, B. (2005). Borderline-SMOTE: A new over-sampling method in imbalanced data sets learning. In Proceedings of advances in intelligent computing (pp. 878–887).
Han, S., Choi, H., Choi, S., & Oh, J. (2019a). Fault diagnosis of planetary gear carrier packs: A class imbalance and multiclass classification problem. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 20(2), 167–179.
Han, T., Liu, C., Yang, W., & Jiang, D. (2019b). Deep transfer network with joint distribution adaptation: A new intelligent fault diagnosis framework for industry application. ISA Transactions, In press.
Hwang, Y., Jen, K., & Shen, Y. (2009). Application of cepstrum and neural network to bearing fault detection. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 23(10), 2730–2737.
Jia, F., Lei, Y., Lu, N., & Xing, S. (2018). Deep normalized convolutional neural network for imbalanced fault classification of machinery and its understanding via visualization. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 110, 349–367.
Jiang, G., He, H., Yan, J., & Xie, P. (2019). Multiscale convolutional neural networks for fault diagnosis of wind turbine gearbox. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 66(4), 3196–3207.
Jiang, Q., Shen, Y., Li, H., & Xu, F. (2018). New fault recognition method for rotary machinery based on information entropy and a probabilistic neural network. Sensors, 18(2), 337–349.
Jiang, W., Spurgeon, S. K., Twiddle, J. A., Schlindwein, F. S., Feng, Y., & Thanagasundram, S. (2016). A wavelet cluster-based band-pass filtering and envelope demodulation approach with application to fault diagnosis in a dry vacuum pump. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 221(11), 1279–1286.
Kang, S. (2018). Joint modeling of classification and regression for improving faulty wafer detection in semiconductor manufacturing. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing,. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-018-1447-2.
Khan, S. H., Hayat, M., Bennamoun, M., Sohel, F. A., & Togneri, R. (2018). Cost-sensitive learning of deep feature representations from imbalanced data. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 29(8), 3573–3587.
Kuo, R. J., Su, P. Y., Zulvia, Ferani E., & Lin, C. C. (2018). Integrating cluster analysis with granular computing for imbalanced data classification problem—a case study on prostate cancer prognosis. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 125, 319–332.
Larsson, E. G., Stoica, P., & Jian, L. (2002). Amplitude spectrum estimation for two-dimensional gapped data. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 50(6), 1343–1354.
Lee, Y., Hu, P. J., Cheng, T., & Hsieh, Y. (2012). A cost-sensitive technique for positive-example learning supporting content-based product recommendations in B-to-C e-commerce. Decision Support Systems, 53(1), 245–256.
Li, P., Hu, W., Hu, R., & Chen, Z. (2020). Imbalance fault detection based on the integrated analysis strategy for variable-speed wind turbines. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems,116, In press.
Liu, J., An, Y., Dou, R., Ji, H., & Liu, Y. (2018a). Helical fault diagnosis model based on data-driven incremental mergence. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 125, 517–532.
Liu, R., Yang, B., Zio, E., & Chen, X. (2018b). Artificial intelligence for fault diagnosis of rotating machinery: A review. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 108, 33–47.
Mathew, J., Pang, C. K., Luo, M., & Leong, W. H. (2018). Classification of imbalanced data by oversampling in kernel space of support vector machines. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 29(9), 4065–4076.
Peng, H., Long, F., & Ding, C. (2005). Feature selection based on mutual information: Criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 27(8), 1226–1238.
Ragab, A., Yacout, S., Ouali, M., & Osman, H. (2019). Prognostics of multiple failure modes in rotating machinery using a pattern-based classifier and cumulative incidence functions. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 30(1), 255–274.
Ren, L., Sun, Y., Cui, J., & Zhang, L. (2018). Bearing remaining useful life prediction based on deep autoencoder and deep neural networks. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 48, 71–77.
Sánchez, R., Lucero, P., Vásquez, R. E., Cerrada, M., Macancela, J., & Cabrera, D. (2018). Feature ranking for multi-fault diagnosis of rotating machinery by using random forest and KNN. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 34(6), 3463–3473.
Santos, P., Maudes, J., & Bustillo, A. (2015). Identifying maximum imbalance in datasets for fault diagnosis of gearboxes. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 29(2), 333–351.
Seera, M., Lim, C. P., & Loo, C. K. (2014). Motor fault detection and diagnosis using a hybrid FMM-CART model with online learning. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 27(6), 1273–1285.
Song, L., Wang, H., & Chen, P. (2018). Vibration-based intelligent fault diagnosis for roller bearings in low-speed rotating machinery. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 67(8), 1887–1899.
Sun, Y., Kamel, M. S., Wong, A. K. C., & Wang, Y. (2007). Cost-sensitive boosting for classification of imbalanced data. Pattern Recognition, 40(12), 3358–3378.
Tao, F., Qi, Q., Liu, A., & Kusiak, A. (2018). Data-driven smart manufacturing. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 48, 157–169.
Tidriri, K., Chatti, N., Verron, S., & Tiplica, T. (2016). Bridging data-driven and model-based approaches for process fault diagnosis and health monitoring: A review of researches and future challenges. Annual Reviews in Control, 42, 63–81.
Wang, P., Ananya, Yan, R., & Gao, R. X. (2017). Virtualization and deep recognition for system fault classification. Journal of Manufacturing Systems,44, 310–316.
Wang, X., Zhang, X., Li, Z., & Wu, J. (2019). Ensemble extreme learning machines for compound-fault diagnosis of rotating machinery. Knowledge-Based Systems, In press.
Wu, C., Jiang, P., Ding, C., Feng, F., & Chen, T. (2019a). Intelligent fault diagnosis of rotating machinery based on one-dimensional convolutional neural network. Computers in Industry, 108, 53–61.
Wu, J., Wu, C., Cao, S., Or, S. W., Deng, C., & Shao, X. (2019b). Degradation data-driven time-to-failure prognostics approach for rolling element bearings in electrical machines. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 66(1), 529–539.
Xie, Y., Peng, L., Chen, Z., Yang, B., Zhang, H., & Zhang, H. (2019). Generative learning for imbalanced data using the gaussian mixed model. Applied Soft Computing, 79, 439–451.
Zadrozny, B. Langford, J., & Abe, N. (2003). Cost-sensitive learning by cost-proportionate example weighting. In Proceedings—IEEE international conference on data mining (pp. 435–442).
Zan, T., Liu, Z., Wang, H., Wang, M., & Gao, X. (2019). Control chart pattern recognition using the convolutional neural network. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, In press.
Zhang, X., & Hu, B. (2014). A new strategy of cost-free learning in the class imbalance problem. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 26(12), 2872–2885.
Zhang, Y., Li, X., Gao, L., Wang, L., & Wen, L. (2018). Imbalanced data fault diagnosis of rotating machinery using synthetic oversampling and feature learning. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 48, 34–50.
Zhang, C., Tan, K. C., Li, H., & Hong, G. S. (2019). A cost-sensitive deep belief network for imbalanced classification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 30(1), 109–122.
Zhang, Z., Verma, A., & Kusiak, A. (2012). Fault analysis and condition monitoring of the wind turbine gearbox. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 27(2), 526–535.
Zhao, M., Jiao, J., & Lin, J. (2019). A data-driven monitoring scheme for rotating machinery via self-comparison approach. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 15(4), 2435–2445.
Zhao, M., & Lin, J. (2018). Health assessment of rotating machinery using a rotary encoder. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 65(3), 2548–2556.
Zhou, Z., & Liu, X. (2006). Training cost-sensitive neural networks with methods addressing the class imbalance problem. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 18(1), 63–77.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Editor-in-Chief, the Associate Editor, and two anonymous referees for their helpful comments and constructive guidance. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71671056), the Humanity and Social Science Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (19YJA790035), and the National Statistical Science Research Projects of China (2019LD05). Special thanks to data support from the industrial partner RONDS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Q., Lu, S., Jia, W. et al. Imbalanced fault diagnosis of rotating machinery via multi-domain feature extraction and cost-sensitive learning. J Intell Manuf 31, 1467–1481 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-019-01522-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-019-01522-8