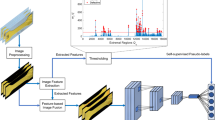
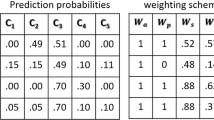
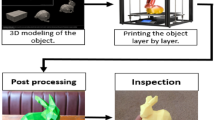
Abstract
As a promising modern technology, additive manufacturing (AM) has been receiving increasing research and industrial attention in the recent years. With its rapid development, the importance of quality monitoring in AM process has been recognized, which significantly affects the property of the manufactured parts. Since the conventional hand-crafted features for quality identification are generally costly, time-consuming and sensitive to noises, the intelligent data-driven automatic process monitoring methods are becoming more and more popular at present. This paper proposes a deep learning-based quality identification method for metal AM process. To alleviate the requirement for large amounts of high-quality labeled training data by most existing data-driven methods, an identification consistency-based approach is proposed to better explore the semi-supervised training data. The proposed method is able to achieve promising performance using limited supervised samples with low quality, such as noisy and blurred images. Experiments on a real-world metal AM dataset are implemented to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, which offers a promising tool for real industrial applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chemali, E., Kollmeyer, P. J., Preindl, M., Ahmed, R., & Emadi, A. (2018). Long short-term memory networks for accurate state-of-charge estimation of li-ion batteries. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 65(8), 6730–6739.
Chua, Z. Y., Ahn, I. H., & Moon, S. K. (2017). Process monitoring and inspection systems in metal additive manufacturing: Status and applications. International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology, 4(2), 235–245.
Everton, S. K., Hirsch, M., Stravroulakis, P., Leach, R. K., & Clare, A. T. (2016). Review of in-situ process monitoring and in-situ metrology for metal additive manufacturing. Materials & Design, 95, 431–445.
Gonzalez-Val, C., Pallas, A., Panadeiro, V., & Rodriguez, A. (2019). A convolutional approach to quality monitoring for laser manufacturing. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing,. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-019-01495-8.
Grasso, M., Laguzza, V., Semeraro, Q., & Colosimo, B. M. (2017). In-process monitoring of selective laser melting: Spatial detection of defects via image data analysis. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 139(5), 051001-051001-16.
Han, T., Liu, C., Yang, W., & Jiang, D. (2019). Learning transferable features in deep convolutional neural networks for diagnosing unseen machine conditions. ISA Transactions, 93, 341–353.
He, M., & He, D. (2017). Deep learning based approach for bearing fault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 53(3), 3057–3065.
Hu, Y., Baraldi, P., Maio, F. D., & Zio, E. (2017). A systematic semi-supervised self-adaptable fault diagnostics approach in an evolving environment. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 88, 413–427.
Hu, Z., Qin, X., Li, Y., Yuan, J., & Wu, Q. (2019). Multi-bead overlapping model with varying cross-section profile for robotic GMAW-based additive manufacturing. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing,. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-019-01501-z.
Khanzadeh, M., Chowdhury, S., Marufuzzaman, M., Tschopp, M. A., & Bian, L. (2018). Porosity prediction: Supervised-learning of thermal history for direct laser deposition. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 47, 69–82.
Kingma, D., Adam, J. B. (2015). A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980
Kwon, O., Kim, H. G., Ham, M. J., Kim, W., Kim, G.-H., Cho, J.-H., et al. (2018). A Deep neural network for classification of melt-pool images in metal additive manufacturing. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing,. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-018-1451-6.
Li, W., Zhang, S., & He, G. (2013). Semisupervised distance-preserving self-organizing map for machine-defect detection and classification. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 62(5), 869–879.
Li, X., Zhang, W., Xu, N., & Ding, Q. (2019). Deep learning-based machinery fault diagnostics with domain adaptation across sensors at different places. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2019.2935987.
Li, X., Zhang, W., & Ding, Q. (2018). A robust intelligent fault diagnosis method for rolling element bearings based on deep distance metric learning. Neurocomputing, 310, 77–95.
Li, X., Zhang, W., & Ding, Q. (2019). Deep learning-based remaining useful life estimation of bearings using multi-scale feature extraction. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 182, 208–218.
Li, X., Zhang, W., & Ding, Q. (2019). Cross-domain fault diagnosis of rolling element bearings using deep generative neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 66(7), 5525–5534.
Li, X., Zhang, W., Ding, Q., & Li, X. (2019). Diagnosing rotating machines with weakly supervised data using deep transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 16(3), 1688–1697.
Li, X., Zhang, W., Ding, Q., & Sun, J.-Q. (2018). Intelligent rotating machinery fault diagnosis based on deep learning using data augmentation. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 31, 433–452.
Li, X., Zhang, W., Ding, Q., & Sun, J.-Q. (2019). Multi-layer domain adaptation method for rolling bearing fault diagnosis. Signal Processing, 157, 180–197.
Rasmus, A., Valpola, H., Honkala, M., Berglund, M., Raiko, T. (2015). Semi-supervised learning with ladder networks. In 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 3546–3554.
Razavi-Far, R., Hallaji, E., Farajzadeh-Zanjani, M., & Saif, M. (2019). A semi-supervised diagnostic framework based on the surface estimation of faulty distributions. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 15(3), 1277–1286.
Ren, W., Pan, J., Zhang, H., Cao, X., & Yang, M.-H. (2019). Single image dehazing via multi-scale convolutional neural networks with holistic edges. International Journal of Computer Vision, 128, 240–259.
Scime, L., & Beuth, J. (2019). Using machine learning to identify in-situ melt pool signatures indicative of flaw formation in a laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing process. Additive Manufacturing, 25, 151–165.
Shevchik, S. A., Kenel, C., Leinenbach, C., & Wasmer, K. (2018). Acoustic emission for in situ quality monitoring in additive manufacturing using spectral convolutional neural networks. Additive Manufacturing, 21, 598–604.
Shevchik, S. A., Masinelli, G. G., Kenel, C., Leinenbach, C., & Wasmer, K. (2019). Deep learning for in situ and real-time quality monitoring in additive manufacturing using acoustic emission. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 15, 5194–5203.
Tapia, G., & Elwany, A. A. (2014). Review on process monitoring and control in metal-based additive manufacturing. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 136(6), 060801-060801-10.
Weston, J., Ratle, F., Mobahi, H., & Collobert, R. (2012). Deep learning via semi-supervised embedding. In G. Montavon, G. B. Orr, & K.-R. Müller (Eds.), Neural networks: Tricks of the trade (2nd ed., pp. 639–655). Berlin: Springer.
Xu, Y., Bao, Y., Chen, J., Zuo, W., & Li, H. (2018). Surface fatigue crack identification in steel box girder of bridges by a deep fusion convolutional neural network based on consumer-grade camera images. Structural Health Monitoring, 18(3), 653–674.
Ye, D., Fuh, J. Y. H., Zhang, Y., Hong, G. S., & Zhu, K. (2018). In situ monitoring of selective laser melting using plume and spatter signatures by deep belief networks. ISA Transactions, 81, 96–104.
Ye, D., Hong, G. S., Zhang, Y., Zhu, K., & Fuh, J. Y. H. (2018). Defect detection in selective laser melting technology by acoustic signals with deep belief networks. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 96(5), 2791–2801.
You, D., Gao, X., & Katayama, S. (2015). WPD-PCA-Based laser welding process monitoring and defects diagnosis by using FNN and SVM. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 62(1), 628–636.
Zhang, Y., Hong, G. S., Ye, D., Zhu, K., & Fuh, J. Y. H. (2018). Extraction and evaluation of melt pool, plume and spatter information for powder-bed fusion am process monitoring. Materials & Design, 156, 458–469.
Zhang, B., Jaiswal, P., Rai, R., Guerrier, P., & Baggs, G. (2019). Convolutional neural network-based inspection of metal additive manufacturing parts. Rapid Prototyping Journal, 25(3), 530–540.
Zhang, W., Li, X., & Ding, Q. (2019). Deep residual learning-based fault diagnosis method for rotating machinery. ISA Transactions, 95, 295–305.
Zhang, W., Li, X., Jia, X.-D., Ma, H., Luo, Z., & Li, X. (2020). Machinery fault diagnosis with imbalanced data using deep generative adversarial networks. Measurement, 152, 107377.
Zhao, D., & Guo, W. (2019). Mixed-layer adaptive slicing for robotic additive manufacturing (AM) based on decomposing and regrouping. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing,. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-019-01490-z.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Jia, X., Yang, Q. et al. Quality analysis in metal additive manufacturing with deep learning. J Intell Manuf 31, 2003–2017 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01549-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-020-01549-2