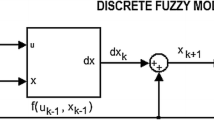
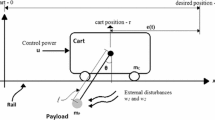
Abstract
In this paper we present a comparison of two fuzzy-control approaches that were developed for use on a non-linear single-input single-output (SISO) system. The first method is Fuzzy Model Reference Learning Control (FMRLC) with a modified adaptation mechanism that tunes the fuzzy inverse model. The basic idea of this method is based on shifting the output membership functions in the fuzzy controller and in the fuzzy inverse model. The second approach is a 2 degrees-of-freedom (2 DOF) control that is based on the Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy model. The T-S fuzzy model is obtained by identification of evolving fuzzy model and then used in the feed-forward and feedback parts of the controller. An error-model predictive-control approach is used for the design of the feedback loop. The controllers were compared on a non-linear second-order SISO system named the helio-crane. We compared the performance of the reference tracking in a simulation environment and on a real system. Both methods provided acceptable tracking performance during the simulation, but on the real system the 2 DOF FMPC gave better results than the FMRLC.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zadeh, L.: Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8(3), 338–353 (1965)
Procyk, T., Mamdani, E.: A linguistic self-organizing process controller. Automatica 15(1), 15–30 (1979)
Shao, S.: Fuzzy self-organizing controller and its application for dynamic processes. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 26(2), 151–164 (1988)
Layne, J., Passino, K.: Fuzzy model reference learning control. In: First IEEE Conference on Control Applications, pp. 686–691. IEEE (1992)
Åström, K.J., Wittenmark, B.: Adaptive Control, 2nd edn. Dover Publications (2008)
Yuan, Y., Feng, Y., Gu, W.: Fuzzy model reference learning control for aircraft pitch autopilot design. In: 8th Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision Conference, ICARCV 2004, vol. 3, pp. 1923–1927. IEEE (2004)
Layne, J., Passino, K.: Fuzzy model reference learning control. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 4(1), 33–47 (1996)
Ling, D.: Fuzzy model reference learning control for a nonlinear model of hydrogenerator unit. In: International Workshop on Intelligent Systems and Applications, pp. 1–4. IEEE (2009)
Zhong, L.: Application of fuzzy model reference learning control in hydraulic power sets. J. Power Eng. 5, 680–683 (2006)
Sheppard, M., Tarbouchi, M.: Design and implementation of a stable fuzzy model reference learning controller applied to a rigid-link manipulator. In: IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology, vol. 3, pp. 1186–1191. IEEE (2004)
Moudgal, V., Kwong, W., Passino, K., Yurkovich, S.: Fuzzy learning control for a flexible-link robot. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 3(2), 199–210 (1995)
Zhen, L., Xu, L.: Fuzzy learning enhanced speed control of an indirect field-oriented induction machine drive. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 8(2), 270–278 (2000)
Rehman, H.u., Dhaouadi, R.: A fuzzy learning–sliding mode controller for direct field-oriented induction machines. Neurocomputing 71(13–15), 2693 (2008)
Ismail, A.: Fuzzy model reference learning control of multi-stage flash desalination plants. Desalination 116(2–3), 157–164 (1998)
Oltean, S.E., Grif, H., Duka, A.V.: Electron beam focusing and deflection control systems. In: Interdisciplinarity in Engineering—Scientific International Conference, pp. 1–6 (2007)
Zhang, J.l., Ning, N., Zheng, M.y.: Application of fuzzy model reference learning control in dynamic hot-box device. J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 4(2), 36–47 (2006)
Xu, S., Pan, H.: Coke oven temperature control based on fuzzy model reference learning control. Control and Instruments in Chemical Industry 3(2), 10–16 (2008)
Su, Y., Zheng, C., Duan, B.: Fuzzy learning tracking of a parallel cable manipulator for the square kilometre array. Mechatronics 15(6), 731–746 (2005)
Naceri, A., Ramdani, Y., Bounouna, H.: A fuzzy model reference learning controller of ASMES to improve transient power system stability. Mediterranean J. Measure. Control 3(3), 126–133 (2007)
Kwong, W., Passino, K.: Dynamically focused fuzzy learning control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 26(1), 53–74 (1996)
Dessouky, A., Tarbouchi, M.: Model reference adaptive fuzzy controller for induction motor using auto-attentive approach. In: Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, vol. 2, pp. 719–723. IEEE (2000)
Oltean, S., Abrudean, M., Gligor, A.: MRAC and FMRLC for a plant with time varying parameters. In: IEEE International Conference on Automation, Quality and Testing, Robotics, vol. 1, pp. 62–67. IEEE (2006)
Kopasakis, G.: Adaptive performance seeking control using fuzzy model reference learning control and positive gradient control. In: 33rd Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, pp. 1–9 (1997)
Passino, K.M., Yurkovich, S.: Fuzzy Control. Addison-Wesley (1998)
Takagi, T., Sugeno, M.: Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 15(1), 116–132 (1985)
Chiu, S.L.: Fuzzy model identification based on cluster estimation. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2, 267–278 (1994)
Angelov, P.P., Filev, D.P.: An approach to online identification of Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy models. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., Part B 34(1), 484–498 (2004)
Memon, M.A., Angelov, P., Ahmed, H.: An approach to real-time color-based object tracking. In: International Symposium on Evolving Fuzzy Systems, pp. 86–91. IEEE (2006)
Angelov, P., Zhou, X.: Evolving fuzzy systems from data streams in real-time. In: International Symposium on Evolving Fuzzy Systems, pp. 29–35. IEEE (2006)
Angelov, P., Filev, D.: Simpl_eTS: a simplified method for learning evolving Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy models. In: 14th IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, pp. 1068–1073. Reno, Nevada, USA (2005)
Angelov, P.: Evolving Intelligent Systems: Methodology and Applications, chap. Evolving Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy Systems From Streaming Data (eTS+), pp. 21–50. Wiley, New Jersey (2010)
Lughofer, E., Klement, E.P.: FLEXFIS: a variant for incremental learning of Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy systems. In: 14th IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, pp. 915–920. IEEE, Reno, Nevada, USA (2005)
Lughofer, E., Bouchot, J.L., Shaker, A.: On-line elimination of local redundancies in evolving fuzzy systems. Evolving Syst. 2(3), 165–187 (2011)
Kasabov, N.K.: Evolving fuzzy neural networks for supervised/unsupervised online knowledge-based learning. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber. Part B 31(6), 902–918 (2001)
Kasabov, N.: Evolving fuzzy neural networks — algorithms, applications and biological motivation. In: Methodologies for the Conceptation, Design and Application of Soft Computing, pp. 271–274. Japan (1998)
Kasabov, N.K., Song, Q.: DENFIS: dynamic evolving neural-fuzzy inference system and its application for time-series prediction. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 10(2), 144 (2002)
Jang, J.S.R.: ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber. 23(3), 665–685 (1993)
Azeem, M.F., Hanmandlu, H., Ahmad, N.: Structure identification of generalized adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 11(5), 666–681 (2003)
Leng, G., Prasad, G., McGinnity, T.M.: An on-line algorithm for creating self-organizing fuzzy neural networks. Neural Netw. 17(10), 1477–1493 (2004)
Rong, H.J., Sundararajan, N., Huang, G.B., Saratchandran, P.: Sequential adaptive fuzzy inference system (SAFIS) for nonlinear system identification and prediction. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 157(9), 1260–1275 (2006)
Lin, F.J., Lin, C.H., Shen, P.H.: Self-constructing fuzzy neural network speed controller for permanent-magnet synchronous motor drive. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 9(5), 751–759 (2001)
Lin, C.T.: A neural fuzzy control system with structure and parameter learning. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 70(2–3), 183–212 (1995)
Wu, S., Er, M.J.: Dynamic fuzzy neural networks — a novel approach to function approximation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber. Part B 30(2), 358–364 (2000)
Wu, S., Er, M.J., Gao, Y.: A fast approach for automatic generation of fuzzy rules by generalized dynamic fuzzy neural networks. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 9(4), 578–594 (2001)
Juang, C.F., Lin, C.T.: An online self-constructing neural fuzzy inference network and its applications. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 6(1), 12–32 (1998)
Tzafestas, S.G., Zikidis, K.C.: NeuroFAST: on-line neuro-fuzzy art-based structure and parameter learning TSK model. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cyber. Part B 31(5), 797–802 (2001)
Platt, J.: A resource-allocating network for function interpolation. Neural Comput. 3(2), 213–225 (1991)
Deng, D., Kasabov, N.: Evolving self-organizing maps for on-line learning, data analysis and modeling. In: Proc. IJCNN 2000 Neural Networks Neural Computing: New Challenges Perspectives New Millenium, vol. 6, pp. 3–8. IEEE, New York (2000)
Fritzke, B.: A growing neural gas network learns topologies. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 7, 845–865 (1995)
Soleimani-B, H., Lucas, C., Araabi, B.N.: Recursive Gath–Geva clustering as a basis for evolving neuro-fuzzy modeling. Evolving Syst. 1(1), 59–71 (2010)
Dovžan, D., Škrjanc, I.: Recursive fuzzy c-means clustering for recursive fuzzy identification of time-varying processes. ISA Trans. 50(2), 159–169 (2011)
Dovžan, D., Škrjanc, I.: Recursive clustering based on a Gustafson–Kessel algorithm. Evolving Syst. 2(1), 15–24 (2011)
Dovžan, D., Škrjanc, I.: Predictive functional control based on an adaptive fuzzy model of a hybrid semi-batch reactor. Control Eng. Pract. 18(8), 979–989 (2010)
Normey-Rico, J.E., Gòmez-Ortega, J., Camacho, E.F.: A Smith-predictor-based generalised predictive controller for mobile robot path-tracking. Control Eng. Pract. 7(6), 729–740 (1999)
Rouhani, R., Mehra, R.K.: Model algorithmic control (MAC); basic theoretical properties. Automatica 18(4), 401–414 (1982)
Richalet, J., O’Donovan, D.: Predictive functional control: principles and industrial applications. Advances in Industrial Control. Springer (2009)
Richalet, J.: Industrial applications of model based predictive control. Automatica 29(5), 1251–1274 (1993)
Škrjanc, I., Matko, D.: Predictive functional control based on fuzzy model for heat-exchanger pilot plant. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 8(6), 705–712 (2000)
Lepetič, M., Škrjanc, I., Chiacchiarini, H.G., Matko, D.: Predictive functional control based on fuzzy model: comparison with linear predictive functional control and PID control. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 36(4), 467–480 (2003)
Blažič, S., Škrjanc, I.: Design and stability analysis of fuzzy model-based predictive control — a case study. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 49(3), 279–292 (2007)
Karer, G., Mušič, G., Škrjanc, I., Zupančič, B.: Feedforward control of a class of hybrid systems using an inverse model. Math. Comput. Simul. 82(3), 414–427 (2011)
Malchow, F., Sawodny, O.: Model based feedforward control of an industrial glass feeder. Control Eng. Pract. 20(1), 62–68 (2012)
Oriolo, G., De Luca, A., Vendittelli, M.: WMR control via dynamic feedback linearization: design, implementation, and experimental validation. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 10(6), 835–852 (2002)
Klančar, G., Škrjanc, I.: Tracking-error model-based predictive control for mobile robots in real time. Robot. Auton. Syst. 55(6), 460–469 (2007)
Škrjanc, I., Klančar, G.: Optimal cooperative collision avoidance between multiple robots based on Bernstein-Beézier curves. Robot. Auton. Syst. 58(1), 1–9 (2010)
Pao, L.Y., Butterworth, J.A., Abramovitch, D.Y.: Combined feedforward/feedback control of atomic force microscopes. In: American Control Conference, pp. 3509–3515. IEEE (2007)
Chiu, C.S.: Mixed feedforward/feedback based adaptive fuzzy control for a class of MIMO nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 14(6), 716–727 (2006)
Wu, Y., Zou, Q.: Robust inversion-based 2-DOF control design for output tracking: piezoelectric-actuator example. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 17(5), 1069–1082 (2009)
Passino, K.: Biomimicry for Optimization, Control, and Automation. Springer (2004)
Cerman, O., Hušek, P.: Fuzzy model reference learning control with modified adaptation mechanism. In: Seventh International Conference on Natural Computation (ICNC), vol. 1, pp. 123–128. IEEE (2011)
de Jesús Rubio, J.: Evolving Intelligent Systems: Methodology and Applications, chap. Stability analysis for an online evolving neuro-fuzzy recurrent network, pp. 173–199. Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey (2010)
Blažič, S., Škrjanc, I., Gerkšič, S., Dolanc, G., Strmčnik, S., Hadjiski, M.B., Stathaki, A.: Online fuzzy identification for an intelligent controller based on a simple platform. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 22(4–5), 628–638 (2009)
Blazinšek, M., Arh, M., Škrjanc, I.: Comparison between the auto-tuning of PID, PFC and modified-PFC controllers. In: 7th Vienna Conference on Mathematical Modelling, MATHMOD 2012, pp. 1–6 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zdešar, A., Cerman, O., Dovžan, D. et al. Fuzzy Control of a Helio-Crane. J Intell Robot Syst 72, 497–515 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-012-9796-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-012-9796-0
Keywords
- Fuzzy Model Reference Learning Control
- Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy model
- Evolving fuzzy model
- 2 DOF control
- Model predictive control