Abstract
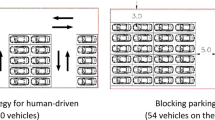
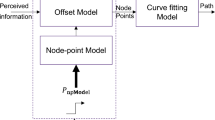
The planning of semi-autonomous vehicles in traffic scenarios is a relatively new problem that contributes towards the goal of making road travel by vehicles free of human drivers. An algorithm needs to ensure optimal real time planning of multiple vehicles (moving in either direction along a road), in the presence of a complex obstacle network. Unlike other approaches, here we assume that speed lanes are not present and that different lanes do not need to be maintained for inbound and outbound traffic. Our basic hypothesis is to carry forward the planning task to ensure that a sufficient distance is maintained by each vehicle from all other vehicles, obstacles and road boundaries. We present here a 4-layer planning algorithm that consists of road selection (for selecting the individual roads of traversal to reach the goal), pathway selection (a strategy to avoid and/or overtake obstacles, road diversions and other blockages), pathway distribution (to select the position of a vehicle at every instance of time in a pathway), and trajectory generation (for generating a curve, smooth enough, to allow for the maximum possible speed). Cooperation between vehicles is handled separately at the different levels, the aim being to maximize the separation between vehicles. Simulated results exhibit behaviours of smooth, efficient and safe driving of vehicles in multiple scenarios; along with typical vehicle behaviours including following and overtaking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai, T., Pagello, E., Parker, L.E.: Editorial: advances in multi-robot systems. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 18(5), 655–661 (2002)
Svestka, P., Overmars, M.H.: Coordinated motion planning for multiple car-like robots using probabilistic roadmaps. In: Proceedings of the 1995 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, vol. 2, pp. 1631–1636. Nagoya, Japan (1995)
Sánchez-Ante, G., Latombe, J.C.: Using a PRM planner to compare centralized and decoupled planning for multi-robot systems. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 2112–211. Washington, DC (2002)
Clark, C.M., Rock, S.M., Latombe, J.C.: Dynamic networks for motion planning in multi-robot space systems. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Artificial Intelligence, Robotics and Automation in Space i-SAIRA. Nara, Japan (2003)
Kala, R., Shukla, A., Tiwari, R.: Robotic path planning using multi neuron heuristic search. In: Proceedings of the ACM 2nd International Conference on Interaction Sciences: Information Technology, Culture and Human, ICIS 2009, pp. 1318–1323. Seoul, Korea (2009)
Xiao, J., Michalewicz, Z., Zhang, L., Trojanowski, K.: Adaptive evolutionary planner/navigator for mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 1(1), 18–28 (1997)
Kala, R., Shukla, A., Tiwari, R.: Robotic path planning using evolutionary momentum based exploration. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell. 23(4), 469–495 (2011)
Khatib, O.: Real-time obstacle avoidance for manipulators and mobile robots. In: Proceedings of the 1985 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 500–505. St. Louis, Missouri (1985)
Kala, R., Shukla, A., Tiwari, R.: Fusion of probabilistic A* algorithm and fuzzy inference system for robotic path planning. Artif. Intell. Rev. 33(4), 275–306 (2010)
Kala, R., Shukla, A., Tiwari, R., Roongta, S., Janghel, R.R.: Mobile robot navigation control in moving obstacle environment using genetic algorithm, artificial neural networks and A* algorithm. In: Proceedings of the IEEE World Congress on Computer Science and Information Engineering, CSIE 2009, pp. 705–713. Los Angeles/Anaheim (2009)
Tu, K.Y., Baltes, J.: Fuzzy potential energy for a map approach to robot navigation. Robot. Auton. Syst. 54(7), 574–589 (2006)
Baxter, J.L., Burke, E.K., Garibald, J.M., Normanb, M.: Shared potential fields and their place in a multi-robot co-ordination taxonomy. Robot. Auton. Syst. 57(10), 1048–1055 (2009)
Lian, F.L., Murray, R.: Cooperative task planning of multi-robot systems with temporal constraints. In: Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, ICRA ’03, vol. 2, pp. 2504–2509. Taipei, Taiwan (2003)
Marchese, F.M.: Multiple mobile robots path-planning with MCA. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Autonomic and Autonomous Systems, ICAS’06, pp. 56–56. Silicon Valley, California (2006)
Klancar, G., Skrjanc, I.: A case study of the collision-avoidance problem based on Bernstein–Bézier path tracking for multiple robots with known constraints. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 60(2), 317–337 (2010)
Asama, H., Matsumoto, A., Ishida, Y.: Design of an autonomous and distributed robot system: ACTRESS. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Workshop on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 283–290. Tsukuba, Japan (1989)
Asama, H., Ozaki, K., Itakura, H., Matsumoto, A., Ishida, Y., Endo, I.: Collision avoidance among multiple mobile robots based on rules and communication. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Workshop on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1215–1220. Osaka, Japan (1991)
Montemerlo, M., Becker, J., Bhat, S., Dahlkamp, H., Dolgov, D., Ettinger, S., Haehnel, D., Hilden, T., Hoffmann, G., Huhnke, B., Johnston, D., Klumpp, S., Langer, D., Levandowski, A., Levinson, J., Marcil, J., Orenstein, D., Paefgen, J., Penny, I., Petrovskaya, A., Pflueger, M., Stanek, G., Stavens, D., Vogt, A., Thrun, S.: Junior: the Stanford entry in the urban challenge. J. Field Rob. 25(9), 569–597 (2008)
Crane, C., Armstrong, D., Arroyo, A., Baker, A., Dankel, D., Garcia, G., Johnson, N., Lee, J., Ridgeway, S., Schwartz, E., Thorn, E., Velat, S., Yoon, J., Washburn, J.: Team gator nation’s autonomous vehicle development for the 2007 DARPA urban challenge. J. Aerosp. Comput. Inform. Commun. 4(12), 1059–1085 (2007)
Vendrell, E., Mellado, M., Crespo, A.: Robot planning and re-planning using decomposition, abstraction, deduction, and prediction. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 14(4), 505–518 (2001)
Latombe, J.C.: Robot Motion Planning. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Norwell (1991)
Snape, J., van den Berg, J., Guy, S.J., Manocha, D.: Independent navigation of multiple mobile robots with hybrid reciprocal velocity obstacles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robotic Systems, pp. 5917–5922. St. Louis, MO (2009)
Ortigosa, N., Morillas, S., Peris-Fajarnes, G.: Obstacle-free pathway detection by means of depth maps. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 63(1), 115–129 (2011)
Shinzato, P.Y., Wolf, D.F.: A road following approach using artificial neural networks combinations. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 62(3–4), 527–546 (2011)
Reif, J.H., Wang, H.: Social potential fields: a distributed behavioral control for autonomous robots. Robot. Auton. Syst. 27(3), 171–194 (1999)
Gayle, R., Moss, W., Lin, M.C., Manocha, D.: Multi-robot coordination using generalized social potential fields. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 106–113. Kobe, Japan (2009)
Bennewitz, M., Burgard, W., Thrun, S.: Finding and optimizing solvable priority schemes for decoupled path planning techniques for teams of mobile robots. Robot. Auton. Syst. 41(2–3), 89–99 (2002)
Todt, E., Raush, G., Sukez, R.: Analysis and classification of multiple robot coordination methods. In: Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation, pp. 3158–3163. San Francisco, CA (2000)
Kant, K., Zucker, S.W.: Toward efficient trajectory planning: the path-velocity decomposition. Int. J. Rob. Res. 5(3), 72–89 (1986)
Wilkie, D., van den Berg, J., Manocha, D.: Generalized velocity obstacles. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 5573–5578. St. Louis, USA (2009)
Cormen, T.H., Leiserson, C.E., Rivest, R.L., Stein, C.: Section 33.3: Finding the Convex Hull, Introduction to Algorithms, 2nd edn, pp. 947–957. MIT Press, MA (2001)
Leroy, S., Laumond, J.P., Simeon, T.: Multiple path coordination for mobile robots: a geometric algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI’99, vol. 2, pp. 1118–1123. San Francisco, CA (1999)
Yahja, A., Stentz, A., Singh, S., Brumitt, B.L.: Framed-quadtree path planning for mobile robots operating in sparse environments. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 650–655. Leuven, Belgium (1998)
Kambhampati, S., Davis, L.S.: Multiresolution path planning for mobile robots. IEEE J. Robot. Auton. 2(3), 135–145 (1986)
Cormen, T.H., Leiserson, C.E., Rivest, R.L., Stein, C.: Section 24.3: Dijkstra’s Algorithm, Introduction to Algorithms, 2nd edn, pp. 595–601. MIT Press, MA (2001)
Urmson, C., Baker, C., Dolan, J.M., Rybski, P., Salesky, B., Whittaker, W.L., Ferguson, D., Darms, M.: Autonomous driving in traffic: boss and the urban challenge. AI Mag. 30(2), 17–29 (2009)
Sewall, J., van den Berg, J., Lin, M.C., Manocha, D.: virtualized traffic: reconstructing traffic flows from discrete spatiotemporal data. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 17(1), 26–37 (2011)
Bartels, R.H., Beatty, J.C., Barsky, B.A.: An Introduction to Splines for Use in Computer Graphics and Geometric Modelling. Morgan Kaufmann, San Francisco, CA (1987)
de Boor, C.: A Practical Guide to Splines. Springer Verlag, Heidelberg (1978)
Xidias, E.K., Azariadis, P.N.: Mission design for a group of autonomous guided vehicles. Robot. Auton. Syst. 59(1) 34–43 (2011)
Peng, J., Akella, S.: Coordinating multiple robots with Kinodynamic constraints along specified paths. Int. J. Robot. Res. 24(4), 295–310 (2005)
Schubert, R., Schulze, K., Wanielik, G.: Situation assessment for automatic lane-change maneuvers. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 11(3), 607–616 (2010)
Furda, A., Vlacic, L.: Enabling safe autonomous driving in real-world city traffic using multiple criteria decision making. IEEE Intel. Trasport. Syst. Magz. 3(1), 4–17 (2011)
Hegeman, G., Tapani, A., Hoogendoorn, S.: Overtaking assistant assessment using traffic simulation. Transp. Res. Part C 17(6), 617–630 (2009)
Wang, F., Yang, M., Yang, R.: Conflict-probability-estimation-based overtaking for intelligent vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 10(2), 366–370 (2009)
Lee, J.W., Choy, Y.I., Sugisakaz, M., Lee, J.J.: Study of novel heterogeneous ant colony optimization algorithm for global path planning. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, pp. 1961–1966 (2010)
Lee, J.W., Choi, B.S., Park, K.T., Lee, J.J.: Comparison between heterogeneous ant colony optimization algorithm and genetic algorithm for global path planning of mobile robot. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, pp. 881–886 (2011)
Alvarez-Sanchez, J.R., de la Paz Lopez, F., Troncoso, J.M.C., de Santos Sierra, D.: Reactive navigation in real environments using partial center of area method. Robot. Auton. Syst. 58(12), 1231–1237 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kala, R., Warwick, K. Multi-Level Planning for Semi-autonomous Vehicles in Traffic Scenarios Based on Separation Maximization. J Intell Robot Syst 72, 559–590 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-013-9817-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-013-9817-7
Keywords
- Unmanned ground vehicles
- Dijkstra’s algorithm
- Optimization
- Robotic motion planning
- Nonholonomic constraints
- Autonomous vehicles