Abstract
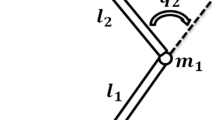
This study mainly focuses on designing a quasi-finite-time tracking control law to improve the dynamic performance for a lightweight tendon-driven joint. The mass of the link and viscous torques of lightweight arms are neglected in the dynamic model. Unlike the traditionally exponentially stabilizing control methods, joint angle is able to reach the desired link position in quasi-finite time by using the modified mapping filtered forwarding technique so that fast and accurate responses are realized in the presence of bounded external torques. While increasing the virtual controller gain, the reaching time will be shortened, and the ability of disturbance attenuation will be enhanced. To make this novel method applicable, only reference command and its first derivative are necessary; at the same time, other differential computations for controller design are obviated. Each manifold is designed insensitive to external disturbances. Quasi-finite-time controller performances are demonstrated and compared with the forwarding based dynamic surface control approach through various simulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirzinger, G., Albu-Schaffer, A., Hahnle, M., Schafer, I.: On a new generation of torque controlled light-weight robots. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 3356–3363. Seoul (2001)
Hirzinger, G., Sporer, N., Albu-Schaffer, A., Hahnle, M.: DLR’s torque-controlled light weight robot III - Are we reaching the technological limits now?. In: 19th IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 1710–1716. Washington, DC (2002)
Migliore, S.A., Brown, E.A., DeWeerth, S.P.: Biologically inspired joint stiffness control. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 4508–4513. Barcelona (2005)
Vanderborght, B., Verrelst, B., Ham, R.V., Damme, M.V., Lefeber, D., Duran, B.M.Y., Beyl, P.: Exploiting natural dynamics to reduce energy consumption by controlling the compliance of soft actuators. Int. J. Robot. Res. 25(4), 343–358 (2006)
Palli, G., Melchiorri, C., Wimböck, T., Grebenstein, M., Hirzinger, G.: Feedback linearization and simultaneous stiffness-position control of robots with antagonistic actuated joints. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 4367–4372. Rome (2007)
Palli, G.: Model and control of tendon actuated robots. Ph.D. dissertation, DEIS. University of Bologna, pp. 43–54 (2007)
Thomas, W., Christian, O., Gerd, H.: Immersion and invariance control for an antagonistic joint with nonlinear mechanical stiffness. In: Proceedings of 49th IEEE conference on decision and control, pp. 1128–1135. Atlanta (2010)
Sun, Z.Y., Xue, L.R., Zhang, K.M.: A new approach to finite-time adaptive stabilization of high-order uncertain nonlinear system. Automatica 58, 60–66 (2015)
Yu, S.H., Long, X.J.: Finite-time consensus for second-order multi-agent systems with disturbances by integral sliding mode. Automatica 54, 158–165 (2015)
Bošković, J.D., Li, S.M., Mehra, R.K.: Robust adaptive variable structure control of spacecraft under control input saturation. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 24(1), 14–22 (2001)
Bošković, J.D., Li, S.M., Mehra, R.K.: Robust tracking control design for spacecraft under control input saturation. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 27(4), 627–633 (2004)
Zhou, N., Xia, Y.Q., Wang, M.L., Fu, M.Y.: Finite-time attitude control of multiple rigid spacecraft using terminal sliding mode. Int. J. Robust Nonlin. 25(12), 1862–1876 (2015)
Zhao, L., Jia, Y.M.: Finite-time attitude tracking control for a rigid spacecraft using time-varying terminal sliding mode techniques. Int. J. Control 88(6), 1150–1162 (2015)
Zhou, J.L., Yang, J.Y.: Smooth sliding mode control for missile interception with finite-time convergence. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 38(7), 1311–1318 (2015)
Mekki, H., Benzineb, O., Boukhetala, D., Tadjine, M., Benbouzid, M.: Sliding mode based fault detection, reconstruction and fault tolerant control scheme for motor systems. ISA Trans. 57, 340–351 (2015)
Gao, F.Z., Yuan, F.S.: Adaptive finite-time stabilization for a class of uncertain high order nonholonomic systems. ISA Trans. 54, 75–82 (2015)
Zhang, X., Huang, X.L., Lu, H.Q.: Mapping filtered forwarding-based trajectory tracking control. J. Franklin Inst. 352(1), 5735–5757 (2015)
Zhang, X., Huang, X.L., Lu, H.Q., Zhang, H.Y.: Forwarding-based immersion and invariance control for n-dimensional strict-feedback nonlinear systems. Nonlin. Dyn. 83(1), 483–496 (2016)
Astolfi, A., Ortega, R.: Immersion and invariance: A new tool for stabilization and adaptive control of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 48(4), 590–606 (2003)
Lee, K.W., Singh, S.N.: Noncertainty-equivalent adaptive missile control via immersion and invariance. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 33(3), 655–665 (2010)
Lee, K., Singh, S.: Immersion and invariance-based adaptive control of a nonlinear aeroelastic system. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 32(4), 1100–1110 (2009)
Tagne, G., Taji, R., Charara, A: Immersion and invariance control for reference trajectory tracking of autonomous vechicles. In: Procedings of 16th IEEE Annual Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, pp. 2322–2328. Haugue (2013)
Acosta, J.Á., Ortega, R., Astolfi, A.: A constructive solution for stabilization via immersion and invariance: The cart and pendulum system. Automatica 44(9), 2352–2357 (2008)
Sarras, I., Siguerdidjane, H.B., Ortega, R.: Stabilization of the experimental Cart-Pendulum system with proven domain of attraction. Eur. J. Control 16(4), 329–340 (2010)
Rapp, P., Klünder, M., Sawodny, O., Tarín, C.: Nonlinear adaptive and tracking control of a pneumatic actuator via immersion and invariance. In: Procedings of 51st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, pp. 4145-4151. Maui (2012)
Manjarekar, N.S., Banavar, R.N., Ortega, R.: Stabilization of a synchronous generator with a controllable series capacitor via immersion and invariance. Int. J. Robust Nonlin. Control 22(8), 858–874 (2012)
Sarras, I., Acosta, J.Á., Ortega, R.: Constructive immersion and invariance stabilization for a class of underactuated mechanical systems. Automatica 49(5), 1442–1448 (2013)
Kemmetmüller, W., Kugi, A.: Immersion and invariance-based impedance control for electrohydraulic systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlin. Control 20(7), 725–744 (2010)
Zhang, X., Huang, X.L., Lu, H.Q.: Quasi-finite-time control for high-order nonlinear systems with mismatched disturbances via mapping filtered forwarding technique. Int. J. Syst. Sci. doi:10.1080/00207721.2016.1197980 (2016)
Palli, G., Hosseini, M., Moriello, L., Melchiorri, C.: Modeling and identification of a variable stiffness joint based on twisted string actuators. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Congress Center Hamburg, pp. 1757–1762. Hamburg (2015)
Kobayashi, H., Ozawa, R.: Adaptive neural network control of tendon-driven mechanisms with elastic tendons. Automatica 39, 1509–1519 (2003)
Zhang, X., Huang, X. L., Lu, H.Q.: Forwarding-based dynamic surface control for antagonistic actuated robots. IET Control Theory A. (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Huang, X. & Lu, H. Quasi-Finite-Time Control of Antagonistic Actuated Robots Using Mapping Filtered Forwarding Techniques. J Intell Robot Syst 86, 49–62 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-016-0435-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-016-0435-z