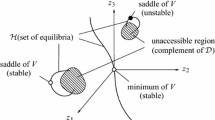
Abstract
This paper presents a theoretical analysis on the stability of nonholonomic systems when a potential field method is applied to them, and shows a numerical example for a nonholonomic underwater vehicle among obstacles. Nonholonomic systems with a potential function have an infinite number of equilibrium points, because the motion of the systems cannot always be generated exactly along the gradient vector of the potential function. By utilizing the component of the input that does not increase or decrease the potential function, the equilibrium points other than the critical points of the function can be destabilized, if the controllability of the systems is satisfied with the first-order Lie brackets of input vector fields. A time-invariant controller is proposed based on the theoretical analysis on the stability of equilibrium points, and applied to an underwater vehicle among obstacles. When the potential function has saddles as its critical points, the potential function is modified to be time-varying near the saddles in order to prevent the system from being trapped in the saddles. Numerical simulation results demonstrate that the underwater vehicle with the proposed controller converges to the desired point without collision with obstacles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khatib, O.: Real-time obstacle avoidance for manipulators and mobile robots. Int. J. Robot. Res. 5(1), 90–98 (1986)
Kim, J.-O., Khosla, P.K.: Real-time obstacle avoidance using harmonic potential functions. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 8(5), 338–349 (1992)
Guldner, J., Utkin, V.I.: Sliding mode control for gradient tracking and robot navigation using artificial potential fields. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 11(2), 247–254 (1995)
Ge, S.S., Cui, Y.J.: New potential functions for mobile robot path planning. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 16(5), 615–620 (2000)
Rimon, E., Koditschek, D.E.: Exact robot navigation using artificial potential functions. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 8(5), 501–518 (1992)
Rimon, E., Koditschek, D.E.: The construction of analytic diffeomorphisms for exact robot navigation on star worlds. Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 327(1), 71–116 (1991)
Koditschek, D.E., Rimon, E.: Robot navigation functions on manifolds with boundary. Adv. Appl. Math. 11(4), 412–442 (1990)
Kolmanovsky, I., McClamroch, N.H.: Developments in nonholonomic control problems. IEEE Control Syst. 15(6), 20–36 (1995)
Brockett, R.W.: Asymptotic stability and feedback stabilization. In: Brockett, R.W., Millman, R.S., Sussman, H.J. (eds.) Differential Geometric Control Theory, pp. 181–191, Birkhäuser (1983)
Samson, C.: Control of chained systems application to path following and time-varying point-stabilization of mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 40(1), 64–77 (1995)
M’Closkey, R.T., Murray, R.M.: Exponential stabilization of driftless nonlinear control systems using homogeneous feedback. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 42(5), 614–628 (1997)
Khennouf, H., Canudas de Wit, C.: Quasi-continuous exponential stabilizers for nonholonomic systems. In: Proceedings of IFAC 13th World Congress, 2b-174 (1996)
Astolfi, A.: Exponential stabilization of a wheeled mobile robot via discontinuous control. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Measur. Control 121(1), 121–125 (1999)
Tayebi, A., Tadjine, M., Rachid, A.: Invariant manifold approach for the stabilization of nonholonomic chained systems: application to a mobile robot. Nonlinear Dyn. 24(2), 167–181 (2001)
Morin, P., Samson, C.: Practical stabilization of driftless systems on Lie groups: the transverse function approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 48(9), 1496–1508 (2003)
Morin, P., Samson, C.: Control of nonholonomic mobile robots based on the transverse function approach. IEEE Trans. Robot. 25(5), 1058–1073 (2009)
Tanner, H.G., Loizou, S., Kyriakopoulos, K.J.: Nonholonomic stabilization with collision avoidance for mobile robots. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1220–1225 (2001)
Tanner, H.G., Loizou, S.G., Kyriakopoulos, K.J.: Nonholonomic navigation and control of cooperating mobile manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 19(1), 53–64 (2003)
Valbuena, L., Tanner, H.G.: Hybrid potential field based control of differential drive mobile robots. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 68(3-4), 307–322 (2012)
Karydis, K., Valbuena, L., Tanner, H.G.: Model predictive navigation for position and orientation control of nonholonomic vehicles. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 3206–3211 (2012)
LaValle, S.M., Kuffner, J.J.: Randomized kinodynamic planning. Int. J. Robot. Res. 20(5), 378–400 (2001)
LaValle, S.M., Konkimalla, P.: Algorithms for computing numerical optimal feedback motion strategies. Int. J. Robot. Res. 20(9), 729–752 (2001)
Que, Z., Wang, J., Plaisted, C.E.: A new analytical solution to mobile robot trajectory generation in the presence of moving obstacles. IEEE Trans. Robot. 20(6), 978–993 (2004)
Papadopoulos, E., Poulakakis, I., Papadimitriou, I.: On path planning and obstacle avoidance for nonholonomic platforms with manipulators: a polynomial approach. Int. J. Robot. Res. 21(4), 367–383 (2002)
Lamiraux, F., Bonnafous, D., Lefebvre, O.: Reactive path deformation for nonholonomic mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 20(6), 967–977 (2004)
Divelbiss, A.W., Wen, J.T.: A path space approach to nonholonomic motion planning in the presence of obstacles. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 13(3), 443–451 (1997)
Weir, M.K., Bott, M.P.: High quality goal connection for nonholonomic obstacle navigation allowing for drift using dynamic potential fields. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 3221–3226 (2010)
Huang, W.H., Fajen, B.R., Fink, J.R., Warren, W.H.: Visual navigation and obstacle avoidance using a steering potential function. Robot. Auton. Syst. 54(4), 288–299 (2006)
Ramírez, G., Zeghloul, S.: Collision-free path planning for nonholonomic mobile robots using a new obstacle representation in the velocity space. Robotica 19(5), 543–555 (2001)
Patel, S., Jung, S.-H., Ostrowski, J.P., Rao, R., Taylor, C.J.: Sensor based door navigation for a nonholonomic vehicle. In: Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 3081–3086 (2002)
Lamiraux, F., Sekhavat, S., Laumond, J.P.: Motion planning and control for Hilare pulling a trailer. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 15(4), 640–652 (1999)
Sekhavat, S., Laumond, J.-P.: Topological property for collision-free nonholonomic motion planning: the case of sinusoidal inputs for chained form systems. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 14(5), 671–680 (1998)
Laumond, J.-P., Jacobs, P.E., Taïx, M., Murray, R.M.: A motion planner for nonholonomic mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 10(5), 577–593 (1994)
Jacobs, P., Canny, J.: Planning smooth paths for mobile robots. In: Li, Z., Canny, J. F. (eds.) Nonholonomic Motion Planning, pp. 271–342. Kluwer (1993)
Yang, S.X., Meng, M.Q.-H.: Real-time collision-free motion planning of a mobile robot using a neural dynamics-based approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 14(6), 1541–1552 (2003)
Kallen, V., Komoroski, A.T., Kumar, V.: Sequential composition for navigating a nonholonomic cart in the presence of obstacles. IEEE Trans. Robot. 27(6), 1152–1159 (2011)
Xiang, X., Lapierre, L., Jouvencel, B.: Guidance based collision avoidance of coordinated nonholonomic autonomous vehicles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 6064–6069 (2010)
Neimark, J.I., Fufaev, N.A.: Dynamics of Nonholonomic Systems. the American Mathematical Society Publisher: the American Mathematical Society (1972)
Zhu, H.P., Yu, A.B.: A contribution to the stability of nonholonomic systems. Mech. Res. Commun. 29(5), 307–314 (2002)
Urakubo, T.: Feedback stabilization of a nonholonomic system with potential fields: application to a two-wheeled mobile robot among obstacles. Nonlinear Dyn. 81(3), 1475–1487 (2015)
Urakubo, T.: Discontinuous feedback stabilization of a class of nonholonomic systems based on Lyapunov control. In: Proceedings of Fifth International Workshop on Robot Motion and Control, pp. 91–96 (2005)
Nakamura, Y., Savant, S.: Nonholonomic motion control of an autonomous underwater vehicle. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp. 1254–1259 (1991)
Egeland, O., Berglund, E., Sørdalen, O.J.: Exponential stabilization of a nonholonomic underwater vehicle with constant desired configuration. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 20–25 (1994)
Bullo, F., Leonard, N.E.: Motion control for underactuated mechanical systems on Lie groups. In: Proceedings of the 1997 European Control Conference, pp. 1830–1835 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Urakubo, T. Stability Analysis and Control of Nonholonomic Systems with Potential Fields. J Intell Robot Syst 89, 121–137 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-017-0473-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-017-0473-1