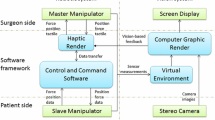
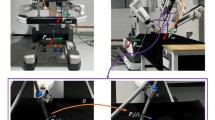
Abstract
Surgery is an effective means of treating cataracts and restoring vision. However, cataract surgery rate (CSR) in developing countries and regions is relatively low due to the lack of experienced high-level surgeons. In this paper, to reduce the reliance of surgery on physician experience and thereby increase CSR, a master-slave robotic system and safety control strategies with a virtual fixture and virtual force feedback are proposed to assist cataract surgery. First, the surgery is divided into four different stages with different robot control modes. Secondly, the virtual constraint area with virtual spring model in the operating stage is established, so that the doctor can distinguish the operation area where the end of the surgical instrument is located by feedback force. Thirdly, safety control algorithm guarantees that the surgical instrument strictly moves around the surgical incision point, which is regarded as a remote centre of motion, so that the cornea outside the incision point is not injured. Finally, the experimental results show that the proposed safety control strategy allows the robotic system to perform the procedure safely.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Macherner, R.: The development of pars plana vitrectomy: a personal account. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 233(8), 453–468 (1995)
Wang, W., Yan, W., Fotis, K., Prasad, N.M., Lansingh, V.C., Taylor, H.R., Finger, R.P., Facciolo, D., He, M.: Cataract surgical rate and socioeconomics: a global study. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 57(14), 5872–5881 (2016)
Community Eye Health: Cataract surgical rates. Commun. Eye Health 100(30), 88–89 (2017)
Tsui, I., Tsirbas, A., Mango, C.W., Schwartz, S.D., Hubschman, J.-P.: Robotic surgery in ophthalmology. In: Robot Surgery. IntechOpen (2010)
Bourcier, T., Chammas, J., Becmeur, P.-H., Sauer, A., Gaucher, D., Liverneaux, P., Marescaux, J., Mutter, D.: Robot-assisted simulated cataract surgery. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 43(4), 552–557 (2017)
Liu, T., Li, C., Inoue, Y., Shibata, K.: Reaction force/torque sensing in a master-slave robot system without mechanical sensors. Sensors 10(8), 7134–7145 (2010)
Balicki, M., Uneri, A., Iordachita, I., Handa, J., Gehlbach, P., Taylor, R.: Micro-force sensing in robot assisted membrane peeling for vitreoretinal surgery. In: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, pp 303–310. Springer (2010)
Taylor, R.H., Balicki, M.A., Handa, J.T., Gehlbach, P.L., Iordachita, I., Uneri, A.: Method for presenting force sensor information using cooperative robot control and audio feedback, February 20 2014. US Patent App. 13/813,727
Huang, L., Zhang, L.Y., Yang, Y., Shen, L.J., Chen, Y.Q.: Design and analysis of a robot-assisted anipulator in retinal vascular bypass surgery. In: Applied Mechanics and Materials, vol. 190, pp 673–678. Trans Tech Publ (2012)
Xiao, J., Yang, Y., Li, D., Huang, L., Zhang, L.: Advances and key techniques of ophthalmic microsurgical robots. J. Mech. Eng. 49(1), 15–22 (2013)
Keenan, T., Rosen, P., Yeates, D., Goldacre, M.: Time trends and geographical variation in cataract surgery rates in england: study of surgical workload. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 91(7), 901–904 (2007)
Yang, Y., Xu, C., Deng, S., Xiao, J.: Insertion force in manual and robotic corneal suturing. Int. J. Med. Rob. Comput. Assisted Surg. 8(1), 25–33 (2012)
Uneri, A., Balicki, M.A., Handa, J., Gehlbach, P., Taylor, R.H., Iordachita, I.: New steady-hand eye robot with micro-force sensing for vitreoretinal surgery. In: 2010 3rd IEEE RAS and EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), pp 814–819. IEEE (2010)
Kong, XB, Yan, SG, Luo, SK, Su, P: Age-related changes of ocular biological structure in the elderly. Rec. Adv. Ophthalmol. 32(7), 668–672 (2012)
Liu, Z., Wang, B., Xu, X., Wang, C.: A study for accommodating the human crystalline lens by finite element simulation. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 30(6–7), 371–376 (2006)
Nasseri, M.A., Eder, M., Nair, S., Dean, EC, Maier, M., Zapp, D., Lohmann, C.P., Knoll, A.: The introduction of a new robot for assistance in ophthalmic surgery. In: 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp. 5682–5685. IEEE (2013)
Barthel, A., Trematerra, D., Nasseri, M.A., Zapp, D., Lohmann, C.P., Knoll, A., Maier, M.: Haptic interface for robot-assisted ophthalmic surgery. In: 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), pp 4906–4909. IEEE (2015)
Nasseri, M.A., Gschirr, P, Eder, M., Nair, S., Kobuch, K., Maier, M., Zapp, D., Lohmann, C., Knoll, A.: Virtual fixture control of a hybrid parallel-serial robot for assisting ophthalmic surgery: an experimental study. In: 5th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, pp 732–738. IEEE (2014)
Charles, MW, Brown, N.: Dimensions of the human eye relevant to radiation protection (dosimetry). Phys. Med. Biol. 20(2), 202 (1975)
Nogueira, P, Zankl, M, Schlattl, H, Vaz, P: Dose conversion coefficients for monoenergetic electrons incident on a realistic human eye model with different lens cell populations. Phys. Med. Biol. 56(21), 6919 (2011)
Prada, R., Payandeh, S.: On study of design and implementation of virtual fixtures. Virtual Real. 13(2), 117–129 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61603374, U1713218 and U1713221), the Key Fundamental Research Program of Shenzhen (Nos. JCYJ20160428144135222 and JCYJ20160427184134564), and in part by the Shenzhen Key Laboratory Project (No. ZDSYS201707271637577).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Jiang, Z., Yang, Y. et al. Safety Control Method of Robot-Assisted Cataract Surgery with Virtual Fixture and Virtual Force Feedback. J Intell Robot Syst 97, 17–32 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-019-01012-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-019-01012-2