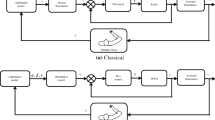
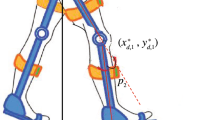
Abstract
In this paper, we proposed a Human-in-the-loop (HITL) control based on the Euler angles solution of the robot end-effector. When humans are in the control loop, we can linearize the Euler angles such that they have direct relation with the joint angles and they are also decoupled. So the Jacobian matrix and the inverse kinematics are not needed. We simplify the admittance control using the Euler angles. The stability of those controllers is proven. The experiments, with a two-degree-of-freedom (2-DOF) pan and tilt robot and a four-degree-of-freedom exoskeleton, show that our Euler angles based controllers are simple and effective.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Yu, W., Rosen, J.: A novel linear PID controller for an upper limb exoskeleton. In: 49th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, pp. 3548–3553 (2010)
Yu, W., Rosen, J., Li, X.: PID admittance control for an upper limb exoskeleton. In: American Control Conference, pp. 1124–1129 (2011)
Perrusquia, A., Yu, W., Soria, A., Lozano, R.: Stable admittance control without inverse kinematics. In: 20th IFAC World Congress (IFAC2017), Toulose, France (2017)
Yu, W., Carmona, R., Li, X.: Neural PID admittance control of a robot. In: American Control Conference, pp. 4963–4968 (2013)
Irawan, A., Moktadir, M., Yin Tan, Y.: PD-FLC with admittance control for hexapod robot’s leg positioning on seabed. IEEE American Control Conference (2015)
Peng Tee, K., Yan, R., Li, H.: Adaptive admittance control of a robot manipulator under task space constraint. In: IEEE International Conference On Robotics And Automation, pp. 5181–5186 (2010)
Hogan, N.: Impedance control: an approach to manipulation. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control 107, 1–24 (1985)
Hoon Kang, S., Jin, M., Hun Chang, P.: A solution to the accuracy/robustness dilemma in impedance control, In: IEEE/ ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, pp. 182–194 (2009)
Ferreti, G., Magnani, G.A., Rocco, P.: Impedance control for elastic joints industrial manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 20(3), 488–498 (2004)
Bonitz, R.G., Hsia, T.C.: Internal Force-Based Impedance Control for Cooperating Manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 12(1), 78–89 (1996)
Singh, S.K., Popa, D.O.: An analysis of some fundamental problems in adaptive control of force and impedance behavior: theory and experiments. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 11(6), 912–921 (1995)
Lu, W.-S., Meng, Q.H.: Impedance control with adaptation for robotic manipulators. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 7(3), 408–415 (1991)
Abdossalami, A., Sirouspour, S.: Adaptive control of haptic interaction with impedance and admittance type virtual environments. In: Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environments and Teleoperator Systems, pp. 145–152 (2008)
Dohring, M., Newman, W.: The passivity of natural admittance control implementations. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 371–376 (2003)
Chih, M., Huang, A.C.: Adaptive impedance control of robot manipulators based on function approximation technique. Robotica, Cambridge University Press 22, 395–403 (2004)
Kelly, R., Carelli, R., Amestegui, M., Ortega, R.: On adaptive impedance control of robots manipulators. IEEE Robot. Autom. 1, 572–577 (1989)
Mut, V., Nasisi, O., Carelli, R., Kuchen, B.: Tracking adaptive impedance robot control with visual feedback, In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 2002–2007 (1998)
Tufail, M., de Silva, C.W.: Impedance control schemes for bilateral teleoperation. In: International Conference on Computer Science and Education, pp. 44–49 (2014)
Ficuciello, F., Villani, L., Siciliano, B.: Variable impedance control of redundant manipulators for intuitive human-robot physical interaction. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31(4), 850–863 (2015)
Manan Khan, A., Yun, D.W., Ali, M.A., Han, J., Shin, K., Han, C.: Adaptive impedance control for upper limb assist exoskeleton. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 4359–4366 (2015)
Mohammadi, H., Richter, H.: Robust tracking/impedance control: application to prosthetics. In: American Control Conference, pp. 2673–2678 (2015)
Garrido, J.: Aprendizaje por demostración en el espacio articular para el seguimiento de trayectorias aplicado en un exoesqueleto de 4 grados de libertad, Centro de Investigación y Estudios Avanzados del Instituto Politécnico Nacional, México (2015)
Ramírez, D., Arturo, O., Parra Vega, V., Díaz Montiel, M.G., Pozas Cardenas, M.J., Hernández Gómez, R.A.: Cartesian sliding PD control of robots manipulators for tracking in finite time: Theory and experiments. DAAAM International Scientific Book 23, 257–272 (2008)
Kazerooni, H., Herm, M.-G.: The Dynamics and Control of a Haptic Interface Device. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 10(4), 453–464 (1994)
Kiguchi, K., Tanaka, T., Fukuda, T.: Nuero-fuzzy control of a robotic exoskeleton with EMG signals. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 12(4), 481–490 (2004)
Kelly, R., Santibáñez, V.: Control de Movimiento de Robots Manipuladores, Pearson Prentice Hall (2003)
Khalil, H.: Nonlinear systems, Prentice Hall (2002)
Dimeas, F., Aspragathos, N.: Online stability in human-robot cooperations with admittance control. IEEE Trans. Haptic 9(2), 267–278 (2016)
Spong, M.W., Hutchinson, S., Vidyasagar, M.: Robot dynamics and control (2004)
Onyango, S.O.: Behaviour modelling and system control with human in the loop. Diss. Université Paris-Est (2017)
Ranatunga, I., Lewis, F.L., Popa, D.O., Tousif, S.M.: Adaptive admittance control for human–robot interaction using model reference design and adaptive inverse filtering. IEEE transactions on control systems technology, 25(1), 278–285 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perrusquía, A., Yu, W. Human-in-the-Loop Control Using Euler Angles. J Intell Robot Syst 97, 271–285 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-019-01058-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-019-01058-2