Abstract
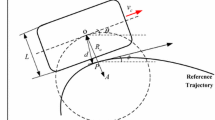
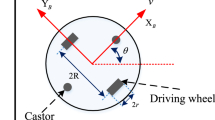
The chattering problem is caused by the switching function of sliding mode controller, which makes the accuracy of autonomous driving limited. To solve this problem, a steering sliding mode controller with improved nonlinear reaching law is proposed. The exponential function is used in the new reaching law to eliminate chattering problem, and the initial value of switching function is employed to avoid output saturation in the case of large initial errors. In the new reaching law, the large slope of sign function coefficient ensures the anti-disturbance ability of the controller after the system converges. A disturbance observer is constructed for real-time observation of the disturbance signals, which makes the controller get rid of the dependence on the prior knowledge of the disturbance. This paper introduces the tuning principle of controller parameters in detail and constructs the simulations and experiments of autonomous driving system. The experiments demonstrate that the proposed controller restrains the path-tracking mean error by 38% and restrains the standard error by 18%, the accuracy and efficiency of autonomous driving system are improved. Furthermore, the proposed reaching law can be used in other systems besides autonomous harvesting robots.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Lipiński, A.J.: Precision of tractor operations with soil cultivation implements using manual and automatic steering modes. Biosyst. Eng. 145, 22–28 (2016)
Wang, Z., Yang, X.: Model establishment of body attitude adjustment system based on Backstepping control algorithm and automatic leveling technology. Cluster Comput. 22(6), 14327–14337 (2019)
Say, S.M.: Adoption of precision agriculture technologies in developed and developing countries. Online J. Sci. Technol. 8(1), 7–15 (2018)
Cheng, S., Li, L., Chen, X.: Model-predictive-control-based path tracking controller of autonomous vehicle considering parametric uncertainties and velocity-varying. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2020.3009585
Kong, L., He, W., Yang, C., et al.: Adaptive fuzzy control for coordinated multiple robots with constraint using impedance learning. IEEE T Cybernetics. 49(8), 3052–3063 (2019)
Bechar, A., Vigneault, C.: Agricultural robots for field operations: concepts and components. Biosyst. Eng. 149, 94–111 (2016)
Qiao, N., Wang L.: An improved path-tracking controller with mid-angle adaptive calibration for combine harvester. JINST. 15(1), (2020)
He, W., Xiaoping, B., Hongbin, L.: Proportional distribution method for estimating actual grain flow under combine harvester dynamics. Int. J. Agr. Biol. Eng. 10(4), 158–164 (2017)
Kong, L., He, W., Dong, Y., et al.: Asymmetric bounded neural control for an uncertain robot by state feedback and output feedback. IEEE T Sys Man CY-S. 51(3), 1735–1746 (2021)
Kong L., He W.., Yang W., et al: Fuzzy approximation-based finite-time control for a robot with actuator saturation under time-varying constraints of work space. IEEE T Cybernetics, (2020)
Zaare, S., Soltanpour, M.R., Moattari, M.: Voltage based sliding mode control of flexible joint robot manipulators in presence of uncertainties. Robot. Auton. Syst. 118, 204–219 (2019)
Wu, X., Wang, C., Hua, S.: Adaptive extended state observer-based nonsingular terminal sliding mode control for the aircraft skin inspection robot. J Intell Robot Syst. 98, 721–732 (2020)
Guo, J., Luo, Y., Li, K.: Adaptive neural-network sliding mode cascade architecture of longitudinal tracking control for unmanned vehicles. Nonlinear Dyn. 87(4), 2497–2510 (2017)
Boukadida, W., Benamor, A., Messaoud, H.: Multi-objective design of optimal higher order sliding mode control for robust tracking of 2-DoF helicopter system based on metaheuristics. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 91, 442–455 (2019)
Jiang, B., Karimi, H.R., Kao, Y.: Takagi–Sugeno model based event-triggered fuzzy sliding-mode control of networked control systems with Semi-Markovian switchings. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 28(4), 673–683 (2019)
Sun, Y., Xu, J., Qiang, H., et al.: Adaptive sliding mode control of Maglev system based on RBF neural network minimum parameter learning method. Measurement. 141, 217–226 (2019)
Chu, Y., Fei, J., Hou, S.: Adaptive global sliding-mode control for dynamic systems using double hidden layer recurrent neural network structure. IEEE Trans. Neur. Net. Lear. 31(4), 1297–1309 (2019)
Utkin, V.: Variable structure systems with sliding modes. IEEE Trans. Automati. Contr. 22(2), 212–222 (1977)
Sun, H., Li, S., Sun, C.: Finite time integral sliding mode control of hypersonic vehicles. Nonlinear Dyn. 73(1–2), 229–244 (2013)
Homaeinezhad, M., Yaqubi, S., Fotoohinia, F.: FEA based discrete-time sliding mode control of uncertain continuum mechanics MIMO vibrational systems. J Sound Vib. 460, 114902 (2019)
Chen, Y., Fei, J.: Dynamic sliding mode control of active power filter with integral switching gain. IEEE Access. 7, 21635–21644 (2019)
Sumantri, B., Uchiyama, N., Sano, S.: Least square based sliding mode control for a quad-rotor helicopter and energy saving by chattering reduction. Mech. Syst. Signal Pr. 66, 769–784 (2016)
Cho, H., Kerschen, G., Oliveira, T.R.: Adaptive smooth control for nonlinear uncertain systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 99, 2819–2833 (2020)
Du, H., Yu, X., Chen, M.Z.Q.: Chattering-free discrete-time sliding mode control. Automatica. 68, 87–91 (2016)
Gang, H., et al.: Estimation of sensor faults and unknown disturbance in current measurement circuits for PMSM drive system. Measurement. 137, 580–587 (2019)
Peng, Y., Liu, J.: Modeling and vibration control for a flexible pendulum inverted system based on a PDE observer. Int. J. Control. 90(8), 1736–1751 (2017)
Guo, L., Cao, S.: Anti-disturbance control theory for systems with multiple disturbances: a survey. Isa Trans. 53(4), 846–849 (2014)
Ma, H., Li, Y., Xiong, Z.: Discrete-time sliding-mode control with enhanced power reaching law. IEEE T. Ind. Electron. 66(6), 4629–4638 (2018)
Sun, C., Gong, G., Yang, H.: Sliding mode control with adaptive fuzzy immune feedback reaching law. Int. J. Control Autom. 18(2), 363–373 (2020)
Gao, W., Hung, J.C.: Variable structure control of nonlinear systems: a new approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 40(1), 45–55 (1993)
Fallaha, C.J., Saad, M., Kanaan, H.Y.: Sliding-mode robot control with exponential reaching law. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 58(2), 600–610 (2010)
Mozayan, S.M., Saad, M., Vahedi, H.: Sliding mode control of PMSG wind turbine based on enhanced exponential reaching law. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63(10), 6148–6159 (2016)
Lin, S., Zhang, W.: Chattering reduced sliding mode control for a class of chaotic systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 93, 2273–2282 (2018)
Pan, Y., Yang, C., Pan, L.: Integral sliding mode control: performance, modification, and improvement. IEEE Tran. Ind. Inform. 14(7), 3087–3096 (2017)
Yang L, Gao D, Hoshino Y, et al. Evaluation of the accuracy of an auto-navigation system for a tractor in mountain areas[C]//2017 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII). IEEE, 2017
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China [61773113, 51875260], Primary Research & Development Plan of Jiangsu Province [BE2018384], National Key Research and Development Program [2016YFD0702000].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. System construct, data collection and analysis were performed by Nan Qiao and Lihui Wang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Nan Qiao, the revision was completed with the help of Mingjie Liu and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China [61773113, 51875260], Primary Research & Development Plan of Jiangsu Province [BE2018384], National Key Research and Development Program [2016YFD0702000].
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript.
Availability of data and material
No applicable.
Code availability
No applicable.
Ethics approval
No applicable.
Consent to participate
No applicable.
Consent for publication
This manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, N., Wang, L., Liu, M. et al. The sliding mode controller with improved reaching law for harvesting robots. J Intell Robot Syst 104, 9 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-021-01536-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-021-01536-6