Abstract
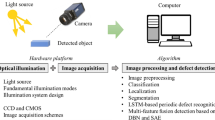
Deep Learning has garnered significant attention in the field of object detection and is widely used in both industry and everyday life. The objective of this study is to investigate the applicability and targeted improvements of Deep Learning-based object detection in complex stacked environments. We analyzed the limitations in practical applications under such conditions, pinpointed the specific problems, and proposed corresponding improvement strategies. First, the study provided an overview of recent advancements in mainstream one-stage object detection algorithms, which included Anchor-based, Anchor-free, and Transformer-based architectures. The high real-time performance of these algorithms holds particular significance in practical engineering applications. It then looked at relevant technologies in three emerging research areas: Parts Recognition, Intelligent Driving, and Agricultural Picking. The study summarized existing limitations in real-time object detection within complex stacked environments and provided a comprehensive analysis of prevalent improvement strategies such as multi-level feature fusion, knowledge distillation, and hyperparameter optimization. Finally, after analyzing the performance of recent advanced one-stage algorithms on official datasets, this paper conducted empirical tests on a self-constructed industrial stacked dataset with algorithms of different structure and analyzed the experimental results in detail. A comprehensive analysis shows that Deep Learning-based object detection algorithms offer extensive applicability in complex stacked environments. In addressing diverse target sizes, overlapping occlusions, real-time constraints, and the need for lightweight solutions in complex stacked environments, each improvement strategy has its own advantages and limitations. Selecting and integrating appropriate enhancement strategies is critical and typically requires holistic evaluation, tailored to specific application contexts and challenges.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. The source codes used during the research are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
The custom code used during the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Viola, P.A., Jones, M.J.: Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In: Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. CVPR 2001, vol. 1 (2001)
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), vol. 1, pp. 886–8931 (2005)
Canny, J.F.: A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. PAMI 8, 679–698 (1986)
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60, 91–110 (2004)
Bay, H., Tuytelaars, T., Gool, L.V.: Surf: Speeded up robust features. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (2006). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:461853
Zhao, K., Wang, Y., Zuo, Y., Zhang, C.: Palletizing robot positioning bolt detection based on improved yolo-v3. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 104 (2022)
Liu, H.-Q., Li, D., Jiang, B., Zhou, J., Wei, T., Yao, X.: Mgbm-yolo: a faster light-weight object detection model for robotic grasping of bolster spring based on image-based visual servoing. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 104, 1–17 (2022)
Tao, H., Qiu, J., Chen, Y., Stojanovic, V., Cheng, L.: Unsupervised cross-domain rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on time-frequency information fusion. J. Frankl. Inst. 360, 1454–1477 (2022)
Zhuang, Z., Tao, H., Chen, Y., Stojanovic, V., Paszke, W.: An optimal iterative learning control approach for linear systems with nonuniform trial lengths under input constraints. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 53, 3461–3473 (2023)
Sun, X., Liu, T., Yu, X., Pang, B.: Unmanned surface vessel visual object detection under all-weather conditions with optimized feature fusion network in yolov4. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 103 (2021)
Sharma, V., Mir, R.N.: A comprehensive and systematic look up into deep learning based object detection techniques: a review. Comput. Sci. Rev. 38, 100301 (2020)
Gupta, A., Anpalagan, A., Guan, L., Khwaja, A.S.: Deep learning for object detection and scene perception in self-driving cars: survey, challenges, and open issues. Array 10, 100057 (2021)
Kamath, V., Renuka, A.: Deep learning based object detection for resource constrained devices: systematic review, future trends and challenges ahead. Neurocomput. 531, 34–60 (2023)
Chen, G., Wang, H., Chen, K., Li, Z., Song, Z., Liu, Y., Chen, W., Knoll, A.: A survey of the four pillars for small object detection: multiscale representation, contextual information, super-resolution, and region proposal. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 52, 936–953 (2022)
Tong, K., Wu, Y.: Deep learning-based detection from the perspective of small or tiny objects: a survey. Image Vis. Comput. 123 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2022.104471
Chahal, K.S., Dey, K.: A survey of modern object detection literature using deep learning (2018). arXiv:1808.07256
Simonyan, K., Zisserman, A.: Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition (2014). arXiv:1409.1556
Noh, S.-H.: Analysis of gradient vanishing of rnns and performance comparison. Inf. 12, 442 (2021)
Canziani, A., Paszke, A., Culurciello, E.: An analysis of deep neural network models for practical applications (2016). arXiv:1605.07678
Broy, M.: Software engineering–from auxiliary to key technologies. In: Broy, M., Denert, E. (eds.) Software Pioneers. Springer, New York, pp. 10–13 (1992)
Szegedy, C., Liu, W., Jia, Y., Sermanet, P., Reed, S., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Vanhoucke, V., Rabinovich, A.: Going deeper with convolutions. In: 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Boston, pp. 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2015.7298594 (2015)
Redmon, J., Divvala, S., Girshick, R., Farhadi, A.: You only look once: unified, real-time object detection. In: 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE Comp Soc; Comp Vis Fdn, Seattle, pp. 779–788. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.91 (2016)
Howard, A.G., Zhu, M., Chen, B., Kalenichenko, D., Wang, W., Weyand, T., Andreetto, M., Adam, H.: Mobilenets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications (2017). arXiv:1704.04861
Howard, A., Sandler, M., Chu, G., Chen, L.-C., Chen, B., Tan, M., Wang, W., Zhu, Y., Pang, R., Vasudevan, V., Le, Q.V., Adam, H.: Searching for mobilenetv3. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2019). IEEE; IEEE Comp Soc; CVF, Seoul, pp. 1314–1324. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00140 (2019)
Dosovitskiy, A., Beyer, L., Kolesnikov, A., Weissenborn, D., Zhai, X., Unterthiner, T., Dehghani, M., Minderer, M., Heigold, G., Gelly, S., Uszkoreit, J., Houlsby, N.: An image is worth 16x16 words: transformers for image recognition at scale (2020). arXiv:2010.11929
Liu, Z., Hu, H., Lin, Y., Yao, Z., Xie, Z., Wei, Y., Ning, J., Cao, Y., Zhang, Z., Dong, L., Wei, F., Guo, B.: Swin transformer v2: scaling up capacity and resolution. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). IEEE; CVF; IEEE Comp Soc., New Orleans, pp. 11999–12009. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01170 (2022)
Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., Usunier, N., Kirillov, A., Zagoruyko, S.: End-to-end object detection with transformers (2020). arXiv:2005.12872
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster r-cnn: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(6), 1137–1149 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
Ren, S., He, K., Girshick, R., Sun, J.: Faster r-cnn: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39(6), 1137–1149 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031
Yu, J., Jiang, Y., Wang, Z., Cao, Z., Huang, T.S.: Unitbox: an advanced object detection network. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (2016)
Zheng, Z., Wang, P., Ren, D., Liu, W., Ye, R., Hu, Q., Zuo, W.: Enhancing geometric factors in model learning and inference for object detection and instance segmentation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 52(8), 8574–8586 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2021.3095305
Zhang, Y.-F., Ren, W., Zhang, Z., Jia, Z., Wang, L., Tan, T.: Focal and efficient iou loss for accurate bounding box regression. Neurocomput. 506, 146–157 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2022.07.042
Bodla, N., Singh, B., Chellappa, R., Davis, L.S.: Soft-nms: improving object detection with one line of code. IEEE, pp. 5562–5570 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.593
Du, L., Zhang, R., Wang, X.: Overview of two-stage object detection algorithms. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1544 (2020)
Chen, Y., Han, C., Wang, N., Zhang, Z.: Revisiting feature alignment for one-stage object detection (2019). arXiv:1908.01570
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: Yolo9000: better, faster, stronger. In: 30TH IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2017). IEEE; IEEE Comp Soc; CVF, Honolulu, pp. 6517–6525. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.690 (2017)
Liu, W., Anguelov, D., Erhan, D., Szegedy, C., Reed, S.E., Fu, C.-Y., Berg, A.C.: Ssd: single shot multibox detector. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (2015)
Fu, C.-Y., Liu, W., Ranga, A., Tyagi, A., Berg, A.C.: Dssd: deconvolutional single shot detector (2017). arXiv:1701.06659
Jeong, J., Park, H., Kwak, N.: Enhancement of ssd by concatenating feature maps for object detection (2017). arXiv:1705.09587
Lin, T.-Y., Goyal, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Dollar, P.: Focal loss for dense object detection. In: 2017 16th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE; IEEE Comp Soc, Venice, pp. 2999–3007. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.324 (2017)
Redmon, J., Farhadi, A.: Yolov3: An incremental improvement (2018). arXiv:1804.02767
Shen, Z., Liu, Z., Li, J., Jiang, Y.-G., Chen, Y., Xue, X.: Dsod: learning deeply supervised object detectors from scratch. In: 2017 16th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE; IEEE Comp Soc, Venice, pp. 1937–1945. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.212 (2017)
Li, Z., Zhou, F.: Fssd: feature fusion single shot multibox detector (2017). arXiv:1712.00960
Zhang, S., Wen, L., Bian, X., Lei, Z., Li, S.: Single-shot refinement neural network for object detection. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4203–4212 (2017)
Law, H., Deng, J.: Cornernet: detecting objects as paired keypoints. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer vision - ECCV 2018, PT XIV. Lecture notes in computer science, vol. 11218, pp. 765–781. 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01264-9_45 (2018)
Duan, K., Bai, S., Xie, L., Qi, H., Huang, Q., Tian, Q.: Centernet: keypoint triplets for object detection. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2019). IEEE; IEEE Comp Soc; CVF, Seoul, pp. 6568–6577. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00667 (2019)
Tian, Z., Shen, C., Chen, H., He, T.: Fcos: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2019). IEEE; IEEE Comp Soc; CVF, Seoul, pp. 9626–9635. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00972 (2019)
Zhou, X., Zhuo, J., Krahenbuhl, P.: Bottom-up object detection by grouping extreme and center points. In: 2019 32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2019). IEEE; CVF; IEEE Comp Soc, Long Beach, pp. 850–859. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00094 (2019)
Zhou, X., Zhuo, J., Krahenbuhl, P.: Bottom-up object detection by grouping extreme and center points. In: 2019 32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2019). IEEE; CVF; IEEE Comp Soc, Long Beach, pp. 850–859. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00094 (2019)
Bochkovskiy, A., Wang, C.-Y., Liao, H.-Y.M.: Yolov4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection (2020). arXiv:2004.10934
Jocher, G.R., Stoken, A., Borovec, J., NanoCode, ChristopherSTAN, Changyu, L., Laughing, tkianai, Hogan, A., lorenzomammana, yxNONG, AlexWang, Diaconu, L., Marc, wanghaoyang, ah, Doug, Ingham, F., Frederik, Guilhen, Hatovix, Poznanski, J., Fang, J., Yu, L., Changyu, Wang, M., Gupta, N.K., Akhtar, O., PetrDvoracek, Rai, P.: ultralytics/yolov5: v3.1 - bug fixes and performance improvements (2020)
Zhang, S., Chi, C., Yao, Y., Lei, Z., Li, S.Z.: Bridging the gap between anchor-based and anchor-free detection via adaptive training sample selection. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 9756–9765 (2019)
Tan, M., Pang, R., Le, Q.V.: Efficientdet: scalable and efficient object detection. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 8–10787 (2019)
Wang, C.-Y., Yeh, I.-H., Liao, H.: You only learn one representation: unified network for multiple tasks. J. Inf. Sci. Eng. 39, 691–709 (2021)
e, Z., Liu, S., Wang, F., Li, Z., Sun, J.: Yolox: exceeding yolo series in 2021 (2021). hyperimagehttp://arxiv.org/abs/2107.08430arXiv:2107.08430
hu, X., Su, W., Lu, L., Li, B., Wang, X., Dai, J.: Deformable detr: deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection (2020). arXiv:2010.04159
Li, C., Li, L., Jiang, H., Weng, K., Geng, Y., Li, L., Ke, Z., Li, Q., Cheng, M., Nie, W., Li, Y., Zhang, B., Liang, Y., Zhou, L., Xu, X., Chu, X., Wei, X., Wei, X.: Yolov6: a single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications (2022). arXiv:2209.02976
Wang, C.-Y., Bochkovskiy, A., Liao, H.-Y.M.: Yolov7: trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors (2022). arXiv:2207.02696
Zhang, X., Zeng, H., Guo, S., Zhang, L.: Efficient long-range attention network for image super-resolution. In: Avidan, S., Brostow, G., Cisse, M., Farinella, G., Hassner, T. (eds.) Computer vision - ECCV 2022, PT XVII. Lecture notes in computer science. 17th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, vol. 13677, pp. 649–667. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-19790-1_39 (2022)
Ultralytics: ultralytics’s official github repository (2023). Available at: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics#documentation
Fang, Y., Liao, B., Wang, X., Fang, J., Qi, J., Wu, R., Niu, J., Liu, W.: You only look at one sequence: rethinking transformer in vision through object detection. In: Ranzato, M., Beygelzimer, A., Dauphin, Y., Liang, P., Vaughan, J. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34 (NEURIPS 2021). 35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), ELECTR NETWORK (2021)
Ying, Z., Lin, Z., Wu, Z., Liang, K., Hu, X.: A modified-yolov5s model for detection of wire braided hose defects. Measurement 190 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110683
Zhao, K., Wang, Y., Zuo, Y., Zhang, C.: Palletizing robot positioning bolt detection based on improved yolo-v3. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 104(3) (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-022-01580-w
Zhang, Y., Liang, J., Lu, Q., Luo, L., Zhu, W., Wang, Q., Lin, J.: A novel efficient convolutional neural algorithm for multi-category aliasing hardware recognition. Sensors 22(14) (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/s22145358
Li, Y., Wang, J., Huang, J., Li, Y.: Research on deep learning automatic vehicle recognition algorithm based on res-yolo model. Sensors 22(10) (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/s22103783
Bie, M., Liu, Y., Li, G., Hong, J., Li, J.: Real-time vehicle detection algorithm based on a lightweight you-only-look-once (yolov5n-l) approach. Exp. Syst. Appl. 213(B) (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.119108
Gong, X., Zhang, X., Zhang, R., Wu, Q., Wang, H., Guo, R., Chen, Z.: U3-yoloxs: an improved yoloxs for uncommon unregular unbalance detection of the rape subhealth regions. Comput. Electron. Agri. 203 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2022.107461
Yang, R., Hu, Y., Yao, Y., Gao, M., Liu, R.: Fruit target detection based on bco-yolov5 model. Mobile Inf. Syst. 2022 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8457173
Jin, Z., Liu, L., Gong, D., Li, L.: Target recognition of industrial robots using machine vision in 5g environment. Front. Neurorobot. 15 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbot.2021.624466
Kapoor, A., Singhal, A.: A comparative study of k-means, k-means++ and fuzzy c-means clustering algorithms. In: 2017 3rd International Conference on Computational Intelligence & Communication Technology (CICT), pp. 1–6 (2017)
Li, F., Gao, D., Yang, Y., Zhu, J.: Small target deep convolution recognition algorithm based on improved yolov4. Int. J Mach. Learn. Cybern. 14(2, SI), 387–394 (2023) .https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-021-01496-1
Yang, J., Wu, S., Gou, L., Yu, H., Lin, C., Wang, J., Wang, P., Li, M., Li, X.: Scd: a stacked carton dataset for detection and segmentation. SENSORS 22(10) (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/s22103617
Zhang, S., Wen, L., Bian, X., Lei, Z., Li, S.Z.: Occlusion-aware r-cnn: detecting pedestrians in a crowd. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer Vision - ECCV 2018, PT III. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, vol. 11207, pp. 657–674. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01219-9_39 (2018)
Gupta, A., Anpalagan, A., Guan, L., Khwaja, A.S.: Deep learning for object detection and scene perception in self-driving cars: survey, challenges, and open issues. Array 10, 100057 (2021)
Ye, T., Zhao, Z., Wang, S., Zhou, F., Gao, X.: A stable lightweight and adaptive feature enhanced convolution neural network for efficient railway transit object detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23(10), 17952–17965 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3156267
Zheng, H., Liu, H., Qi, W., Xie, H.: Little-yolov4: a lightweight pedestrian detection network based on yolov4 and ghostnet. Wireless Commun. Mobile Comput. 2022 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/5155970
Yun, J., Jiang, D., Liu, Y., Sun, Y., Tao, B., Kong, J., Tian, J., Tong, X., Xu, M., Fang, Z.: Real-time target detection method based on lightweight convolutional neural network. Frontiers Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.861286
Zhang, F., Lv, Z., Zhang, H., Guo, J., Wang, J., Lu, T., Zhangzhong, L.: Verification of improved YOLOX model in detection of greenhouse crop organs: Considering tomato as example. Comput. Electron. Agric. 205, (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2022.107582
Liu, M., Jia, W., Wang, Z., Niu, Y., Yang, X., Ruan, C.: An accurate detection and segmentation model of obscured green fruits. Comput. Electron. Agri. 197 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2022.106984
Yan, B., Fan, P., Lei, X., Liu, Z., Yang, F.: A real-time apple targets detection method for picking robot based on improved yolov5. Remote Sens. 13(9) (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091619
Zhang, Y., Zhang, W., Yu, J., He, L., Chen, J., He, Y.: Complete and accurate holly fruits counting using yolox object detection. Comput. Electron. Agri. 198 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2022.107062
Zhao, F., Wei, R., Chao, Y., Shao, S., Jing, C.: Infrared bird target detection based on temporal variation filtering and a gaussian heat-map perception network. Appl. Sciences-Basel 12(11) (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/app12115679
Zhu, G., Wei, Z., Lin, F.: An object detection method combining multi-level feature fusion and region channel attention. IEEE ACCESS 9, 25101–25109 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3057086
Luo, Y., Cao, X., Zhang, J., Pan, L., Wang, T., Feng, Q.: Multi-scale reinforcement learning strategy for object detection. In: 2022 47th IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Inst Elect & Elect Engineers; Inst Elect & Elect Engineers Signal Proc Soc, Singapore, pp. 2015–2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9746264 (2022)
Priyanka, Baranwal, N., Singh, K.N., Singh, A.K.: Yolo-based roi selection for joint encryption and compression of medical images with reconstruction through super-resolution network. Future Gen. Comput. Syst.(2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2023.08.018
Hsu, W.-Y., Chen, P.-C.: Pedestrian detection using stationary wavelet dilated residual super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Inst. Meas. 71 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2022.3142061
Zhao, J., Guo, W., Zhang, Z., Yu, W.: A coupled convolutional neural network for small and densely clustered ship detection in sar images. Sci. China-Information Sci. 62(4) (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-017-9405-6
Li, K., Cheng, G., Bu, S., You, X.: Rotation-insensitive and context-augmented object detection in remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 56(4), 2337–2348 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2017.2778300
Sun, X., Wang, P., Wang, C., Liu, Y., Fu, K.: Pbnet: part-based convolutional neural network for complex composite object detection in remote sensing imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 173, 50–65 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.12.015
Zhang, D., Zeng, W., Yao, J., Han, J.: Weakly supervised object detection using proposal- and semantic-level relationships. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44(6), 3349–3363 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2020.3046647
Liu, J., Li, S., Zhou, C., Cao, X., Gao, Y., Wang, B.: Sraf-net: a scene-relevant anchor-free object detection network in remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 60 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2021.3124959
Han, J., Liu, S., Qin, G., Zhao, Q., Zhang, H., Li, N.: A local contrast method combined with adaptive background estimation for infrared small target detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 16(9), 1442–1446 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2019.2898893
Wei, J., He, J., Zhou, Y., Chen, K., Tang, Z., Xiong, Z.: Enhanced object detection with deep convolutional neural networks for advanced driving assistance. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 21(4), 1572–1583 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2019.2910643
Li, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, N., Zhang, Z.: Scale-aware trident networks for object detection. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2019). IEEE; IEEE Comp Soc; CVF, Seoul, pp. 6053–6062. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00615 (2019)
Piao, Z., Wang, J., Tang, L., Zhao, B., Zhou, S.: Anchor-free object detection with scale-aware networks for autonomous driving. Electronics 11(20) (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11203303
Sun, S.-G., Park, H.: Segmentation of forward-looking infrared image using fuzzy thresholding and edge detection. Optic. Eng. 40, 2638–2645 (2001)
Liu, M., Chai, Z., Deng, H., Liu, R.: A cnn-transformer network with multiscale context aggregation for fine-grained cropland change detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 15, 4297–4306 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3177235
Shakibania, H., Raoufi, S., Khotanlou, H.: Cdan: convolutional dense attention-guided network for low-light image enhancement (2023). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:261101157
Qi, G., Zhang, Y., Wang, K., Mazur, N., Liu, Y., Malaviya, D.: Small object detection method based on adaptive spatial parallel convolution and fast multi-scale fusion. Remote. Sens. 14, 420 (2022)
Chen, H., Wang, Q., Ruan, W., Zhu, J., Lei, L., Wu, X., Hao, G.: Alfpn: adaptive learning feature pyramid network for small object detection. Int. J. Intell. Syst. (2023)
Dong, R., Pan, X., Li, F.: Denseu-net-based semantic segmentation of objects in urban remote sensing images. IEEE ACCESS 7, 65347–65356 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2917952
Luo, Y., Cao, X., Zhang, J., Cheng, P., Wang, T., Feng, Q.: Dynamic multi-scale loss balance for object detection. In: 2022 47th IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Inst Elect & Elect Engineers; Inst Elect & Elect Engineers Signal Proc Soc, Singapore, pp. 4873–4877. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9747148 (2022)
Cao, K., Wei, C., Gaidon, A., Arechiga, N., Ma, T.: Learning imbalanced datasets with label-distribution-aware margin loss. In: Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Beygelzimer, A., d’Alche-Buc, F., Fox, E., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2019). 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, vol. 32 (2019)
Hu, J., Shen, L., Albanie, S., Sun, G., Wu, E.: Squeeze-and-excitation networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 42(8), 2011–2023 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372
Woo, S., Park, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kweon, I.S.: Cbam: convolutional block attention module. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer vision - ECCV 2018, PT VII. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, vol. 11211, pp. 3–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1 (2018)
Lang, N., Wang, D., Cheng, P.: A learning-based approach for aluminum tube defect detection using imbalanced dataset. Meas. 218, 113018 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2023.113018
Chen, G., Qin, H.: Class-discriminative focal loss for extreme imbalanced multiclass object detection towards autonomous driving. Vis. Comput. 38, 1051–1063 (2021)
Wang, S., Wang, Y., Chang, Y., Zhao, R., She, Y.: Ebse-yolo: high precision recognition algorithm for small target foreign object detection. IEEE Access 11, 57951–57964 (2023)
Cong, P., Lv, K., Feng, H., Zhou, J.: Improved yolov3 model for workpiece stud leakage detection. Electronics 11(21) (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11213430
Phan, T.H., Yamamoto, K.: Resolving class imbalance in object detection with weighted cross entropy losses (2020). arXiv:2006.01413
Wang, X., Wei, J., Liu, Y., Li, J., Zhang, Z., Chen, J., Jiang, B.: Research on morphological detection of fr i and fr ii radio galaxies based on improved yolov5. UNIVERSE 7(7) (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/universe7070211
Duan, K., Du, D., Qi, H., Huang, Q.: Detecting small objects using a channel-aware deconvolutional network. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Vid. Technol. 30, 1639–1652 (2020)
Zeng, Y., Zhang, T., He, W., Zhang, Z.: Yolov7-uav: An unmanned aerial vehicle image object detection algorithm based on improved yolov7. Electronics 12(14) (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12143141
Deng, C., Jing, D., Han, Y., Wang, S., Wang, H.: Far-net: fast anchor refining for arbitrary-oriented object detection. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 19 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1109/LGRS.2022.3144513
Zhu, Y., Seneviratne, L.D.: On the recognition and location of partially occluded objects. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 25, 133–151 (1999)
Sun, J., He, X., Wu, M., Wu, X., Shen, J., Lu, B.: Detection of tomato organs based on convolutional neural network under the overlap and occlusion backgrounds. Mach. Vis. Appl. 31(5) (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-020-01081-6
Zhou, J., Yang, D., Cui, Z., Wang, S., Sheng, H.: Lrfnet: an occlusion robust fusion network for semantic segmentation with light field. In: 2021 IEEE 33RD International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI 2021). Proceedings-International Conference on Tools With Artificial Intelligence. IEEE; IEEE Comp Soc; Biol Artificial Intelligence Fdn, pp. 1178–1186. Electr Network. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTAI52525.2021.00186 (2021)
Sahin, G., Itti, L.: Multi-task occlusion learning for real-time visual object tracking. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Electr network. IEEE; Inst Elect & Elect Engineers Signal Proc Soc, pp. 524–528 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP42928.2021.9506239
Hanson, N., Lvov, G., Padir, T.: Occluded object detection and exposure in cluttered environments with automated hyperspectral anomaly detection. Front. Robot. AI 9 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2022.982131
Deng, B., Lin, M., Long, S.: Object occlusion of adding new categories in objection detection (2022). arXiv:2206.05730
Jiao, Z., Huang, K., Jia, G., Lei, H., Cai, Y., Zhong, Z.: An effective litchi detection method based on edge devices in a complex scene. Biosyst. Eng. 222, 15–28 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2022.07.009
Yang, X., Wu, J., He, L., Ma, S., Hou, Z., Sun, W.: Cpss-fat: a consistent positive sample selection for object detection with full adaptive threshold. Pattern Recognit. 141, 109627 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109627
Zhao, J., Zhu, H., Niu, L.: Bitnet: a lightweight object detection network for real-time classroom behavior recognition with transformer and bi-directional pyramid network. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 35(8), 101670 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2023.101670
Heo, J., Wang, Y., Park, J.: Occlusion-aware spatial attention transformer for occluded object recognition. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 159, 70–76 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2022.05.006
Shang, Q., Zhang, J., Yan, G., Hong, L., Zhang, R., Li, W., Xia, H.: Target tracking algorithm based on occlusion prediction. Displays 79, 102481 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.displa.2023.102481
Sheng, X., Kang, C., Zheng, J., Lyu, C.: An edge-guided method to fruit segmentation in complex environments. Comput. Electro. Agri. 208, 107788 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2023.107788
Xu, C., Lang, W., Xin, R., Mao, K., Jiang, H.: Generative detect for occlusion object based on occlusion generation and feature completing. J. Vis. Commun. Image Repre. 78, 103189 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvcir.2021.103189
Ma, N., Zhang, X., Zheng, H.-T., Sun, J.: Shufflenet v2: practical guidelines for efficient cnn architecture design. In: Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y. (eds.) Computer vision - ECCV 2018, PT XIV. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 11218, pp. 122–138. 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01264-9_8 (2018)
Han, S., Pool, J., Tran, J., Dally, W.J.: Learning both weights and connections for efficient neural networks. In: Cortes, C., Lawrence, N., Lee, D., Sugiyama, M., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28 (NIPS 2015). Advances in neural information processing systems, vol. 28. 29th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Montreal (2015)
Xue, G., Li, S., Hou, P., Gao, S., Tan, R.: Research on lightweight yolo coal gangue detection algorithm based on resnet18 backbone feature network. Int. Things 22, 100762 (2023)
Cui, J., Zheng, H., Zeng, Z., Yang, Y., Ma, R., Tao, N., Tan, J.X., Feng, X., Qi, L.: Real-time missing seedling counting in paddy fields based on lightweight network and tracking-by-detection algorithm. Comput. Electron. Agric. 212, 108045 (2023)
Mahaur, B., Mishra, K.K., Kumar, A.: An improved lightweight small object detection framework applied to real-time autonomous driving. Exp. Syst. Appl. (2023)
Ge, S., Luo, Z., Zhao, S., Jin, X., Zhang, X.-Y.: Compressing deep neural networks for efficient visual inference. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). IEEE, Hong Kong, pp. 667–672 (2017)
Wang, J.: Lightweight and real-time object detection model on edge devices with model quantization. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1748 (2021)
Liqun, C., Lei, H.: Clipping-based neural network post training quantization for object detection. In: 2023 IEEE International Conference on Control, Electronics and Computer Technology (ICCECT), pp 1192–1196 (2023)
Zhang, W., Biswas, G., Zhao, Q., Zhao, H., Feng, W.: Knowledge distilling based model compression and feature learning in fault diagnosis. Appl. Soft Comput. 88 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105958
Wang, W., Su, C., Han, G., Zhang, H.: A lightweight crack segmentation network based on knowledge distillation. J. Building Eng. (2023)
Shang, Y., Xu, X., Jiao, Y., Wang, Z., Hua, Z., Song, H.: Using lightweight deep learning algorithm for real-time detection of apple flowers in natural environments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 207, 107765 (2023)
Zhang, Y., Yang, Y., Sun, J., Zhang, P.P., Ji, R., Shan, H.: Surface defect detection of wind turbine based on lightweight yolov5s model. SSRN Electron. J. (2023)
Zhao, S., Zhang, S., Lu, J., Wang, H., Feng, Y., Shi, C., Li, D., Zhao, R.: A lightweight dead fish detection method based on deformable convolution and yolov4. Comput. Electron. Agric. 198, 107098 (2022)
Bie, M., Liu, Y., Li, G., Hong, J., Li, J.: Real-time vehicle detection algorithm based on a lightweight you-only-look-once (yolov5n-l) approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 213, 119108 (2022)
Park, K., Jang, W., Lee, W., Nam, K., Seong, K., Chai, K., Li, W.-S.: Real-time mask detection on google edge tpu. (2020). arXiv:2010.04427
Zeng, K., Ma, Q., Wu, J.W., Chen, Z., Shen, T., Yan, C.: Fpga-based accelerator for object detection: a comprehensive survey. J. Supercomput. 78(12), 14096–14136 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-022-04415-5
Zhang, F., Li, Y., Ye, Z.: Apply yolov4-tiny on an fpga-based accelerator of convolutional neural network for object detection. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2303 (2022)
Li, W., Hu, H.: Fpga-based object detection acceleration architecture design. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2405 (2022)
Xu, J., Du, W., Jin, Y., He, W., Cheng, R.: Ternary compression for communication-efficient federated learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 33(3), 1162–1176 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3041185
Liang, J., Zhang, Y., Xue, J., Hu, Y.: Lightweight image super-resolution network using involution. Mach. Vis. Appl. 33(5) (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-022-01307-9
Zhong, X., Wang, M., Liu, W., Yuan, J., Huang, W.: Scpnet: self-constrained parallelism network for keypoint-based lightweight object detection. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 90, 103719 (2022)
Zhang, T., Pan, Y.: Real-time detection of a camouflaged object in unstructured scenarios based on hierarchical aggregated attention lightweight network. Adv. Eng. Inf. (2023)
Huang, J., Chen, J., Wang, H.: A lightweight and efficient one-stage detection framework. Comput. Electr. Eng. 105, 108520 (2023)
Xu, H., Li, B., Zhong, F.: Light-yolov5: a lightweight algorithm for improved yolov5 in complex fire scenarios (2022). arXiv:2208.13422
Wang, Z., Jin, L., Wang, S., Xu, H.: Apple stem/calyx real-time recognition using yolo-v5 algorithm for fruit automatic loading system. Postharvest Bio. Technol. (2022)
Hou, Z., Kung, S.Y.: Parameter efficient dynamic convolution via tensor decomposition. In: British Machine Vision Conference (2021). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:249892686
Li, Y., Shi, Z., Liu, C., Tian, W., Kong, Z.J., Williams, C.B.: Augmented time regularized generative adversarial network (atr-gan) for data augmentation in online process anomaly detection. IEEE Trans. Auto. Sci. Eng. 19, 3338–3355 (2022)
Malialis, K., Papatheodoulou, D., Filippou, S., Panayiotou, C.G., Polycarpou, M.M.: Data augmentation on-the-fly and active learning in data stream classification. In: 2022 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), pp. 1408–1414 (2022)
Regulariza, B., Uddin, A.F.M.S., Monira, S., Shin, W., Chung, T., Bae, S.-H.: Saliencymix: a saliency guided data augmentation strategy for better regularization (2020). arXiv:2006.01791
Choi, H.K., Choi, J., Kim, H.J.: Tokenmixup: efficient attention-guided token-level data augmentation for transformers (2022). arXiv:2210.07562
Han, K., Wang, Y., Tian, Q., Guo, J., Xu, C., Xu, C.: Ghostnet: more features from cheap operations. In: 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1577–1586 (2019)
Srinivas, A., Lin, T.-Y., Parmar, N., Shlens, J., Abbeel, P., Vaswani, A.: Bottleneck transformers for visual recognition. In: 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 16514–16524 (2021)
Liang, T., Chu, X., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Tang, Z., Chu, W., Chen, J., Ling, H.: Cbnet: a composite backbone network architecture for object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 31, 6893–6906 (2021)
Jiang, Y., Tan, Z., Wang, J., Sun, X., Lin, M., Li, H.: Giraffedet: a heavy-neck paradigm for object detection (2022). arXiv:2202.04256
Lee, Y., Kim, J., Willette, J., Hwang, S.J.: Mpvit: multi-path vision transformer for dense prediction. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7277–7286 (2021)
Ghiasi, G., Lin, T.-Y., Pang, R., Le, Q.V.: Nas-fpn: learning scalable feature pyramid architecture for object detection. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7029–7038 (2019)
Park, H.-J., Choi, Y.J., Lee, Y.-W., Kim, B.-G.: ssfpn: scale sequence (s2) feature-based feature pyramid network for object detection. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 23 (2022)
Liu, Z., Cheng, J.: Cb-fpn: object detection feature pyramid network based on context information and bidirectional efficient fusion. Pattern Anal. Appl. 26, 1441–1452 (2023)
Hou, Q., Zhou, D., Feng, J.: Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 13708–13717 (2021)
Sagar, A.: Dmsanet: dual multi scale attention network (2021). arXiv:2106.08382
Cao, J., Chen, Q., Guo, J., Shi, R.: Attention-guided context feature pyramid network for object detection (2020). arXiv:2005.11475
Li, Z., Lang, C., Liang, L., Zhao, J., Feng, S., Hou, Q., Feng, J.: Dense attentive feature enhancement for salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. Vid. Technol. 32, 8128–8141 (2021)
Gevorgyan, Z.: Siou loss: more powerful learning for bounding box regression (2022). arXiv:2205.12740
Oksuz, K., Cam, B.C., Akbas, E., Kalkan, S.: Rank & sort loss for object detection and instance segmentation. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 2989–2998 (2021)
Wang, J., Xu, C., Yang, W., Yu, L.: A normalized gaussian wasserstein distance for tiny object detection (2021). arXiv:2110.13389
He, J., Erfani, S.M., Ma, X., Bailey, J., Chi, Y., Hua, X.: Alpha-iou: a family of power intersection over union losses for bounding box regression (2021). arXiv:2110.13675
Chen, D., Miao, D.: Control distance iou and control distance iou loss function for better bounding box regression (2021). arXiv:2103.11696
Dai, J., Qi, H., Xiong, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, G., Hu, H., Wei, Y.: Deformable convolutional networks. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 764–773 (2017)
Yu, F., Koltun, V.: Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions (2015). arXiv:1511.07122
Chen, J., Kao, S.-h., He, H., Zhuo, W., Wen, S., Lee, C.-H., Chan, S.-H.G.: Run, don’t walk: chasing higher flops for faster neural networks. 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 12021–12031 (2023)
Park, H.-J., Choi, Y.J., Lee, Y.-W., Kim, B.-G.: ssfpn: scale sequence (s2) feature-based feature pyramid network for object detection. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 23 (2022)
Zhang, H., Li, F., Liu, S., Zhang, L., Su, H., Zhu, J.-J., Ni, L.M.-s., Shum, H.-y.: Dino: Detr with improved denoising anchor boxes for end-to-end object detection (2022). arXiv:2203.03605
Zand, M., Etemad, A., Greenspan, M.A.: Objectbox: From centers to boxes for anchor-free object detection. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (2022). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:250526817
Kim, K.-j., Lee, H.S.: Probabilistic anchor assignment with iou prediction for object detection (2020). arXiv:2007.08103
Liu, Y.-C., Ma, C.-Y., Kira, Z.: Unbiased teacher v2: semi-supervised object detection for anchor-free and anchor-based detectors. 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 9809–9818 (2022)
Dai, X., Chen, Y., Xiao, B., Chen, D., Liu, M., Yuan, L., Zhang, L.: Dynamic head: unifying object detection heads with attentions. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 7369–7378 (2021)
Zhu, X., Lyu, S., Wang, X., Zhao, Q.: Tph-yolov5: improved yolov5 based on transformer prediction head for object detection on drone-captured scenarios. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), pp. 2778–2788 (2021)
Wu, Y., Chen, Y., Yuan, L., Liu, Z., Wang, L., Li, H., Fu, Y.R.: Rethinking classification and localization for object detection. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 10183–10192 (2019)
Baidya, R., Jeong, H.-J.: Yolov5 with convmixer prediction heads for precise object detection in drone imagery. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 22 (2022)
Solovyev, R.A., Wang, W., Gabruseva, T.: Weighted boxes fusion: ensembling boxes from different object detection models. Image Vis. Comput. 107, 104117 (2021)
Bodla, N., Singh, B., Chellappa, R., Davis, L.S.: Soft-nms - improving object detection with one line of code. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 5562–5570 (2017)
Zhao, H., Wang, J.-K., Dai, D., Lin, S., Chen, Z.: D-nms: a dynamic nms network for general object detection. Neurocomput. 512, 225–234 (2022)
Liu, L., Hirakawa, T., Yamashita, T., Fujiyoshi, H.: Class-wise fm-nms for knowledge distillation of object detection. 2022 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 1641–1645 (2022)
Mantovani, R.G., Horváth, T., Cerri, R., Junior, S.B., Vanschoren, J., Carvalho, A.C.P.: An empirical study on hyperparameter tuning of decision trees (2018). arXiv:1812.02207
Duarte, E., Wainer, J.: Empirical comparison of cross-validation and internal metrics for tuning svm hyperparameters. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 88, 6–11 (2017)
Zhou, Y., Cahya, S., Combs, S.A., Nicolaou, C.A., Wang, J.-B., Desai, P.V., Shen, J.: Exploring tunable hyperparameters for deep neural networks with industrial adme data sets. J. Chem. Inf. Model 59(3), 1005–1016 (2018)
Probst, P.: Hyperparameters, tuning and meta-learning for random forest and other machine learning algorithms. (2019). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:201710457
Goyal, P., Dollár, P., Girshick, R.B., Noordhuis, P., Wesolowski, L., Kyrola, A., Tulloch, A., Jia, Y., He, K.: Accurate, large minibatch sgd: training imagenet in 1 hour (2017). arXiv:1706.02677
Kingma, D.P., Ba, J.: Adam: a method for stochastic optimization (2014). arXiv:1412.6980
Zhuang, J., Tang, T.M., Ding, Y., Tatikonda, S.C., Dvornek, N.C., Papademetris, X., Duncan, J.S.: Adabelief optimizer: adapting stepsizes by the belief in observed gradients (2020). arXiv:2010.07468
Isa, I.S., Rosli, M.S.A., Yusof, U.K., Maruzuki, M.I.F., Sulaiman, S.N.: Optimizing the hyperparameter tuning of yolov5 for underwater detection. IEEE Access 10, 52818–52831 (2022)
Kingma, D.P., Salimans, T., Welling, M.: Variational dropout and the local reparameterization trick. In: NIPS (2015). https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:46343823
Mobiny, A., Nguyen, H.V., Moulik, S., Garg, N., Wu, C.C.: Dropconnect is effective in modeling uncertainty of bayesian deep networks. Scientific Reports 11 (2019)
Bouthillier, X., Delaunay, P., Bronzi, M., Trofimov, A., Nichyporuk, B., Szeto, J., Sepah, N., Raff, E., Madan, K., Voleti, V.S., Kahou, S.E., Michalski, V., Serdyuk, D., Arbel, T., Pal, C., Varoquaux, G., Vincent, P.: Accounting for variance in machine learning benchmarks (2021). arXiv:2103.03098
Takenaga, S., Watanabe, S., Nomura, M., Ozaki, Y., Onishi, M., Habe, H.: Evaluating initialization of nelder-mead method for hyperparameter optimization in deep learning. 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 3372–3379 (2021)
Yin, Y., Zhang, G.: Object detection based on multiple trick feature pyramid networks and dynamic balanced l1 loss. Int. J. Wirel. Mob. Comput. 22, 93–103 (2022)
Li, T., Shu, X., Chen, G., Wang, Y.: Size-sensitive optimization of loss function on vision-based object detection. Proceedings of the 2021 5th International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Computer Engineering (2021)
Zhang, Y.Y., Wang, H., Lv, X., Zhang, P.: Capturing the grouping and compactness of high-level semantic feature for saliency detection. Neural Netw. 142, 351–362 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2021.04.028
Rao, Y., Mu, H., Yang, Z., Zheng, W., Wang, F., Pu, J., Zeng, S.: B-pesnet: smoothly propagating semantics for robust and reliable multi-scale object detection for secure systems. CMES-Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 132(3), 1039–1054 (2022). https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2022.020331
Rao, Y., Mu, H., Yang, Z., Zheng, W., Wang, F., Pu, J., Zeng, S.: B-pesnet: smoothly propagating semantics for robust and reliable multi-scale object detection for secure systems. CMES-Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 132(3), 1039–1054 (2022). https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2022.020331
Li, J., Zhu, Z., Liu, H., Su, Y., Deng, L.: Strawberry r-cnn: Recognition and counting model of strawberry based on improved faster r-cnn. Eco. Inf. 77 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2023.102210
Zhang, Y., Sung, Y.: Traffic accident detection using background subtraction and cnn encoder-transformer decoder in video frames. Math. 11(13) (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/math11132884
Li, C.-j., Qu, Z., Wang, S.-y.: A method of knowledge distillation based on feature fusion and attention mechanism for complex traffic scenes. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intelli. 124 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106533
Zeng, Y., Zhang, T., He, W., Zhang, Z.: Yolov7-uav: an unmanned aerial vehicle image object detection algorithm based on improved yolov7. Electronics 12(14) (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12143141
Wang, T., Wang, J., Wang, R.: Camouflaged object detection with a feature lateral connection network. Electronics 12(12) (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122570
Yi, C., Liu, J., Huang, T., Xiao, H., Guan, H.: An efficient method of pavement distress detection based on improved yolov7. Meas. Sci. Technol. 34(11) (2023). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6501/ace929
Shen, J., Zhou, Y.: Accurate and real-time object detection in crowded indoor spaces based on the fusion of dbscan algorithm and improved yolov4-tiny network. J. Intell. Syste. 32(1) (2023). https://doi.org/10.1515/jisys-2022-0268
Nag, S., Bhattacharyya, M., Mukherjee, A., Kundu, R.: Serf: towards better training of deep neural networks using log-softplus error activation function. In: 2023 23rd IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). IEEE; CVF; IEEE Comp Soc, Waikoloa, pp. 5313–5322. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00529 (2023)
Devries, T., Taylor, G.W.: Improved regularization of convolutional neural networks with cutout (2017). arXiv:1708.04552
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Shandong Province Science and Technology Small and Medium-sized Enterprise Innovation Capability Improvement Project, “Research and Development of Intelligent Aluminum Alloy Casting Production System”(Grant No. 2022TSGC2051).Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation, “Real-time Reconstruction of Physical 3D Model of Colon Based on Active Flexible Endoscope”(Grant No. ZR2020ME116).Shandong Province Key Support Area Introduction of Urgently Needed and Scarce Talents Project, “Research and Industrialization of Intelligent Loading System for Smart Mines”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jinwei Qiao made primary contributions to the conception or design of the work. Kaiguo Geng made optimization of the concept reconsideration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Approval was obtained from the ethics committee of the Qilu University of Technology.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
The participant has consented to the submission of the research manuscript to the journal.
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, K., Qiao, J., Liu, N. et al. Research on Real-time Detection of Stacked Objects Based on Deep Learning. J Intell Robot Syst 109, 82 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-023-02009-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-023-02009-8