Abstract
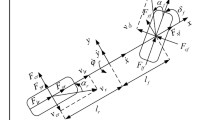
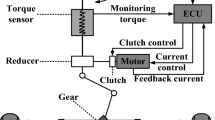
With the continuous advancement of electric vehicles and smart internet technologies, ensuring vehicle safety through electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing in complex electromagnetic environments has become increasingly critical. However, due to the significant variability in vehicle response characteristics under electromagnetic interference, traditional PID control methods for steering robots struggle to meet the high-precision requirements of such tests. In this study, a novel fuzzy PID parameter self-tuning method is proposed, leveraging a Sparrow Search Algorithm-Back Propagation (SSA-BP) neural network. This method optimizes the fuzzy controller's quantization factor by constructing a neural network system where the expected motor angle serves as the input and the quantization factor as the output. The quantization factor is then calibrated online through iterative training.The proposed approach enables the steering robot to achieve real-time, adaptive tuning of the PID parameters for the drive motor by adjusting the steering torque according to different vehicle characteristics, thereby enhancing the robot's anti-interference capability and robustness in EMC testing. The effectiveness of this method is validated through Matlab/Simulink simulations, experiments conducted on the Sensodrive platform, and tests performed in an EMC anechoic chamber. The results indicate that the method offers substantial improvements in control accuracy and anti-interference capabilities, highlighting its strong potential for practical application.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Data Availability
The data are not publicly available due to their containing information that could compromise the privacy of research participants.
References
Petrauskien, K., Tverskyt, R., Dvarionien, J.: Environmental and economic benefits of electric, hybrid and conventional vehicle treatment: A case study of Lithuania. Waste Manag. 140, 55–62 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2022.01.009
GB 17675–2021, Steering system of motor vehicles—Basic requirements[S].
GB 34660–2017, Road vehicles—Requirements and test methods of electromagnetic compatibility[S].
A.P.J.: Intelligent Control, American Cancer Society (1999).
X. Y. L i Shaoyuan, Chen Zengqiang, Yuan Zhuzhi, The New Progresses in Intelligent Control ((I) . Control and Decision. (2000). https://doi.org/10.13195/j.cd.2000.01.1.lishy.001.
Wang, J.G., Wang, Y.J., Wan S.Y.: PID parameter self-tuning and real-time control based on dynamic neural network. Syst Eng Electron (2004). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/21/5/051
Xie, W., Duan, J.: The Design and Simulation of Fuzzy PID Parameter Self-tuning Controller. TELKOMNIKA Indonesian J. Electr. Eng. 14, (2015). https://doi.org/10.11591/telkomnika.v14i2.7674
Yuan, T., Guo, G., Du, B., et al.: The adaptive sliding mode control using improved genetic algorithm tuning PID controller for the planetary rover. Aircraft Eng. Aerospace Technol. ahead-of-print, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1108/AEAT-05-2019-0096
Wang, X., Bian, S.: PID Parameters Self-tuning Based on Genetic Algorithm and Neural Network. J. Jilin Univ. Sci. Ed. 56, 953–958 (2018). https://doi.org/10.13413/j.cnki.jdxblxb.2018.04.30
Peng, Y., Changfeng, X., Jun, Z., et al.: Research on Improved Anti-Interference Fuzzy PID of AGV Control System. Mach. Des. Manufact. 212–216 (2023). https://doi.org/10.19356/j.cnki.1001-3997.2023.03.022
Hang, Y., Ling, L., Junkang, M., et al.: An Adaptive BP Neural Network Algorithm for 2-Joint Rigid Robots. J. XI’AN Jiaotong Univ. 52, 8 (2018). https://doi.org/10.7652/xjtuxb201801019
Yangyang, X., Ying, W., Dongbin, X.: Research on motion error of mobile robot controlled by improved fuzzy neural network PID. Chi. J. Constr. Mach. 510–514 (2019). https://doi.org/10.15999/j.cnki.311926.2019.06.008.
Lang, T.: Research on the design and control strategy of rope-driven snake robot Nanjing, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology (2021)
Feng, J., Zhang, W., Ni, H., et al.: Trajectory Tracking Control of Wheeled Mobile Robots Using PID Control Method. Inf. Control. 46, 385–393 (2017). https://doi.org/10.13976/j.cnki.xk.2017.0385
Das, M.S., Samanta, A., Sanyal, S., et al.: AKH-NFIS: Adaptive Krill Herd Network Fuzzy Inference System for Mobile Robot Navigation. Wireless Personal Commun. 120, 3389–3413 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08619-5
Wan, H., Luan, X., Stojanovic, V., et al.: Self-triggered finite-time control for discrete-time Markov jump systems. Inf. Sci. 634, 101–121 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2023.03.070
Song, X., Wu, C., Song, S., et al.: Fuzzy wavelet neural adaptive finite-time self-triggered fault-tolerant control for a quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle with scheduled performance. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 131, 107832 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107832
Yu, H., Wang, J., Xin, Z.: Model Predictive Control for PMSM Based on Discrete Space Vector Modulation with RLS Parameter Identification. Energies. 15, (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/en15114041
Yumei, Q., Jinwen, Z.: Design of Direct Torque Control System for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. 2023 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electronic Technology, Commun. Inf. (ICETCI). 58–61 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICETCI57876.2023.10176731
Xie, F., Hong, W., Qiu, C.: Speed fluctuation suppression of PMSM using active disturbance rejection and feedback compensation control. IET Electr. Power Appl. 15, (2021). https://doi.org/10.1049/elp2.12079
Dogruer, T., Can, M.S.: Design and robustness analysis of fuzzy PID controller for automatic voltage regulator system using genetic algorithm. Transact. Inst. Meas. Control. 44, 1862–1873 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1177/01423312211066758
Toumi, D., Mihoub, Y., Hassaine, S. et al.: Design and implementation of adaptive fuzzy‐RST digital speed control of PMSM drive. Asian Journal of Control: Affiliated with ACPA, the Asian Control Professors Association. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1002/asjc.2683
Wang, G., Zhang, H.: A Second-order Sliding Mode Observer Optimized by Neural Network for Speed and Position Estimation of PMSMs. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 17, 415–423 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-021-00892-5
Xin, J., Chen, J., Li, C., et al.: Deformation characterization of oil and gas pipeline by ACM technique based on SSA-BP neural network model. Meas. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110654
Chaabane, S.B., Belazi, A., Kharbech, S. et al.: Improved Salp Swarm Optimization Algorithm: Application in Feature Weighting for Blind Modulation Identification. Electronics. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10162002
Zhai, Y., Li, W.: SSA-BP network model based Hong-Ou-Mandel interference delay measurement and its application in quantum gyroscope. Acta Physica Sinica. 72, (2023). https://doi.org/10.7498/aps.72.20230283
Funding
This work was supported by [the National Key Research and Development Program of China] (Grant numbers [No. 2022YFB4701104]), [Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province of China] (Grant numbers [No. F2021202062]) and [National Natural Science Foundation of China] (Grant numbers [No. U1913211]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by [Xuan Liu], [Yuzhe Xing],[Yuqing Liu] and [Yuan Wan]. The first draft of the manuscript was written by [Yuzhe Xing] and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Xuan Liu made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work. Yuzhe Xing drafted the work or revised it critically for important intellectual content. Yuqing Liu analyzed and processed data. Yuan Wan agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This is an observational study. This Research Ethics Committee has confirmed that no ethical approval is required.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to Publish
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the images in Figure(s) 13, 16,17,18 and 20.
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Project supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2022YFB4701104),Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province of China (No. F2021202062), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1913211).
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Xing, Y., Liu, Y. et al. Study on Self-tuning of Robot Parameters for EMC Vehicle Steering Test. J Intell Robot Syst 110, 170 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-024-02200-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10846-024-02200-5