Abstract
This paper deals with restricting curve evolution to a finite and not necessarily flat space of curves, obtained as a subspace of the infinite dimensional space of planar curves endowed with the usual but weak parametrization invariant curve L 2-metric.
We first show how to solve differential equations on a finite dimensional Riemannian manifold defined implicitly as a submanifold of a parameterized one, which in turn may be a Riemannian submanifold of an infinite dimensional one, using some optimal control techniques.
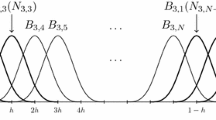
We give an elementary example of the technique on a spherical submanifold of a 3-sphere and then a series of examples on a highly non-linear subspace of the space of closed spline curves, where we have restricted mean curvature motion, Geodesic Active contours and compute geodesic between two curves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kass, M., Witkin, A., Terzopoulos, D.: Snakes: active contour models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 321–331 (1987)
Sethian, J.A.: Level Set Methods, 1st edn. Cambridge Monograph on Applied and Computational Mathematics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1996)
Kimmel, R.: Numerical Geometry of Images, Theory, Algorithms and Applications, 1st edn. Springer, New York (2004). Department of Computer Science, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa 32000, Israel
Blake, A., Isard, M.: Active Contours. Springer, Berlin (1998)
Epstein, C.L., Gage, M.: The curve shortening flow. In: Wave Motion: Theory, Modeling and Computation. Springer, New York (1987)
Yezzi, A.J., Mennucci, A.: Metrics in the space of curves. Technical Report (2005). arXiv:math.DG/0412454
Charpiat, G., Keriven, R., Pons, J., Faugeras, O.: Designing spatially coherent minimizing flows for variational problems based on active contours. In: Tenthf ICCV, vol. 2, Beijing, China. IEEE, New York, pp. 1403–1408 (2005)
Caselles, V., Kimmel, R., Sapiro, G.: Geodesic active contours. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 22, 61–79 (1997)
Sundaramoorthi, G., Yezzi, A., Mennucci, A.C.: Sobolev active contours. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 73, 345–366 (2007)
Charpiat, G., Maurel, P., Pons, J.P., Keriven, R., Faugeras, O.: Generalized gradients: priors on minimization flows. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 73, 325–344 (2007)
Michor, P.W., Mumford, D.: Riemannian geometries on spaces of plane curves. J. Eur. Math. Soc. 8, 1–48 (2006)
Sundaramoorthi, G., Mennucci, A., Soatto, S., Yezzi, A.: Tracking deforming objects by filtering and prediction in the space of curves. CDC (2009)
Glaunés, J., Qui, A., Miller, M.I.: Large deformation diffeomorphic metric curve mapping. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 80, 317–336 (2008)
Miller, M.I., Younes, L.: Group actions, homeomorphisms, and matching: a Cambridge general framework. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 41, 61–84 (2001)
Younes, L.: Computable elastic distances between shapes. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 58, 565–586 (1998)
Micheli, M.: The differential geometry of landmark shape manifolds: metrics, geodesics and curvature. PhD thesis, Brown University, Providence, Rhodes Island (2008)
Unal, G., Yezzi, A., Krim, H.: Information-theoretic active polygons for unsupervised texture segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 62, 199–220 (2005)
Srivastava, A., Mio, W., Klassen, E., Liu, X.: Geometric analysis of constrained curves for image understanding. In: Proc. 2nd IEEE International Workshop on Variational, Geometric and Level-Set Methods in Computer Vision (VLSM) (2003)
Tatu, A., Lauze, F., Nielsen, M., Olsen, O.F.: Curve evolution in subspaces. In: Scale Space and Variational Methods in Computer Vision (2007)
Hairer, E.: Geometric integration of ordinary differential equations on manifolds. BIT Numer. Math. 41, 996–1007 (2001)
do Carmo, M.P.: Riemannian Geometry. Mathematics: Theory and Applications. Birkhäuser, Basel (1992)
Luenberger, D.G.: Optimization by Vector Space Methods. Wiley, New York (1969)
Pontryagin, L.S., Boltyanskii, V.G., Gamkrelidze, R.V., Mishchenko, E.F.: The Mathematical Theory of Optimal Processes. Interscience, New York (1962)
Kamien, M.I., Schwartz, N.L.: Dynamic Optimization: The Calculus of Variations and Optimal Control in Economics and Management. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1991)
Dedieu, J.P., Nowicki, D.: Symplectic methods for the approximation of the exponential map and the newton iteration on Riemannian submanifolds. J. Complex. 21, 487–501 (2005)
Gallot, S., Hulin, D., Lafontaine, J.: Riemannian Geometry, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin (2004)
Kamaraj, K., Sivakumar, K.C.: Moore-penrose inverse in an indefinite inner product space. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 19, 297–310 (2005)
Keller, H.B.: Numerical Methods for Two-Point Boundary-Value Problems. Blaisdell, Waltham (1968)
Keller, H.B.: Numerical Solution of Two Point Boundary Problems. CBMF-NSF Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics, vol. 24. SIAM, Philadelphia (1976)
Lee, J.M.: Riemannian Manifolds: An Introduction to Curvature. Springer, Berlin (1997)
Unser, M.: Splines: a perfect fit for signal and image processing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. (1999)
Unser, M., Aldroubi, A., Eden, M.: B-spline signal processing: Part 1—theory. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 41, 821–832 (1993)
Unser, M., Aldroubi, A., Eden, M.: B-spline signal processing: Part 2—efficient design and applications. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 41, 834–848 (1993)
Sommer, S., Tatu, A., Chen, C., de Bruijne, M., Loog, M., Jorgensen, D., Nielsen, M., Lauze, F.: Bicycle chain shape models. In: CVPR Workshop on Mathematical Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis (2009)
Grayson, M.A.: The heat equation shrinks embedded plane curves to round points. J. Differ. Geom. 26 (1987)
Aubert, G., Kornprobst, P.: Mathematical Problems in Image Processing. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tatu, A., Lauze, F., Sommer, S. et al. On Restricting Planar Curve Evolution to Finite Dimensional Implicit Subspaces with Non-Euclidean Metric. J Math Imaging Vis 38, 226–240 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-010-0218-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-010-0218-2