Abstract
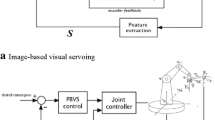
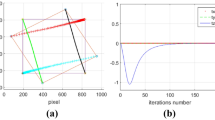
We build and test a Visual Servoing for all degrees of freedom of a legged robot. We provide a detailed geometrical description relevant to the construction of the Jacobian matrix containing the dependencies of the visual features on the robot joint angles. This matrix embodies the forward kinematics model. To obtain an autonomous control system invariant to world position, we define the ground reference system relative to the basic support points. The control of the robot is computed by the inversion of the forward kinematics model, with two corrections. First, to preserve the ground reference system we must correct the motion of the supporting points. Second, we test a stability condition to avoid the robot to move into unstable configurations. We have tested the approach on a controlled environment to assess its real life performance. The experimental results show the robustness of the approach.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altendorfer, R., Koditschek, D.E., Holmes, P.: Towards a factored analysis of legged locomotion models. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, 2003. Proceedings ICRA ’03, vol. 1, pp. 37–44 (2003)
Bretl, T., Lall, S.: Testing static equilibrium for legged robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 24(4), 794–807 (2008)
Chalup, S.K., Murch, C.L., Quinlan, M.J.: Machine learning with Aibo robots in the four-legged league of RoboCup. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., Part C, Appl. Rev. 37(3), 297–310 (2007)
Cherubini, A., Giannone, F., Iocchi, L., Nardi, D., Palamara, P.F.: Policy gradient learning for quadruped soccer robots. Robot. Auton. Syst. 58(7), 872–8787 (2010)
Colombo, C., Kruse, E., Sabatini, A.M., Dario, P.: Vision-based relative positioning through active fixation and contour tracking. In: Proceedings 2nd International Symp. on Intelligent Robotic Systems, SIRS’94, Grenoble, France, July, pp. 319–325 (1994)
Corke, P.: Visual Control of Robot Manipulators—A Review. Robotics and Automated Systems, vol. 7, pp. 1–31. World Scientific, Singapore (1993)
Sony Corporation: OPEN-R SDK model information for ERS-7 (2003)
Coste-Manière, E., Couvignou, P., Khosla, P.K.: Visual servoing in the task-function framework: a contour following task. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 12(1), 1–21 (1995)
Deakin, G.J.: Legged robots. Prod. Eng. 64(9), 8 (1985)
Echegoyen, Z., d’Anjou, A., Graña, M.: Contribution to legged robot visual servoing. In: Apolloni, B., Howlett, R.J., Jain, L. (eds.) Knowledge-Based Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems, KES 2007. LNAI, vol. 4693, pp. 1179–1186. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Echegoyen, Z., d’Anjou, A., Graña, M.: Modeling a legged robot for visual servoing. In: Gervasi, O., Gavrilova, M.L. (eds.) Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2007. LNCS, vol. 4707, pp. 798–810. Springer, Berlin (2007)
Espiau, B., Chaumette, F., Rives, P.: A new approach to visual servoing in robotics. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 8, 313–326 (1992)
Go, Y., Xiaolei, Y., Bowling, A.: Navigability of multi-legged robots. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 11(1), 1–8 (2006)
Graña, M., Torrealdea, F.J.: Hierarchically structured systems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 25, 20–26 (1986)
Hager, G.: The “xvision” system: a general purpose substrate for real-time vision-based robotics. In: Proceedings of the Workshop on Vision for Robotics, pp. 56–63 (1995)
Hill, J., Park, W.T.: Real-time control of a robot with a mobile camera. In: Proceedings of the 9th ISIR, Washington, DC, March, pp. 233–246 (1979)
Hoff, J., Bekey, G.A.: A cerebellar approach to adaptive locomotion for legged robots. In: 1997 IEEE International Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Robotics and Automation, CIRA’97 Proceedings, July, pp. 94–100 (1997)
Hornby, G.S., Takamura, S., Yamamoto, T., Fujita, M.: Autonomous evolution of dynamic gaits with two quadruped robots. IEEE Trans. Robot. 21(3), 402–410 (2005)
Hosoda, K., Kamado, M., Asada, M.: Vision-based servoing control for legged robots. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, vol. 4, pp. 3154–3159 (1997)
Hosoda, K., Miyashita, T., Takeuchi, S., Asada, M.: Adaptive visual servoing for legged robots-vision-cued swaying oflegged robots in unknown environments. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, vol. 2, pp. 778–784 (1997)
Hutchinson, S., Hager, G.D., Corke, P.I.: A tutorial on visual servo control. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 12(5), 651–670 (1996)
Kitano, H., Fujita, M., Zrehen, S., Kageyama, K.: Sony legged robot for RoboCup challenge. In: 1998 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Proceedings, May, vol. 3, pp. 2605–2612 (1998)
Krasny, D.P., Orin, D.E.: Generating high-speed dynamic running gaits in a quadruped robot using an evolutionary search. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., Part B, Cybern. 34(4), 1685–1696 (2004)
Prajoux, R., de Martins, L.S.F.: A walk supervisor architecture for autonomous four-legged robots embedding real-time decision-making. In: Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems ’96, IROS 96, November, vol. 1, pp. 200–207 (1996)
Quinlan, M., Murch, C., Moore, T., Middleton, R., Li, L., King, R., Chalup, S.: The 2004 nubots team report. Technical report (2004)
Raibert, M.H., Tello, E.R.: Legged robots that balance. IEEE Expert 1(4), 89–89 (1986)
Rives, P., Chaumette, F., Espiau, B.: Visual servoing based on a task function approach. In: Experimental Robotics I, Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Experimental Robotics, Montreal, Canada, June, pp. 412–428 (1990)
Rosen, C., Nitzan, D., Agin, G., Bavarsky, A., Gleason, G., Hill, J., McGhie, D., Park, W.: Machine intelligence research applied to industrial automation. Technical Report NSF Grant APR-75-13074, SRI Project 4391, 6th Report, SRI International, Menlo Park, CA, November 1976
Rosen, C., Nitzan, D., Agin, G., Bavarsky, A., Gleason, G., Hill, J., McGhie, D., Park, W.: Machine intelligence research applied to industrial automation. Technical report, 8th Report, SRI International, August 1978
Röfer, Th., Burkhard, H.-D., Düert, U., Homann, J., Göhring, D., Jüngel, M., Lötzsch, M., v. Stryk, O., Brunn, R., Kallnik, M., Kunz, M., Petters, S., Risler, M., Stelzer, M., Dahm, I., Wachter, M., Engel, K., Osterhues, A., Schumann, C., Ziegler, J.: Germanteam robocup 2003. Technical report, http://www.robocup.de/germanteam/GT2003.pdf, 2003
Samson, C., Le Borgne, M., Espiau, B.: Robot control: the task function approach. In: Oxford Engineering Science Series, vol. 22, 1st edn. Clarendon Press, Oxford University Press, Oxford (1991)
Sanderson, A.C., Weiss, L.E.: Image-based visual servo control using relational graph error signals. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Cybernetics and Society, vol. 1, pp. 1074–1077 (1980)
Shirai, Y., Inoue, H.: Guiding a robot by visual feedback in assembling tasks. Pattern Recognit. 5(2), 99–108 (1973)
Tira-Thompson, E.J.: Tekkotsu: A rapid development framework for robotics. Master’s thesis, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA (2004)
Veloso, M., Uther, W., Fijita, M., Asada, M., Kitano, H.: Playing soccer with legged robots. In: 1998 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Proceedings, October, vol. 1, pp. 437–442 (1998)
Weiss, L.E.: Dynamic visual servo control of robots: an adaptive image-based approach. PhD thesis, Carnegie-Mellon University, April 1984
Wichman, W.M.: Use of optical feedback in the computer control of an arm. Technical report, Standford AI project, AI memo 55, August 1967
Yang, J.-M.: Fault-tolerant gaits of quadruped robots for locked joint failures. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., Part C, Appl. Rev. 32(4), 507–516 (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Echegoyen, Z., Lopez-Guede, J.M., Fernandez-Gauna, B. et al. Visual Servoing of Legged Robots. J Math Imaging Vis 42, 196–211 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-011-0286-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-011-0286-y