Abstract
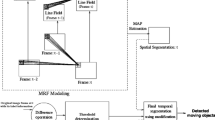
In this paper, a novel method for locating multiple moving objects in a video sequences captured by a stationary camera is proposed. In order to determine the precise location of the objects in an image, a new local regions based level set model is carried out. The whole process consists of two main parts: the global detection and the fine localization. During the global detection, the presence or absence of an object in an image is determined by the Mixture of Gaussians method. For the fine localization, we propose to reformulate global energies by utilizing little squared windows centered on each point over a thin band surrounding the zero level set, hence the object contour can be reshaped into small local interior and exterior regions that lead to compute a family of adaptive local energies, which enables us to well localize the moving objects. Moreover, we propose to adapt the smoothness of the contours, and the accuracy of the objects’ perimeter of different shapes with an automatic stopping criterion. The proposed method has been tested on different real urban traffic videos, and the experiment results demonstrate that our algorithm can locate effectively and accurately the moving objects; optimize the results of the localized objects and also decrease the computations load.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CFL::
-
Courant-Friedrichs-Lewy
- CV::
-
Chan-Vese
- MoG::
-
Mixture of Gaussians
- PC::
-
Piecewise Constant
- PS::
-
Piecewise Smooth
- SDF::
-
Signed Distance Function
References
Paragios, N., Tziritas, G.: Adaptive detection and localisation of moving objects in image sequences. Signal Process. Image Commun. 14(4), 277–296 (1999)
Sifakis, E., Tziritas, G.: Moving object localisation using a multi-label fast marching algorithm. Signal Process. Image Commun. 16(10), 963–976 (2001)
Jong Ryul, K., Young Shik, M.: Automatic localization and tracking of moving objects using adaptive snake algorithm. In: IEEE Proc., Information, Communications and Signal Processing, pp. 729–733 (2003)
Sifakis, E., Tziritas, G.: Robust object boundary determination using a locally adaptive level set algorithm. In: IEEE Proc., Image Processing, pp. 141–144 (2003)
Agarwal, S., Awan, A., Roth, D.: Learning to detect objects in images via a sparse, part-based representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 26(11), 1475–1490 (2004)
Frejlichowski, D.: Automatic localization of moving vehicles in image sequences using morphological operations. In: IEEE Proc., Information Technology, pp. 1–4 (2008)
Li, C., Kao, C., Gore, J., Ding, Z.: Implicit active contours driven by local binary fitting energy. In: IEEE Proc., Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–7 (2007)
Wang, L., Li, C., Sun, Q., Xia, D., Kao, C.: Active contours driven by local and global intensity fitting energy with application to brain MR image segmentation. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 33(7), 520–531 (2009)
Zhang, K., Song, H., Zhang, L.: Active contours driven by local image fitting energy. Pattern Recognit. 43(4), 1199–1206 (2010)
H, C., Wang, Y., Chen, Q.: Active contours driven by weighted region-scalable fitting energy based on local entropy. Signal Process. 92(2), 587–600 (2011)
Tao, W., Tai, X.-C.: Multiple piecewise constant with geodesic active contours (MPC-GAC) framework for interactive image segmentation using graph cut optimization. Image Vis. Comput. 29, 499–508 (2011)
Chan, T., Vese, L.: Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10(2), 266–277 (2001)
Yezzi, J.A., Tsai, A., Willsky, A.: A fully global approach to image segmentation via coupled curve evolution equations. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 13(1), 195–216 (2002)
Vese, L., Chan, T.: A multiphase level set framework for image segmentation using the Mumford and Shah model. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 50(3), 271–293 (2002)
Lankton, S., Nainb, D., Yezzi, A., Tannenbaum, A.: Hybrid geodesic region-based curve evolutions for image segmentation. Proc. SPIE Med. Imaging Symp. 6510(3), 6510–6519 (2007)
Lankton, S., Tannenbaum, A.: Localizing region-based active contours. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 17(11), 2029–2039 (2008)
Rousson, M., Lenglet, C., Deriche, R.: Level set and region based propagation for diffusion tensor MRI segmentation. Comput. Vis. Math. Methods Med. Biom. Image Anal. 3117(2004), 123–134 (2004)
Stauffer, C., Grimson, W.: Adaptive background mixture models for real time tracking. In: IEEE Proc. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 246–252 (1999)
Cheung, S.-C.S., Kamath, C.: Robust background subtraction with foreground validation for urban traffic video. EURASIP J. Appl. Signal Process. 2005(14), 2330–2340 (2005)
Al Najjar, M., Ghosh, S., Bayoumi, M.: A hybrid adaptive scheme based on selective Gaussian modeling for real-time object detection. In: IEEE Proc., Circuits and Systems, pp. 936–939 (2009)
He, F., Wang, J., Zhang, X., Gao, Y.: A moving objects detection algorithm using iterative division and Gaussian mixture model. In: IEEE Proc., Advanced Computer Control, pp. 229–233 (2010)
Shi, Y., Cheng, S., Quan, S., Chen, J., Chen, D.: Moving objects detection by Gaussian mixture model: a comparative analysis. In: IEEE Proc., Electrical and Control Engineering, pp. 1121–1124 (2011)
Ardila, J., Bijker, W., Tolpekin, A., Stein, A.: Multitemporal change detection of urban trees using localized region-based active contours in VHR images. Remote Sens. Environ. 124, 413–426 (2012)
Zhang, K., Zhang, L., Song, H., Zhou, W.: Active contours with selective local or global segmentation: a new formulation and level set method. Image Vis. Comput. 28(4), 668–676 (2010)
Dzyubachyk, O., Niessen, W., Meijering, E.: Advanced level-set based multiple-cell segmentation and tracking in time-lapse fluorescence microscopy images. In: IEEE Proc., Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, pp. 185–188 (2008)
Kass, M., Witkin, A., Terzopoulos, D.: Snakes: active contour models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1(4), 321–331 (1998)
Caselles, V., Kimmel, R., Sapiro, G.: Geodesic active contours. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 22(1), 61–79 (1997)
Osher, S.: Fronts propagating with curvature dependent speed algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J. Comput. Phys. 79(1), 12–49 (1988)
Zhu, G.P., Zhang Sh, Q., Zeng, Q.S.H., Wang, Ch.H.: Boundary-based image segmentation using binary level set method. SPIE Opt. Eng. 46(5) (2007)
Lie, J., Lysaker, M., Tai, X.C.: A binary level set model and some application to Mumford–Shah image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 15(5), 1171–1181 (2006)
Mumford, D., Shah, J.: Boundary detection by minimizing functional. In: IEEE Proc., Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 22–26 (1985)
Li, C.M., Xu, C.Y., Gui, C.F., Fox, M.D.: Level set evolution without re-initialization: a new variational formulation. In: IEEE Proc., Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 430–436 (2005)
Brox, T., Cremers, D.: On the statistical interpretation of the piecewise smooth Mumford-Shah functional. Scale Space Var. Methods Comput. Vis. 4485(2007), 203–213 (2007)
Paragios, N., Deriche, R.: Geodesic active contours and level sets for detection and tracking of moving objects. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22(4), 1–15 (2000)
Tsai, A., Yezzi, A., Willsky, A.S.: Curve evolution implementation of the Mumford–Shah functional for image segmentation, denoising, interpolation, and magnification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 10(8), 1169–1186 (2001)
Vese, L.A., Chan, T.F.: A multiphase level set framework for image segmentation using the Mumford–Shah model. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 50, 271–293 (2002)
Ronfard, R.: Region-based strategies for active contour models. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 13(2), 229–251 (1994)
Paragios, N., Deriche, R.: Geodesic active regions and level set methods for supervised texture segmentation. In: IEEE Proc., Computer Vision, pp. 926–932 (1999)
Vasilevskiy, A., Siddiqi, K.: Flux-maximizing geometric flows. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24(12), 1565–1578 (2002)
Adalsteinsson, D., Sethian, J.A.: The fast construction of extension velocities in level set methods. J. Comput. Phys. 148(1), 2–22 (1999)
Sussman, M., Smereka, P., Osher, S.: A level set approach for computing solutions to incompressible two phase flow. J. Comput. Phys. 114(1), 146–159 (1994)
Rosenthal, P., Molchanov, V., Linsen, L.: A narrow band level set method for surface extraction from unstructured point-based volume data. In: WSCG Proc., Computer Graphics, Visualization and Computer Vision, pp. 73–80 (2010)
Moursi, S.G., El-Sakka, M.R.: Active contours initialization for ultrasound Carotid Artery image. In: IEEE, International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications, pp. 629–636 (2008)
http://i21www.ira.uka.de/image_sequences/, Institut für Algorithmen und Kognitive Systeme
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boumehed, M., Alshaqaqi, B., Ouamri, A. et al. Moving Objects Localization by Local Regions Based Level Set: Application on Urban Traffic. J Math Imaging Vis 46, 258–274 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-012-0400-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-012-0400-9