Abstract
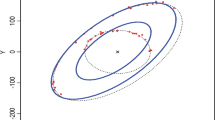
Geometric fitting is present in different fields of science, engineering and astronomy. In particular, ellipse shapes are some of the most commonly employed geometric features in digital image analysis and visual pattern recognition. Most geometric and algebraic methods are sensitive to noise and outlier points and so the results are not usually acceptable. In this paper, a robust geometric multicriteria method based on the mean absolute geometric error and the eccentricity to fit an ellipse to set of points is proposed. It is well known that the least mean absolute error criterion leads to robust estimations.
The experimental results on different real and synthetic data have shown that the proposed algorithm is robust to outliers. Moreover, it allows us to identify outliers and remove them.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kåsa, I.: A circle fitting procedure and its error analysis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 25, 8–14 (1976)
Pratt, V.: Direct least-squares fitting of algebraic surfaces. Comput. Graph. 21, 145–152 (1987)
Bookstein, F.L.: Fitting conic sections to scattered data. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 9, 56–91 (1979)
Forbes, A.B.: Least-squares best fit geometric elements. In: Mason, J.C., Cox, M.G. (eds.) Algorithms for Approximation II, pp. 311–319. Chapman and Hall, London (1990)
Rosin, P.L.: A note on the least squares fitting of ellipses. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 14, 799–808 (1993)
Butler, B.P., Forbes, A.B., Harris, P.M.: Algorithms for geometric tolerance assessment. NPL Report DITC 228/94 Teddington, UK (1994)
Zwick, D.S.: Applications of orthogonal distance regression in metrology. In: Van Huffel, S. (ed.) Recent Advances in Total Least Squares and Errors-in-Variables Techniques, pp. 265–272. SIAM, Philadelphia (1997)
Nakagawa, Y., Rosenfeld, A.: A note on “Polygonal and elliptical approximation of mechanical parts”. Pattern Recognit. 11, 133–142 (1979)
Foster, N.J., Sanderson, A.C.: Determining object orientation using ellipse fitting. SPlE Proc. Intell. Robots Comput. Vis. 521, 34–43 (1984)
Nagata, T., Tamura, H., Ishibashi, K.: Detection of an ellipse by use of a recursive least-squares estimator. I. Robot. Syst. 2, 163–177 (1985)
Hainesa, C., Goodhill, G.J.: Analyzing neurite outgrowth from explants by fitting ellipses. J. Neurosci. Methods 187, 52–58 (2010)
Lamard, M., Hamitouche-Djabou, C., Develay Morice, J.E., Bressolette, L., Roux, C.: Interactive ellipse fitting in ultrasound images. In: Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS, Cancun, Mexico, September 17–21 (2003)
Mulchronea, K.F., Choudhuryb, K.R.: Fitting an ellipse to an arbitrary shape: implications for strain analysis. J. Struct. Geol. 26, 143–153 (2004)
Wynna, T.J., Stewartb, S.A.: Comparative testing of ellipse-fitting algorithms: implications for analysis of strain and curvature. J. Struct. Geol. 27, 1973–1985 (2005)
Ray, A., Srivastava, D.C.: Non-linear least squares ellipse fitting using the genetic algorithm with applications to strain analysis. J. Struct. Geol. 30, 1593–1602 (2008)
Ramos, P.M., Janeiro, F.M., Tlemçani, M., Cruz Serra, A.: Uncertainty analysis of impedance measurements using DSP implemented ellipse fitting algorithms. In: IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Victoria, Vancouver Island, Canada, May 12–15 (2008)
Gander, W., Golub, G.H., Strebel, R.: Least-square fitting of circles and ellipses. BIT 34, 558–578 (1994)
Fitzgibbon, A.W., Fisher, R.B.: A Buyer’s guide to conic fitting. In: British Machine Vision Conf., pp. 513–522 (1995)
Pearson, K.: On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Philos. Mag. Ser. 6 2(11), 559–572 (1901)
DIN 32880-1: Coordinate Metrology; Geometrical Fundamental Principles, Terms and Definitions, German Standard. Beuth Verlag, Berlin (1986)
Rosin, P.L.: Analysing error of fit functions for ellipses. Graph. Models Image Process. 58(5), 494–502 (1996)
Taubin, G.: Estimation of planar curves, surfaces and nonplanar space curves defined by implicit equations, with applications to edge and range image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 13, 1115–1138 (1991)
Kanatani, K.: Statistical bias of conic fitting and renormalization. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 16(3), 320–326 (1994)
Sampson, P.D.: Fitting conic sections to “very scattered” data: an iterative refinement of the bookstein algorithm. Comput. Graph. Image Process. 18, 97–108 (1982)
Kanatani, K., Rangarajan, P.: Hyper least squares fitting of circles and ellipses. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 55(6), 2197–2208 (2011)
Paton, K.: Conic sections in chromosome analysis. Pattern Recognit. 2, 39–51 (1970)
Paton, K.A.: Conic sections in automatic chromosome analysis. Mach. Intell. 5, 411 (1970)
Porrill, J.: Fitting ellipses and predicting confidence envelopes using a bias corrected Kalman filter. Image Vis. Comput. 8, 37–41 (1990)
Ahn, S.J., Rauh, W., Warnecke, H.J.: Least-squares orthogonal distances fitting of circle, sphere, ellipse, hyperbola and parabola. Pattern Recognit. 34, 2283–2303 (2001)
Kanatani, K.: Statistical optimization for geometric fitting: theoretical accuracy bound and high order error analysis. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 80(2), 167–188 (2008)
Fitzgibbon, A., Pilu, M., Fisher, R.B.: Direct least square fitting of ellipses. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 21(5), 476–480 (1999)
Halíi, R., Flusser, J.: Numerically stable least squares fitting of ellipses. In: Proc. Sixth Int. Conf. in Central Europe on Computer Graphics, Visualization and Interactive Digital Media, vol. 1, pp. 125–132 (1998)
Maini, E.S.: Enhanced direct least squares fitting of ellipses. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 20(6), 939–953 (2006)
Halíi, R.: Robust bias-corrected least squares fitting of ellipses. In: Proc. Eighth Int. Conf. in Central Europe on Computer Graphics, Visualization and Interactive Digital Media, vol. 1 (2000)
Chojnacki, W., Brooks, M.J., van den Hengel, A., Gawley, D.: On the fitting of surfaces to data with covariances. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22(11), 1294–1303 (2000)
Leedan, Y., Meer, P.: Heteroscedastic regression in computer vision: problems with bilinear constraint. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 37(2), 127–150 (2000)
Matei, J., Meer, P.: Estimation of nonlinear errors-in-variables models for computer vision applications. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28(10), 1537–1553 (2006)
Kanatani, K., Sugaya, Y.: Unified computation of strict maximum likelihood for geometric fitting. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 38(1), 1–13 (2010)
Calafiore, G.: Approximation of n-dimensional data using spherical and ellipsoidal primitives. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern., Part A, Syst. Hum. 32, 269–278 (2002)
de la Fraga, L.G., Vite Silva, I., Cruz-Cortés, N.: Euclidean distance fit of ellipses with a genetic algorithm. In: EvoWorkshops 2007. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci., vol. 4448, pp. 359–366 (2007)
Ray, A., Srivastava, D.C.: Non-linear least squares ellipse fitting using the genetic algorithm with applications to strain analysis. J. Struct. Geol. 30, 1593–1602 (2008)
Rousseeuw, P.J., Leroy, A.M.: Robust Regression and Outlier Detection. Wiley, New York (1987)
Roth, G., Levine, M.D.: Extracting geometric primitives. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 58(1), 1–22 (1993)
Rosin, P.L.: Further five-point fit ellipse fitting. Graph. Models Image Process. 61(5), 245–259 (1999)
Yu, J., Kulkarni, S.R., Poor, H.V.: Robust ellipse and spheroid fitting. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 33, 492–499 (2012)
Meer, P., Mintz, D., Rosenfeld, A., Kim, D.Y.: Robust regression methods for computer vision: a review. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 6, 59–70 (1991)
Huber, P.J.: Robust Statistics. Wiley, New York (1981)
Trucco, E., Verri, A.: Introductory Techniques for 3-D Computer Vision. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River/New York (1998)
Calafiore, G.C.: Outliers robustness in multivariate orthogonal regression. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 30, 674–679 (2000)
Bolles, R.C., Fischler, M.A.: A RANSAC-based approach to model fitting and its applications to finding cylinders in range data. In: Proc. 7th, IJCAI, pp. 637–643. Springer, Berlin (1981)
Fischler, M.A., Bolles, R.C.: Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 24, 381–395 (1981)
Rosin, P.L.: Feature fitting. http://users.cs.cf.ac.uk/Paul.Rosin/fitting.html. Accessed 14 November 2013
Canny, J.: A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 8, 679–698 (1986)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Coordinating Editor and the referees for their valuable comments and suggestions. This work is partially supported by Junta de Andalucía (Spain) under contract TIC-6213, project name DERENA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muñoz-Pérez, J., de Cózar-Macías, O.D., Blázquez-Parra, E.B. et al. Multicriteria Robust Fitting of Elliptical Primitives. J Math Imaging Vis 49, 492–509 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-013-0480-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-013-0480-1