Abstract
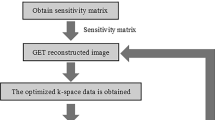
We propose a recovery approach for highly subsampled dynamic parallel MRI image without auto-calibration signals (ACSs) or prior knowledge of coil sensitivity maps. By exploiting the between-frame redundancy of dynamic parallel MRI data, we first introduce a new low-rank matrix recovery-based model, termed as calibration using spatial–temporal matrix (CUSTOM), for ACSs recovery. The recovered ACSs from data are used for estimating coil sensitivity maps and further dynamic image reconstruction. The proposed non-convex and non-smooth minimization for the CUSTOM step is solved by a proximal alternating linearized minimization method, and we provide its convergence result for this specific minimization problem. Numerical experiments on several highly subsampled test data demonstrate that the proposed overall approach outperforms other state-of-the-art methods for calibrationless dynamic parallel MRI reconstruction.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attouch, H., Al, E.: Proximal alternating minimization and projection methods for nonconvex problems: an approach based on the Kurdyka–Łojasiewicz inequality. Math. Oper. Res. 35(2), 438–457 (2010)
Beck, A., Teboulle, M.: A fast iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 2(1), 183–202 (2009)
Bhatia, R.: Matrix analysis. Grad. Texts Math. 169(8), 1–17 (1996)
Bolte, J., Sabach, S., Teboulle, M.: Proximal alternating linearized minimization for nonconvex and nonsmooth problems. Math. Program. 146(1–2), 459–494 (2014)
Breuer, F.A., Kellman, P., Griswold, M.A., Jakob, P.M.: Dynamic autocalibrated parallel imaging using temporal GRAPPA (TGRAPPA). Magn. Reson. Med. 53(4), 981–985 (2005)
Bruno, M., Glover, G.H., Pelc, N.J.: Unaliasing by Fourier-encoding the overlaps using the temporal dimension (UNFOLD), applied to cardiac imaging and fMRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 42(5), 813–828 (1999)
Cai, J.F., Candès, E.J., Shen, Z.: A singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion. SIAM J. Optim. 20(4), 1956–1982 (2010)
Candès, S.E.J., Li, X., Ma, Y., Wright, J.: Robust principal component analysis. J. ACM 58(3), 1–73 (2011)
Chandrasekaran, V., Sanghavi, S., Parrilo, P., Willsky, A.S., et al.: Sparse and low-rank matrix decompositions. In: 47th Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing, 2009. Allerton 2009. pp. 962–967. IEEE (2009)
Daubechies, I., Defrise, M., De Mol, C.: An iterative thresholding algorithm for linear inverse problems with a sparsity constraint. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 57(11), 1413–1457 (2004)
Ding, Q., Zan, Y., Huang, Q., Zhang, X.: Dynamic spect reconstruction from few projections: a sparsity enforced matrix factorization approach. Inverse Probl. 31(2) (2015). doi:10.1088/0266-5611/31/2/025004
Gao, H., Cai, J.F., Shen, Z., Zhao, H.: Robust principal component analysis-based four-dimensional computed tomography. Phys. Med. Biol. 56(11), 3181–3198 (2011)
Gao, H., Rapacchi, S., Wang, D., Moriarty, J., Meehan, C., Sayre, J., Laub, G., Finn, P., Hu, P.: Compressed sensing using prior rank, intensity and sparsity model (PRISM): applications in cardiac cine MRI. In: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Melbourne, Australia, p. 2242 (2012)
Gao, H., Yu, H., Osher, S., Wang, G.: Multi-energy CT based on a prior rank, intensity and sparsity model (PRISM). Inverse Probl. 27(11), 115012–115033 (2011)
Griswold, M.A., Jakob, P.M., Heidemann, R.M., Nittka, M., Jellus, V., Wang, J., Kiefer, B., Haase, A.: Generalized autocalibrating partially parallel acquisitions (GRAPPA). Magn. Reson. Med. 47(6), 1202–1210 (2002)
Kellman, P., Epstein, F., Mcveigh, E.: Adaptive sensitivity encoding incorporating temporal filtering (TSENSE). Magn. Reson. Med. 45(45), 846–852 (2001)
Kruse, F.A.: Detecting plumes in LWIR using robust nonnegative matrix factorization with graph-based initialization. In: Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series (2015)
Kurdyka, K.: On gradients of functions definable in o-minimal structures. Ann. Inst. Fourier 48(3), 769–783 (1998)
Liang, D., Liu, B., Wang, J., Ying, L.: Accelerating SENSE using compressed sensing. Magn. Reson. Med. 62(6), 1574–1584 (2009)
Liu, J., Zhang, X., Zhang, X., Zhao, H., Gao, Y., Thomas, D., Low, D.A., Gao, H.: 5D respiratory motion model based image reconstruction algorithm for 4D cone-beam computed tomography. Inverse Probl. 31(11) (2015). doi:10.1088/0266-5611/31/11/115007
Łojasiewicz, S.: Sur la géométrie semi- et sous-analytique. Ann. Inst. Fourier 43(5), 1575–1595 (1993)
Lustig, M., Donoho, D., Pauly, J.M.: Sparse MRI: the application of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 58(6), 1182–1195 (2007)
Lustig, M., Pauly, J.M.: SPIRiT: iterative self-consistent parallel imaging reconstruction from arbitrary k-space. Magn. Reson. Med. 64(2), 457–471 (2010)
Otazo, R., Candès, E., Sodickson, D.K.: Low-rank plus sparse matrix decomposition for accelerated dynamic MRI with separation of background and dynamic components. Magn. Reson. Med. 73(3), 1125–1136 (2014)
Pruessmann, K.P., Weiger, M., Scheidegger, M.B., Boesiger, P.: SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 42, 952–962 (1999)
Shin, P.J., Larson, P.E., Ohliger, M.A., Elad, M., Pauly, J.M., Vigneron, D.B., Lustig, M.: Calibrationless parallel imaging reconstruction based on structured low-rank matrix completion. Magn. Reson. Med. 72(4), 959–970 (2014)
Sodickson, D.K., Manning, W.J.: Simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics (SMASH): fast imaging with radiofrequency coil arrays. Magn. Reson. Med. 38(4), 591–603 (1997)
Tseng, P., Yun, S.: A coordinate gradient descent method for nonsmooth separable minimization. Math. Program. 117(1), 387–423 (2008)
Uecker, M., Lai, P., Murphy, M.J., Virtue, P., Elad, M., Pauly, J.M., Vasanawala, S.S., Lustig, M.: ESPIRiT an eigenvalue approach to autocalibrating parallel MRI: where SENSE meets GRAPPA. Magn. Reson. Med. 71(3), 990–1001 (2014)
Wakabayashi, S., Wakabayashi, S.: Remarks on semi-algebraic functions. ResearchGate (2008)
Wang, H., Liang, D., King, K.F., Nagarsekar, G., Chang, Y., Ying, L.: Improving GRAPPA using cross-sampled autocalibration data. Magn. Reson. Med. 67(4), 1042–1053 (2012)
Wang, J., Kluge, T., Nittka, M., Jellus, V., Kuhn, B., Kiefer, B.: Using reference lines to improve the SNR of mSENSE. In: Proceedings of the 10th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Honolulu, p. 2392 (2002)
Xu, Y., Yin, W.: A globally convergent algorithm for nonconvex optimization based on block coordinate update. Eprint Arxiv (2014)
Zhang, T., Pauly, J.M., Vasanawala, S.S., Lustig, M.: Coil compression for accelerated imaging with Cartesian sampling. Magn. Reson. Med. 69(2), 571–582 (2013)
Acknowledgments
Xue Zhang, Likun Hou and Xiaoqun Zhang are partially supported by NSFC (Nos. 91330102 and GZ1025) and 973 Program (No. 2015CB856004). Hao Gao is partially supported by the NSFC (No. 11405105), the 973 Program (No. 2015CB856004), and the Shanghai Pujiang Talent Program (No. 14PJ1404500). We would thank the authors of [23, 24, 26, 29] for making their codes, demos and experimental datasets free for academic use.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Hou, L., Gao, H. et al. CUSTOM: A Calibration Region Recovery Approach for Highly Subsampled Dynamic Parallel Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J Math Imaging Vis 57, 366–380 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-016-0682-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-016-0682-4