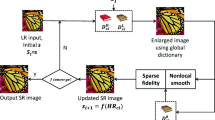
Abstract
Single-image nonparametric blind super-resolution is a fundamental image restoration problem yet largely ignored in the past decades among the computational photography and computer vision communities. An interesting phenomenon is observed that learning-based single-image super-resolution (SR) has been experiencing a rapid development since the boom of the sparse representation in 2005s and especially the representation learning in 2010s, wherein the high-res image is generally blurred by a supposed bicubic or Gaussian blur kernel. However, the parametric assumption on the form of blur kernels does not hold in most practical applications because in real low-res imaging a high-res image can undergo complex blur processes, e.g., Gaussian-shaped kernels of varying sizes, ellipse-shaped kernels of varying orientations, curvilinear kernels of varying trajectories. The paper is mainly motivated by one of our previous works: Shao and Elad (in: Zhang (ed) ICIG 2015, Part III, Lecture notes in computer science, Springer, Cham, 2015). Specifically, we take one step further in this paper and present a type of adaptive heavy-tailed image priors, which result in a new regularized formulation for nonparametric blind super-resolution. The new image priors can be expressed and understood as a generalized integration of the normalized sparsity measure and relative total variation. Although it seems that the proposed priors are simple, the core merit of the priors is their practical capability for the challenging task of nonparametric blur kernel estimation for both super-resolution and deblurring. Harnessing the priors, a higher-quality intermediate high-res image becomes possible and therefore more accurate blur kernel estimation can be accomplished. A great many experiments are performed on both synthetic and real-world blurred low-res images, demonstrating the comparative or even superior performance of the proposed algorithm convincingly. Meanwhile, the proposed priors are demonstrated quite applicable to blind image deblurring which is a degenerated problem of nonparametric blind SR.





































Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In [48] blur kernels are typically solved with size 9 × 9, 11 × 11 or 13 × 13 for various blind SR problems.
References
Freeman, W.T., Pasztor, E.C.: Learning to estimate scenes from images. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), pp. 775–781. (1999)
Baker S., Kanade, T.: Hallucinating faces. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp. 83–88. (2000)
Milanfar, P.: Super-Resolution Imaging. CRC Press, Boca Raton (2011)
Tian, J., Ma, K.-K.: A survey on super-resolution Imaging. SIViP 5(3), 329–342 (2011)
Nasrollahi, K., Moeslund, T.B.: Super-resolution: a comprehensive survey. Mach. Vis. Appl. 25, 1423–1468 (2014)
Yang, C.-Y., Ma, C., Yang, M.-H.: Single-image super-resolution: a benchmark. In: Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 372–386. (2014)
Goodfellow, I., Bengio, Y., Courville, A.: Deep Learning. MIT Press, Cambridge (2016)
LeCun, Y., Yoshua, B., Hinton, G.: Deep learning. Nature 521(7553), 436–444 (2015)
Schmidhuber, J.: Deep learning in neural networks: an overview. Neural Networks 61, 85–117 (2015)
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., Hinton, G.: ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inform Process Syst (NIPS) 25(2), 1097–1105 (2012)
Bevilacqua, M., Roumy, A., Guillemot, C., Morel, M.-L.A.: Low-complexity single-Image super-resolution based on nonnegative neighbor embedding. In: British Machine Vision Conference pp. 1–10. (2012)
Chang, H., Yeung, D.-Y., Xiong, Y.: Super-resolution through neighbor embedding. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 275–282. (2004)
Zhang, K., Gao, X., Li, X., Tao, D.: Partially supervised neighbor embedding for example-based image super-resolution. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 5(2), 230–239 (2011)
Gao, X., Zhang, K., Li, X., Tao, D.: Joint learning for single-image super-resolution via a coupled constraint. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(2), 469–480 (2012)
Yang, J., Wright, J., Huang, T.S., Ma, Y.: Image super-resolution via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19(11), 2861–2873 (2010)
Zeyde, R., Elad, M., Protter, M.: On single image scale-up using sparse representation. Int. Conf. Curves Surf. 6920, 711–730 (2010)
Yang, J., Wang, Z., Lin, Z., Cohen, S., Huang, T.: Coupled dictionary training for image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 21(8), 3467–3478 (2012)
Tang, Y., Yuan, Y., Yan, P., Li, X.: Greedy regression in sparse coding space for single-image super-resolution. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 24(2), 148–159 (2013)
Peleg, T., Elad, M.: A statistical prediction model based on sparse representations for single image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 23(6), 2569–2582 (2014)
Purkait, P., Chanda, B.: Image upscaling using multiple dictionaries of natural image patches. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science (11th Asian Conference on Computer Vision), vol. 7726, pp. 284–295. (2013)
He, L., Qi, H., Zaretzki, R.: Beta process joint dictionary learning for coupled feature spaces with application to single image super-resolution. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 345–352. (2013)
Wang, S., Zhang, L., Liang, Y., Pan, Q.: Semi-coupled dictionary learning with applications to image super-resolution and photo-sketch synthesis. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2216–2223. (2012)
Jia, K., Tang, X., Wang, X.: Image transformation based on learning dictionaries across image spaces. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (PAMI) 35(2), 367–380 (2013)
Timofte, R., De Smet, V., Van Gool, L.: Anchored neighborhood regression for fast example-based super-resolution. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 1920–1927. (2013)
Timofte, R., De Smet, V., Van Gool, L.: A+: Adjusted anchored neighborhood regression for fast super-resolution. In: Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV), pp. 111–126. (2014)
Schulter, S., Leistner, C., Bischof, H.: Fast and accurate image upscaling with super-resolution forests. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. (CVPR), pp. 3791–3799, (2015)
Dong, C., Loy, C.C., He, K., Tang, X.: Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 184–199. (2014)
Cui, Z., Chang, H., Shan, S., Zhong, B., Chen, X.: Deep network cascade for image super-resolution. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 49–64. (2014)
Kim, J., Kwon Lee, J., Mu Lee, K.: Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks. In: IEEE Conference Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1646–1654. (2015)
Kim, J., Kwon Lee, J., Mu Lee, K.: Deeply-recursive convolutional network for image super-resolution. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1637–1645. (2015)
Johnson, J., Alahi, A., Fei-Fei, L.: Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 694–711. (2016)
Wang, Z., Liu, D., Yang, J., Han, W., Huang, T.: Deep networks for image super-resolution with sparse prior. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 370–378. (2015)
Bruna, J., Sprechmann, P., LeCun, Y.: Super-resolution with deep convolutional sufficient statistics. In: International Conference on Learning Representation (ICLR), (2016)
Dong, C., Loy, C.C., Tang, X.: Accelerating the super-resolution convolutional neural network. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 391–407. (2016)
Shi, W., Caballero, J., Huszar, F., et al.: Real-time single image and video super-resolution using an efficient sub-pixel convolutional neural network. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1874–1883. (2016)
Sajjadi, M., Scholkopf, B., Hirsch, M.: EnhanceNet: single image super-resolution through automated texture synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv:1612.07919, (2016)
Lim, B., Son, S., Kim, H., Nah, S., Lee, K.M.: Enhanced deep residual networks for single image super-resolution. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Honolulu, pp. 1132–1140. (2017)
Zhu, S., Liu, S., Loy, C.C., Tang, X.: Deep cascaded bi-network for face hallucination. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 614–630. (2016)
Yu, X., Porikli, F.: Ultra-resolving face images by discriminative generative networks. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 318–333. (2016)
Fattal, R.: Image upsampling via imposed edge statistics. ACM Trans. Graph. 26, Article No. 95, (2007)
Marquina, A., Osher, S.J.: Image super-resolution by TV-regularization and Bregman iteration. J. Sci. Comput. 37, 367–382 (2008)
Dong, W., Zhang, L., Shi, G., Li, X.: Nonlocally centralized sparse representation for image restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 22(4), 1620–1630 (2013)
Efrat, N., Glasner, D., Apartsin, A., Nadler, B., Levin, A.: Accurate blur models vs. image priors in single image super-resolution. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 2832–2839. (2013)
Begin, I., Ferrie, F.R.: PSF recovery from examples for blind super-resolution. IEEE Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 421–424. (2007)
Wang, Q., Tang, X., Shum, H.: Patch based blind image super resolution. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 709–716. (2005)
He, Y., Yap, K.H., Chen, L., Chau, L.P.: A soft MAP framework for blind super-resolution image reconstruction. Image Vis. Comput. 27, 364–373 (2009)
Joshi, N., Szeliski, R., Kriegman, D.J.: PSF estimation using sharp edge prediction. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1–8. (2008)
Michaeli, T., Irani, M.: Nonparametric blind super-resolution. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 945–952. (2013)
Michaeli, T., Irani, M.: Blind deblurring using internal patch recurrence. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 783–798. (2014)
Shao, W., Elad, M.: Simple, accurate, and robust nonparametric blind super-resolution. In: Zhang, Y.J. (ed.) ICIG 2015 Part III Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 9219, pp. 333–348. Springer, Cham (2015)
Shao, W., Li, H., Elad, M.: Bi-L 0–L 2-norm regularization for blind motion deblurring. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 33, 42–59 (2015)
Fergus, R., Singh, B., Hertzmann, A., Roweis, S.T., Freeman, W.T.: Removing camera shake from a single photograph. ACM Trans. Graph. 25(3), 787–794 (2006)
Lai, W.S., Huang, J.B., Hu, Z., Ahuja, N., Yang, M.H.: A comparative study for single image blind deblurring. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1701–1709. (2016)
Pan, J., Sun, D., Pfister, H., Yang, M.H.: Blind image deblurring using dark channel prior. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1628–1636. (2016)
Pan, J., Hu, Z., Su, Z., Yang, M.-H.: Debluring low-resolution images. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science. ACCV 2016 Workshops, Part I, vol. 10116, pp. 111–127. (2017)
Pan, J., Hu, Z., Su, Z., Yang, M.-H.: Deblurring text images via L0-regularized intensity and gradient prior. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1628–1636. (2014)
Rudin, L., Osher, S.: Total variation based image restoration with free local constraints. In: Proceedings of 1st IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Austin, pp. 31–35. (1994)
Chan, S.H., Khoshabeh, R., Gibson, K.B., Gill, P.E., Nguyen, T.Q.: An augmented Lagrangian method for total variation video restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(11), 3097–3111 (2011)
Chan, T.F., Wong, C.K.: Total variation blind deconvolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 7(3), 370–375 (1998)
Perrone, D., Favaro, P.: A clearer picture of total variation blind deconvolution. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(6), 1041–1055 (2016)
Ng, M.K., Weiss, P., Yuan, X.: Solving constrained total-variation image restoration and reconstruction problems via alternating direction methods. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 32, 2710–2736 (2010)
Krishnan, D., Fergus, R.: Fast image deconvolution using hyper-laplacian priors. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Neural Information and Processing Systems (NIPS), pp. 1033–1041. (2009)
Tappen, M.F., Russel, B.C., Freeman, W.T.: Exploiting the sparse derivative prior for super-resolution and image demosaicing. In: Proceedings of IEEE Workshop on Statistical and Computational Theories of Vision. (2003)
Kotera, J., Sroubek, F., Milanfar, P.: Blind deconvolution using alternating maximum a posteriori estimation with heavy-tailed priors. In: Wilson, R. et al. (eds.) Lecture Notes in Computer Science CAIP, Part II, vol. 8048, pp. 59–66. (2013)
Almeida, M., Almeida, L.: Blind and semi-blind deblurring of natural images. IEEE Trans. Image Processing 19(1), 36–52 (2010)
Zuo, W., Ren, D., Gu, S., Lin, L., Zhang, L.: Learning iteration-wise generalized shrinkage–thresholding operators for blind deconvolution. IEEE Trans. Image Process 25(4), 1751–1764 (2016)
Krishnan, D., Tay, T., Fergus, R.: Blind deconvolution using a normalized sparsity measure. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 233–240. (2011)
Money, J.H., Kang, S.H.: Total variation minimizing blind deconvolution with shock filter reference. Image Vis. Comput. 26(2), 302–314 (2008)
Cho, S., Lee, S.: Fast motion deblurring. ACM Trans. Graph. 28(5), Article No. 145. (2009)
Xu, L., Jia, J.: Two-phase kernel estimation for robust motion deblurring. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, Part I, LNCS 6311, pp. 157–170. (2010)
Xu, L., Zheng, S., Jia, J.: Unnatural L 0 sparse representation for natural image deblurring. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1107–1114. (2013)
Xu, L., Yan, Q., Xia, Y., Jia, J.: Structure extraction from texture via relative total variation. ACM Trans. Graph. 31(6), Article 139. (2012)
Levin, A., Weiss, Y., Durand, F., Freeman, W.T.: Understanding blind deconvolution algorithms. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33(12), 2354–2367 (2011)
Chan, S.H., Wang, X., Elgendy, O.A.: Plug-and-play ADMM for image restoration: fixed point convergence and application. In: IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging, (In press). ArXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.01710. (2016)
Zhao, N., Wei, Q., Basarab, A., Kouame, D., Toureneret, J.Y.: Fast single image super-resolution using a new analytical solution for L 2–L 2 problems. http://arXiv.org/abs/1510.00143v3. (2016)
Dabov, K., Foi, A., Katkovnik, V., Egiazarian, K.: Image denoising by sparse 3D transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16(8), 2080–2095 (2007)
Schuler, C., Hirsch, M., Harmeling, S., Scholkopf, B.: Learning to Deblur. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(7), 1439–1451 (2016)
Nguyen, K., Fookes, C., Sridharan, S., Tistarelli, M., Nixon, M.: Super-resolution for biometrics: a comprehensive survey. Pattern Recognit. 78, 23–42 (2018)
Wei, X., Li, Y., Shen, H., Xiang, W., Murphey, Y.: Joint learning sparsifying linear transformation for low-resolution image synthesis and recognition. Pattern Recognit. 66, 412–424 (2018)
Wang, L., Huang, Z., Gong, Y., Pan, C.: Ensemble based deep networks for image super-resolution. Pattern Recognit. 68, 191–198 (2017)
Kumar, N., Verma, R., Sethi, A.: Convolutional neural networks for wavelet domain super resolution. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 90, 65–71 (2017)
Jebadurai, J., Peter, J.D.: SK-SVR: sigmoid kernel support vector regression based in-scale single image super-resolution. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 94, 144–153 (2017)
Kwon, Y., Kim, K.I., Tompkin, J., et al.: Efficient learning of image super-resolution and compression artifact removal with semi-local Gaussian processes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(9), 1792–1805 (2015)
Polatkan, G., Zhou, M., Carin, L.L., et al.: A Bayesian nonparametric approach to image super-resolution. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(2), 346–358 (2015)
Khare, V., Shivakumara, P., Raveendran, P., Blumenstein, M.: A blind deconvolution model for scene text detection and recognition in video. Pattern Recognit. 54, 128–148 (2016)
Li, W., Chen, D., Lv, Z., Yan, Y., Cosker, D.: Learn to model blurry motion via directional similarity and filtering. Pattern Recognit. 75, 327–338 (2018)
Pan, J., Sun, D., Pfister, H., Yang, M.H.: Deblurring image via dark channel prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2017.275380
Zhang, H., Wipf, D., Zhang, Y.: Multi-observation blind deconvolution with an adaptive sparse prior. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 36(8), 1628–1643 (2014)
Tai, Y.W., Chen, X., Kim, S., et al.: Nonlinear camera response functions and image deblurring: theoretical analysis and practice. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(10), 2498–2512 (2013)
Kupyn, O., Budzan, V., Mykhailych, M., Mishkin, D., Matas, J.: DeblurGAN: blind motion deblurring using conditional adversarial networks. https://arXiv.org/abs/1711.07064v2. (2018)
Nah, S., Kim, T.H., Lee, K.M.: Deep multi-scale convolutional neural network for dynamic scene deblurring. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, pp. 257–265. (2017)
Nimisha, T.M., Singh, A.K., Rajagopalan, A.N.: Blur-invariant deep learning for blind-deblurring. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, pp. 4762–4770. (2018)
Zhou, E., Fan, H., Cao, Z., Jiang, Y., Yin, Q.: Learning face hallucination in the wild. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, (2015)
Xu, X., Sun, D., Pan, J., Zhang, Y., Pfister, H., Yang, M.: Learning to super-resolve blurry face and text images. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, pp. 251–260. (2018)
Feng, N., Wang, J., Wang, W.: Sparse signal recovery with prior information by iterative reweighted least squares algorithm. J. Inverse Ill-posed Problems 36(2), 171–184 (2017)
Lu, C., Lin, Z., Yan, S.: Smoothed low rank and sparse matrix recovery by iteratively reweighted least squares minimization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(2), 646–654 (2015)
Zhang, K., Zuo, W., Gu, S., Zhang, L.: Learning deep CNN denoiser prior for image restoration. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2808–2817 (2017)
Acknowledgements
Many thanks are given to the anonymous reviewers for their careful, pertinent and serious comments on this paper which has been strengthened a lot after revision. Wen-Ze Shao is grateful to Prof. Zhi-Hui Wei, Prof. Michael Elad, Prof. Yi-Zhong Ma, Dr. Min Wu and Mr. Ya-Tao Zhang for their kind support in the past years. The study is supported in part by the Natural Science Foundation (NSF) of China (61771250, 61402239, 61602257, 61502244, 11671004), the NSF of Jiangsu Province (BK20160904, BK20150859), the NSF for Jiangsu Institutions (16KJB520035) and the Open Fund of National Engineering Research Center of Communications and Networking (Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, TXKY17008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shao, WZ., Ge, Q., Wang, LQ. et al. Nonparametric Blind Super-Resolution Using Adaptive Heavy-Tailed Priors. J Math Imaging Vis 61, 885–917 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-019-00876-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10851-019-00876-1