Abstract
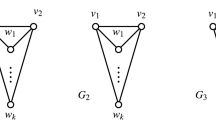
Let \(G=(V,E)\) be a graph. A function \(f : V \rightarrow \{0, 1, 2\}\) is an outer independent Roman dominating function (OIRDF) on a graph G if for every vertex \(v \in V\) with \(f (v) = 0\) there is a vertex u adjacent to v with \(f (u) = 2\) and \(\{x\in V:f(x)=0\}\) is an independent set. The weight of f is the value \( f(V)=\sum _{v\in V}f(v)\). An outer independent total Roman dominating function (OITRDF) f on G is an OIRDF on G such that for every \(v\in V\) with \(f(v)>0\) there is a vertex u adjacent to v with \(f (u)>0\). The minimum weight of an OIRDF on G is called the outer independent Roman domination number of G, denoted by \(\gamma _{oiR}(G)\). Similarly, the outer independent total Roman domination number of G is defined, denoted by \(\gamma _{oitR}(G)\). In this paper, we first show that computing \(\gamma _{oiR}(G)\) (respectively, \(\gamma _{oitR}(G)\)) is a NP-hard problem, even when G is a chordal graph. Then, for a given proper interval graph \(G=(V,E)\) we propose an algorithm to compute \(\gamma _{oiR}(G)\) (respectively, \(\gamma _{oitR}(G)\)) in \({\mathcal {O}}(|V| )\) time.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdollahzadeh Ahangar H, Chellali M, Samodivkin V (2017) Outer independent Roman dominating functions in graphs. Int J Comput Math 94:2547–2557
Araki T, Miyazaki H (2018) Secure domination in proper interval graphs. Discrete Appl Math 247:70–76
Braga A, de Souza CC, Lee O (2015) The eternal dominating set problem for proper interval graphs. Inform Process Lett 115:582–587
Chiarelli N, Hartinger TR, Leoni VA, Pujato MIL, Milanič M (2019) New algorithms for weighted \(k\)-domination and total \(k\)-domination problems in proper interval graphs. Theoret Comput Sci 795:128–141
Garey MR, Johnson DS (1979) Computers and intractability: a guide to the theory of NP-Completeness. W. H. Freeman, New York
Haynes TW, Hedetniemi ST, Slater PJ (1998) Fundamentals of domination in graphs. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York
Looges PJ, Olariu S (1993) Optimal greedy algorithms for indifference graphs. Comput Math Appl 25(7):15–25
Martínez AC, Kuziak D, Yero IG (2019) Outer-independent total Roman domination in graphs. Discrete Appl Math 296:107–119
Panda BS, Paul S (2013) A linear time algorithm for liar’s domination problem in proper interval graphs. Inform Process Lett 113:815–822
Revelle CS, Rosing KE (2000) Defendens imperium romanum: a classical problem in military strategy. Am Math Monthly 107:585–594
Stewart I (1999) Defend the roman empire!. Sci Am 281:136–139
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poureidi, A., Ghaznavi, M. & Fathali, J. Algorithmic complexity of outer independent Roman domination and outer independent total Roman domination. J Comb Optim 41, 304–317 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-020-00682-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-020-00682-1