Abstract
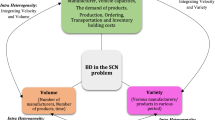
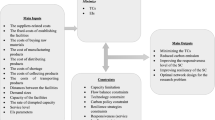
This study proposes a framework for the main parties of a sustainable supply chain network considering lot-sizing impact with quantity discounts under disruption risk among the first studies. The proposed problem differs from most studies considering supplier selection and order allocation in this area. First, regarding the concept of the triple bottom line, total cost, environmental emissions, and job opportunities are considered to cover the criteria of sustainability. Second, the application of this supply chain network is transformer production. Third, applying an economic order quantity model lets our model have a smart inventory plan to control the uncertainties. Most significantly, we present both centralized and decentralized optimization models to cope with the considered problem. The proposed centralized model focuses on pricing and inventory decisions of a supply chain network with a focus on supplier selection and order allocation parts. This model is formulated by a scenario-based stochastic mixed-integer non-linear programming approach. Our second model focuses on the competition of suppliers based on the price of products with regard to sustainability. In this regard, a Stackelberg game model is developed. Based on this comparison, we can see that the sum of the costs for both levels is lower than the cost without the bi-level approach. However, the computational time for the bi-level approach is more than for the centralized model. This means that the proposed optimization model can better solve our problem to achieve a better solution than the centralized optimization model. However, obtaining this better answer also requires more processing time. To address both optimization models, a hybrid bio-inspired metaheuristic as the hybrid of imperialist competitive algorithm (ICA) and particle swarm optimization (PSO) is utilized. The proposed algorithm is compared with its individuals. All employed optimizers have been tuned by the Taguchi method and validated by an exact solver in small sizes. Numerical results show that striking similarities are observed between the results of the algorithms, but the standard deviations of PSO and ICA–PSO show better behavior. Furthermore, while PSO consumes less time among the metaheuristics, the proposed hybrid metaheuristic named ICA–PSO shows more time computations in all small instances. Finally, the provided results confirm the efficiency and the performance of the proposed framework and the proposed hybrid metaheuristic algorithm.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Akarte G-H, Chaing C-H, LI, C.-W. (2007) Evaluating intertwined effects in e-learning programs: a novel hybrid MCDM model based on factor analysis and DEMATEL. Expert Syst Appl 32:1028–1044
Atashpaz-Gargari E, Lucas C (2007) Imperialist competitive algorithm: an algorithm for optimization inspired by imperialistic competition. In: IEEE Congress on evolutionary computation, 2007. CEC 2007, pp 4661–4667. IEEE
Bicocchi N, Cabri G, Mandreoli F, Mecella M (2019) Dynamic digital factories for agile supply chains: an architectural approach. J Ind Inf Integr 15:111–121
Bohner C, Minner S (2017) Supplier selection under failure risk, quantity and business volume discounts. Comput Ind Eng 104:145–155
Castellano D, Glock CH (2021) The average-cost formulation of lot sizing models and inventory carrying charges: a technical note. Oper Manag Res 14(1):194–201
Chang B, Chang C-W, WU, C.-H. (2012) Fuzzy DEMATEL method for developing supplier selection criteria. Expert Syst Appl 38:1850–1858
Chatterjee, S., & Chaudhuri, R. (2021). Supply chain sustainability during turbulent environment: examining the role of firm capabilities and government regulation. Oper Manag Res, 1–15
Chen Q, Xu Q (2020) Joint optimal pricing and advertising policies in a fashion supply chain under the ODM strategy considering fashion level and goodwill. J Comb Optim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-020-00623-y
Cheraghalipour A, Farsad S (2018) A bi-objective sustainable supplier selection and order allocation considering quantity discounts under disruption risks: a case study in plastic industry. Comput Ind Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2018.02.041
Devika K, Jafarian A, Kaviani A (2014) Sustainable closed-loop supply chain network design: hybrid metaheuristic algorithms based on triple line theories. Eur J Oper Res 25:243–257
Dweiri A, Lewandski L, Apte A (2015) Stochastic optimization for natural disaster asset prepositioning. Prod Oper Manag 19:561–574
Eslamipoor R, Sepehriar A (2014) Firm relocation as a potential solution for environment improvement using a SWOT-AHP hybrid method. Process Saf Environ Prot 92(3):269–276
Fallahpour A, Olugu EU, Musa SN, Khezrimotlagh D, Wong KY (2016) An integrated model for green supplier selection under fuzzy environment: application of data envelopment analysis and genetic programming approach. Neural Comput Appl 27(3):707–725
Fard AMF, Gholian-Jouybari F, Paydar MM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M (2017) A bi-objective stochastic closed-loop supply chain network design problem considering downside risk. Indust Eng Manag Syst 16(3):342–362
Fard AMF, Hajaghaei-Keshteli M (2018) A tri-level location-allocation model for forward/reverse supply chain. Appl Soft Comput 62:328–346
Fathollahi-Fard AM, Ahmadi A, Mirzapour Al-e-Hashem SMJ (2020b) Sustainable closed-loop supply chain network for an integrated water supply and wastewater collection system under uncertainty. J Environ Manag 275:111277
Fathollahi-Fard AM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Mirjalili S (2018) Multi-objective stochastic closed-loop supply chain network design with social considerations. Appl Soft Comput 71:505–525
Fathollahi-Fard AM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Mirjalili S (2020c) A set of efficient heuristics for a home healthcare problem. Neural Comput Appl 32(10):6185–6205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04126-8
Fathollahi-Fard AM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Tian G, Li Z (2020a) An adaptive Lagrangian relaxation-based algorithm for a coordinated water supply and wastewater collection network design problem. Inf Sci 512:1335–1359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.10.062
Feng Y, Zhang Z, Tian G, Fathollahi-Fard AM, Hao N, Li Z, Tan J (2019) A novel hybrid fuzzy grey TOPSIS method: supplier evaluation of a collaborative manufacturing enterprise. Appl Sci 9(18):3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9183770
Golmohamadi S, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M (2017) Solving a fuzzy fixed charge solid transportation problem using batch transferring by new approaches in meta-heuristic. Electron Notes Discrete Math 58:143–150
Ha DE, Murray AT, Li TC (2008) Decision support for network disruption mitigation. Decis Support Syst 44:954–969
Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Aminnayeri M, Ghomi SF (2014) Integrated scheduling of production and rail transportation. Comput Ind Eng 74:240–256
Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Fathollahi Fard AM (2019) Sustainable closed-loop supply chain network design with discount supposition. Neural Comput Appl 31(9):5343–5377
Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Aminnayeri M (2013) Keshtel Algorithm (KA); a new optimization algorithm inspired by Keshtels’ feeding. In: Proceeding in IEEE conference on industrial engineering and management systems, pp. 2249–2253
Hamdan S, Cheaitou A (2017) Supplier selection and order allocation with green criteria: An MCDM and multi-objective optimization approach. Comput Oper Res 81:282–304
Jadidi O, Jaber MY, Zolfaghri S, Pinto R, Firouzi F (2021) Dynamic pricing and lot sizing for a newsvendor problem with supplier selection, quantity discounts, and limited supply capacity. Comput Ind Eng 154(January):107113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2021.107113
Jahre M, Persson G, Kovacs G, Spens KM (2007) Humanitarian logistics in disaster relief operations. Int J Phys Distrib Logist Manag 37:99–114
Jianying F, Bianyu Y, Xin L, Dong T, Weisong M (2021) Evaluation on risks of sustainable supply chain based on optimized BP neural networks in fresh grape industry. Comput Electron Agric 183(January):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2021.105988
Karampour MM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Fathollahi-Fard AM, & Tian G (2020). Metaheuristics for a bi-objective green vendor managed inventory problem in a two-echelon supply chain network. Scientia Iranica. https://doi.org/10.24200/SCI.2020.53420.3228
Keshavarz-Ghorbani F, Arshadi Khamseh A (2021) Modeling and optimizing a multi-period closed-loop supply chain for pricing, warranty period, and quality management. J Ambient Intell Humanized Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-021-02971-x
Keshavarz-Ghorbani F, Pasandideh SHR (2021) Modeling and optimizing an agro-supply chain considering different quality grades and storage systems for fresh products: a Benders decomposition solution approach. J Comb Optim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-021-00802-5
Lahyani R, Alsaad F, Merdad L, Alzamel M (2021) Supply chain resilience vs. COVID-19 disruptions during the second wave. Procedia CIRP 103:42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2021.10.006
Li S, Chen X (2019) The role of supplier collaboration and risk management capabilities in managing product complexity. Oper Manag Res 12(3):146–158
Liu X, Tian G, Fathollahi-Fard AM, Mojtahedi M (2020) Evaluation of ship’s green degree using a novel hybrid approach combining group fuzzy entropy and cloud technique for the order of preference by similarity to the ideal solution theory. Clean Technol Environ Policy 22:493–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-019-01798-7
Lotfi R, Kargar B, Hoseini SH, Nazari S, Safavi S, Weber GW (2021) Resilience and sustainable supply chain network design by considering renewable energy. Int J Energy Res 45(12):17749–17766. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.6943
Ma C, Huang D (2019) Research on the impact of green innovation alliance mode on decision - making of two - cycle closed - loop supply chain. J Comb Optim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-019-00496-w
Mazdeh MM, Emadikhiav M, Parsa I (2015) A heuristic to solve the dynamic lot sizing problem with supplier selection and quantity discounts. Comput Ind Eng 85:33–43
Menon RR, Ravi V (2021) Analysis of enablers of sustainable supply chain management in electronics industries: the Indian context. Cleaner Eng Technol 5:100302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2021.100302
Molla-Alizadeh-Zavardehi S, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Lotfi FH (2016) A modified imperialist competitive algorithm for scheduling single batch-processing machine with fuzzy due date. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 85(9–12):2439–2458
Nezhadroshan AM, Fathollahi-Fard AM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M (2020) A scenario-based possibilistic-stochastic programming approach to address the resilient humanitarian logistics considering travel time and resilience levels of facilities. Int J Syst Sci Opera Logist 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/23302674.2020.1769766
Nourmohamadi Shalke P, Paydar MM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M (2018) Sustainable supplier selection and order allocation through quantity discounts. Int J Manage Sci Eng Manag 13(1):20–32
Perfetti, J., (2015). Fai fiorire il cielo, Sperling & Kupfer editori.
Rafigh P, Akbari AA, Bidhandi HM, Kashan AH (2021a) Sustainable closed-loop supply chain network under uncertainty: a response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16077-6
Rafigh P, Akbari AA, Bidhendi HM, Kashan AH (2021b) A fuzzy rule-based multi-criterion approach for a cooperative green supplier selection problem. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-17015-2
Rahimi M, Ghezavati V, Asadi F (2019) A stochastic risk-averse sustainable supply chain network design problem with quantity discount considering multiple sources of uncertainty. Comput Ind Eng 130:430–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2019.02.037
Roozbeh Nia A, Hemmati Far M, Niaki STA (2015) A hybrid genetic and imperialist competitive algorithm for green vendor managed inventory of multi-item multi-constraint EOQ model under shortage. Appl Soft Comput J 30:353–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2015.02.004
Sadeghi-Moghaddam S, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Mahmoodjanloo M (2017) New approaches in metaheuristics to solve the fixed charge transportation problem in a fuzzy environment. Neural Comput Appl, 1–21
Safaeian M, Fathollahi-Fard AM, Tian G, Li Z, Ke H (2019) A multi-objective supplier selection and order allocation through incremental discount in a fuzzy environment. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 37(1):1435–1455. https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-182843
Samadi A, Mehranfar N, Fathollahi Fard AM, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M (2018) Heuristic-based metaheuristics to address a sustainable supply chain network design problem. J Ind Prod Eng 35:1–16
Scheller C, Schmidt K, Spengler TS (2021) Decentralized master production and recycling scheduling of lithium-ion batteries: a techno-economic optimization model. J Bus Econ 91(2):253–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11573-020-00999-7
Singh Yadav, A., Pandey, G., Kumar Arora, T., & Kumar Chaubey, P. (2021). Block-chain application based economic impact of coronavirus pandemic on medicine industry inventory system for deteriorating objects with two-warehouse and wastewater treatment using PSO. In: Materials Today: Proceedings, (xxxx), pp 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.06.307
Snyder LV, Daskin MS (2006) A random-key genetic algorithm for the generalized traveling salesman problem. Eur J Oper Res 174:38–53
Soltanifar M, Sharafi H (2022) A modified DEA cross efficiency method with negative data and its application in supplier selection. J Comb Optim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-021-00765-7
Taguchi G, Jugulum R (2002) The Mahalanobis-Taguchi strategy: a pattern technology system. Wiley, Hoboken
Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Hajiaghaei-Keshteli M, Mousavi M, Ranjbar-Bourani M (2016) Two meta-heuristics to solve a coordinated air transportation and production scheduling problem with time windows for the due date. In: 2016 IEEE international conference on systems, man, and cybernetics (SMC), pp 004663–004668. IEEE
Tirkolaee EB, Aydın NS, Ranjbar-Bourani M, Weber GW (2020a) A robust bi-objective mathematical model for disaster rescue units allocation and scheduling with learning effect. Comput Ind Eng 149(September):106790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.106790
Tirkolaee EB, Dashtian Z, Weber GW, Tomaskova H, Soltani M, Mousavi NS (2021) An integrated decision-making approach for green supplier selection in an agri-food supply chain: threshold of robustness worthiness. Mathematics 9(11):1–30. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9111304
Tirkolaee EB, Mahdavi I, Esfahani MMS, Weber GW (2020b) A robust green location-allocation-inventory problem to design an urban waste management system under uncertainty. Waste Manag 102:340–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.10.038
Tirkolaee, E. B., Abbasian, P., & Weber, G. (2020c). Sustainable fuzzy multi-trip location-routing problem for medical waste management during the COVID-19 outbreak. (January).
Venegas BB, Ventura JA (2018) A two-stage supply chain coordination mechanism considering price sensitive demand and quantity discounts. Eur J Oper Res 264(2):524–533
Vieira AA, Dias LM, Santos MY, Pereira GA, Oliveira JA (2020) Supply chain data integration: a literature review. J Ind Inf Integr 19:100161
Wang SC, Tsai YT, Ciou YS (2020) A hybrid big data analytical approach for analyzing customer patterns through an integrated supply chain network. J Indus Inf Integr 20:100177
Wolpert DH, Macready WG (1997) No free lunch theorems for optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 1(1):67–82
Yu H, Dai H, Tian G, Wu B, Xie Y, Zhu Y, Zhang T, Fathollahi-Fard AM, He Q, Tang H (2021) Key technology and application analysis of quick coding for recovery of retired energy vehicle battery. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 135:110129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.110129
Zandieh M, Aslani B (2019) A hybrid MCDM approach for order distribution in a multiple-supplier supply chain: a case study. J Ind Inf Integr 16:100104
Zhang C, Tian G, Fathollahi-Fard AM, Li Z (2020) Interval-valued intuitionistic uncertain linguistic cloud petri net and its application in risk assessment for subway fire accident. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/TASE.2020.3014907
Önüt S, Kara SS, Işik E (2009) Long term supplier selection using a combined fuzzy MCDM approach: a case study for a telecommunication company. Expert Syst Appl 36(2):3887–3895
Şenyiğit E, Düğenci M, Aydin ME, Zeydan M (2013) Heuristic-based neural networks for stochastic dynamic lot sizing problem. Appl Soft Comput 13(3):1332–1339
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rafigh, P., Akbari, A.A., Bidhandi, H.M. et al. A sustainable supply chain network considering lot sizing with quantity discounts under disruption risks: centralized and decentralized models. J Comb Optim 44, 1387–1432 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-022-00891-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-022-00891-w