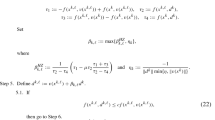Abstract
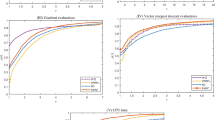
This paper presents a new approach based on extrapolation to accelerate the linear convergence process of Vectorized Moore–Skelboe (VMS) algorithm. The VMS is a modified version of basic Moore–Skelboe (MS) algorithm, where the vectorization is used as a means to speed up the basic MS algorithm. We propose to further accelerate the converging process of VMS from linear to quadratic by combining the Richardson extrapolation technique with VMS. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is tested on various multivariate examples and compared with the unaccelerated conventional method, i.e., MS and well-known optimization software GlobSol. The test results show that the proposed extrapolation-based VMS offer considerable speed improvements over both the existing algorithms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brezinski C.: Error control in convergence acceleration processes. IMA J. Numer. Anal. 3, 65–80 (1983)
Brezinski C., Zaglia M.R.: Extrapolation Methods: Theory and Practice. North-Holland, Amsterdam (2002)
Floudas, C.A., Pardalos, P.M. (eds): Encyclopedia of Optimization, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Hansen E.: Global Optimization using Interval Analysis. Marcel Dekker, New York (1992)
Himmelblau D.M., Yates R.V.: Applied Non-Linear Programming. McGraw-Hill, New York (1972)
Hock W., Schittkowski K.: Test Examples for Nonlinear Programming Codes. Springer, Berlin (1981)
Ichida K., Fuiji Y.: An interval arithmetic method for global optimization. Computing 23, 85–97 (1979)
Kearfott R.B.: Rigorous Global Search: Continuous Problems. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1996)
Kearfott R.B.: Interval analysis: unconstrained and constrained optimization. In: Floudas, C.A., Pardalos, P.M. (eds) Encyclopedia of Optimization, pp. 1727–1730. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Leclerc A.P.: Interval analysis: parallel methods for global optimization. In: Floudas, C.A., Pardalos, P.M. (eds) Encyclopedia of Optimization, pp. 1709–1717. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Moore R.E.: Interval Analysis. 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1966)
Moore R.E.: Methods and Applications of Interval Analysis. SIAM, Philadelphia (1979)
Moore R.E., Ratschek H.: Inclusion functions and global optimization II. Math. Programming 41, 341–356 (1988)
More J.J., Garbow B.S., Hillstrom K.E.: Testing unconstrained optimization software. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 7(1), 17–41 (1981)
Nataraj P.S.V., Sondur S.: Experiments with range computations using extrapolation. Reliable Comput. 13, 1–23 (2007)
Prakash, A.K.: Vectorized Interval Analysis Algorithms and their Applications. PhD thesis, Systems and Control Engineering, IIT Bombay (2002)
Ratschek H.: Inclusion functions and global optimizations. Math. Programming 33, 300–317 (1985)
Ratschek H., Rokne J.: Computer Methods for the Range of Functions. Ellis Horwood, Chichester (1984)
Ratschek H., Rokne J.: New Computer Methods for Global Optimization. Wiley, New York (1988)
Ratschek H., Rokne J.G.: Interval global optimization. In: Floudas, C.A., Pardalos, P.M. (eds) Encyclopedia of Optimization, pp. 1739–1757. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Ratz D., Csendes T.: On the selection of subdivision directions in interval branch-and-bound methods for global optimization. J. Global Optim. 7, 183–207 (1995)
Sidi A.: Practical Extrapolation Methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2003)
Stoer J., Bulirsch R.: Introduction to Numerical Analysis, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (1991)
Walz G.: Asymptotics and Extrapolation. Akademie, Berlin (1996)
Zilinskas J., Bogle I.D.L.: Global optimization: interval analysis and balanced interval arithmetic. In: Floudas, C.A., Pardalos, P.M. (eds) Encyclopedia of Optimization, 2nd edn, pp. 1346–1350. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nataraj, P.S.V., Sondur, S. The extrapolated interval global optimization algorithm. J Glob Optim 50, 249–270 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-010-9578-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-010-9578-9