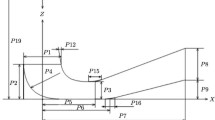
Abstract
In recent years, numerical and experimental investigations on the draft tube performance have confirmed the importance of the inlet swirling flow created by the runner vanes. The results indicate that it is still a challenge to get the optimal flow distribution at the draft tube inlet which gives the best machine performance over a range of operation points. Consequently, there is a need to adjust the runner-draft tube coupling to minimize the losses arising from the inlet flow distribution. This paper focus on establishing an optimization methodology for maximizing the draft tube performance as a function of the inlet velocity profile. The overall work is divides into two parts: The part one establish the inlet velocity parametrization, the numerical optimization set-up and the objective function definition. The part two validate the numerical CFD draft tube model. These steps are represented by the coupling of the commercial softwares MATLAB, FLUENT and iSIGHT. It is considered that this proved methodology will help to find a inlet velocity profile shape which will be able to suppress or mitigate the undesirable draft tube flow characteristics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, U.: Test case T- some news results and updates since workshop 1. In: Proceedings of Turbine 99-WS2, The Second ERCOFTAC Workshop on Draft Tube Flow. Alvkarleby, Sweden (2001)
Bergström, J.: Approximations of numerical errors and boundary conditions in a draft tube. In: Proceedings of Turbine 99 Workshop on Draft Tube Flow. Porjus Hydropower Center, Sweden (1999)
Burman, J., Gebart, B., Mårtensson, H.: Developement of a blade geometry definition with implicit design variables. In: 38th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Mettingand Exhibit, Reno, N.Y, 0671 (2000)
Cervantes M., Engström F.: Factorial design applied to CFD. J. Fluids Eng. 126, 791–798 (2004)
Cervantes M., Gustavsson L.: On the use of squire-long equation to estimate radial velocities in swirling flows. J. Fluids Eng. 129(February), 209–217 (2007)
Coley D.: An Introduction to Genetic Algorithms for Scientists and Engineers. World Scientific Publishing, Singapore (1999)
Eisinger, R., Ruprecht, A.: Automatic shape optimization of hydro turbine components based on CFD. In: Seminar on CFD for Turbomachinery Applications, Gdansk, v2001-05 (2001). http://www.ihs.uni-stuttgart.de/forschung/veroeff/stroem/v2001_05.pdf
Eklund S.: A massively parallel architecture for distributed genetic algorithms. Science@Direct. Parallel Comput. 30(5–6), 647–676 (2004)
Enomoto, Y.: Design optimization of a Francis turbine runner using multi-objective genetic algorithm. In: 22nd IAHR Symposium on Hydraulic Machinery and Systems, Stockholm, Sweden, June 29-July 2, vol. A01–2 pp. 1–10 (2004)
Fan H.Y.: An inverse design method of diffuser blades by genetic algorithms. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 112(4), 261–268 (1998)
Fluent Inc.: Fluent 6.1 User’s Guide. Fluent Inc. (2003)
Galván, S.: Optimization of the inlet velocity profile of the turbine 99 draft tube. Ph.D. thesis, École Polytechnique de Montréal. (2007)
Galván, S., Page, M., Guibault F.and Reggio, M.: Numerical validation of different CFD k-e turbulent models using FLUENT code. In: Turbine-99 III, Proceedings of the third IAHR/ERCOFTAC Workshop on the Draft Tube Flow, 8–9 December 2005, Porjus Sweden. paper 4 (2005)
Hiroyasu, T., Miki, M., Negami, M.: Distributed genetic algorithms with randomized migration rate. In: Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1999. IEEE SMC ’99 Conference Proceedings, vol. 1, pp. 689–694. Tokyo Japan (1999)
Engenious Software Inc. iSight Version 9.0 Reference Guide
Jae-Yong, K., Afshin, J., Clement, T., F., G.: Comparison of near-wall treatment methods for high reynolds number backward-facing step flow. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 19(7), 493–500(2005)
Kazan, M.: Étude de l’écoulement à à la sortie d’une roue Francis. Ph.D. thesis, École Polytechnique de l’Université de Lausanne. (1962)
Lèonard, O., Rothilde, A., Duysinx, P.: Compressor and turbine blade design by optimization. In: Proceedings of the Third World Congress of Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization WCSMO3, Buffalo, USA, 43-EOA3-1 (1999)
Lindgren, M.: Automatic shape optimization of hydropower flows: the draf tube. Master’s thesis, Luleä University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden (2002)
Lipej A., Poloni C.: Design of Kaplan runner using multiobjective genetic algorithm optimization. J. Hydraul. Res. 38(1), 73–79 (2000)
Madsen J., Shyy W., Haftka R.: Response surface techniques for diffuser shape optimization. AIAA J. 38(9), 1512–1518 (2000)
Marjavaara, D., Lundström, T.: Shape optimization of a hydropower draft tube. In: 22nd IAHR Symposium on Hydraulic Machinery and Systems. Design Methods Turbines. Stockholm Sweden, vol. A03-2 (2004)
Marjavaara D., Lundström T.: Redesign of a sharp heel draft tube by a validated CFD-optimization. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 50, 911–924 (2005)
Massé, B., Page, M., Grioux, A., Magnan, R.: Improving Efficiency of a 195 MW Francis turbine using numerical simulation tools. CFD–F08
The MathWorks Inc., MATLAB, version 7.1.0.183 (R14). http://www.mathworks.com/productsmatlab (2010)
Mauri, S., Kueny, J., Avellan, F.: Flow simulation in an elbow diffuser: verification and validation. In: Proceedings of the Hydraulic Machinery and Systems XXIst IAHR Symposium, Lausanne (2002)
Mengistu, T., Ghaly, W.: Global optimization methods for the aerodynamic shape design of transonic cascades. In: Proceedings of the 11th CFD Conference of the Canadian Society of CFD, Vancouver, BC, vol. 1, pp. 238–243 (2003)
Miki, M., Hiroyasu, T., Kaneko, M., Hatanaka, K.: A parallel genetic algorithm with distributed environment scheme. In: Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1999. IEEE SMC ’99 Conference Proceedings, vol. 1, pp. 695–700. Tokyo, Japan (1999)
Muntean, S., Susan-Resiga, R., Bernard, S., Anton, I.: 3D turbulent flow analysis of the GAMM Francis turbine for variable discharge. In: 22nd IAHR Symposium on Hydraulic Machinery and Cavitation. Stockholm, Sweden (2004)
Nechleba, M.: Hydraulic turbines their design and equipment. Artia, c1957, Prague Czechoslovakia (1957)
Oyama, A., Liou, M., Obayashi, S.: Transonic axial-flow blade shape optimization using evolutionary algorithm and three-dimensional Navier-Stokes solver. In: 9th AIAA/ISSMO Symposium on Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization, Atlanta, Georgia, vol. AIAA 2002-5642 (2002)
Peng G., Cao S., Ishizuca M., Hayama S.: Design optimization of axial flow hydraulic turbine runner; part II - multi - objective constrained optimization method. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 39, 533–548 (2002)
Puente, L., Reggio, M., Guibault, F.: Automatic shape optimization of a hydraulic turbine draft tube. In: CFD 2003: The Eleventh Annual Conference of the CFD Society of Canada, Vancouver, BC (2003). http://tetra.mech.ubc.ca/CFD03/papers/paper29PB1.pdf
Ruiz, E.: Polyfit Software. Chaire de Recherche sur le Composite Haute Performance CCHP, École Polytechnique de Montréal (2004)
Ruprecht, A., Eisinger, R., Göde, E.: Innovative design environments for hydro turbine components. In: HYDRO 2000, Bern, v2000-05 (2000). http://www.ihs.uni-stuttgart.de/forschung/veroeff/stroem/v2000_05.pdf
Ruprecht, A., Eisinger, R., Göde, E., Rainer, D.: Virtual numerical test bed for intuitive design of hydro turbine components. In: Hydropower into the Next Century, Gmunden, Austria, v1999-04 (1999). http://www.ihs.uni-stuttgart.de/forschung/veroeff/stroem/v1999_04.pdf
Susan-Resiga R., Ciocan G., Anton I., Avellan F.: Analysis of the swirling flow downstream a Francis turbine runner. J Fluids Eng. 128, 177–189 (2006)
Swiderski, J., Martin, J., Norrena, R.: Automated runner blade design optimization process based on CFD verification. In: Waterpower XII, Utah USA, July 9 (2001)
Tomas, L., Pedretti, C., Chiappa, T., François, M., Stoll, P.: Automated design of a Francis turbine runer using global optimization algorithms. In: Proceedings of the XXIst IAHR Symposioum on Hydraulic Machinery and Systems, Lausanne, (2002)
Zangeneh M., Goto A., Harada H.: On the role of three-dimensional inverse design methods in turbomachinery shape optimization. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci 213(1), 27–42 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galván, S., Rubio, C., Pacheco, J. et al. Optimization methodology assessment for the inlet velocity profile of a hydraulic turbine draft tube: part I—computer optimization techniques. J Glob Optim 55, 53–72 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-012-9946-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10898-012-9946-8