Abstract
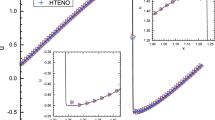
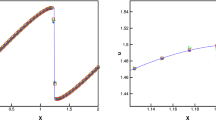
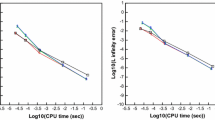
In this paper, a class of weighted essentially non-oscillatory (WENO) schemes based on Hermite polynomials, termed HWENO (Hermite WENO) schemes, for solving one and two dimensional nonlinear hyperbolic conservation law systems is presented. The construction of HWENO schemes is based on a finite difference formulation, Hermite interpolation, and nonlinearly stable Runge–Kutta methods. The idea of the reconstruction in the HWENO schemes comes from the original WENO schemes, however both the function and its first derivative values are evolved in time and used in the reconstruction, while only the function values are evolved and used in the original WENO schemes. Comparing with the original finite difference WENO schemes of Jiang and Shu (J Comput Phys 126:202–228, 1996), one major advantage of HWENO schemes is its compactness in the reconstruction. For example, five points are needed in the stencil for a fifth order WENO (WENO5) reconstruction, while only three points are needed for a fifth order HWENO (HWENO5) reconstruction. Some benchmark numerical experiments are presented to illustrate efficiency of HWENO schemes.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Harten, A.: High resolution schemes for hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 49, 357–393 (1983)
Harten, A., Engquist, B., Osher, S., Chakravarthy, S.R.: Uniformly high order accurate essentially non-oscillatory schemes, III. J. Comput. Phys. 71, 231–303 (1987)
Harten, A., Osher, S.: Uniformly high-order accurate non-oscillatory schemes I. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 24, 279–309 (1987)
Hu, X.Y., Adams, N.A., Shu, C.-W.: Positivity-preserving method for high-order conservative schemes solving compressible Euler equations. J. Comput. Phys. 242, 169–180 (2013)
Jiang, G., Shu, C.-W.: Efficient implementation of weighted ENO schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 126, 202–228 (1996)
Liu, X.D., Osher, S., Chan, T.: Weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 115, 200–212 (1994)
Qiu, J., Shu, C.-W.: Hermite WENO schemes and their application as limiters for Runge–Kutta Galerkin method: one-dimension case. J. Comput. Phys. 193, 115–135 (2004)
Qiu, J., Shu, C.-W.: Hermite WENO schemes and their application as limiters for Runge–Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method II: two-dimensional case. Comput. Fluids 34, 642–663 (2005)
Qiu, J., Shu, C.-W.: Hermite WENO schemes for Hamilton–Jacobi equations. J. Comput. Phys. 204, 82–99 (2005)
Shu, C.-W.: High order weighted essentially nonoscillatory schemes for convection dominated problems. SIAM Rev. 51, 82–126 (2009)
Shu, C.-W., Osher, S.: Efficient implementation of essentially non-oscillatory shock-capturing schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 77, 439–471 (1988)
Shu, C.-W., Osher, S.: Efficient implementation of essentially non-oscillatory shock-capturing schemes, II. J. Comput. Phys. 83, 32–78 (1989)
Woodward, P., Colella, P.: The numerical simulation of two-dimensional fluid flow with strong shocks. J. Comput. Phys. 54, 115–173 (1984)
Zhang, X., Shu, C.-W.: Maximum-principle-satisfying and positivity-preserving high-order schemes for conservation laws: survey and new developments. Proc. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 467, 2752–2776 (2011)
Zhang, X., Shu, C.-W.: Positivity-preserving high order finite difference WENO schemes for compressible Euler equations. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 2245–2258 (2012)
Zhu, J., Qiu, J.: A class of the fourth order finite volume Hermite weighted essentially non-oscillatory schemes. Sci. China Ser. A Math. 51, 1549–1560 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The research was partially supported by NSFC Grant 91230110, 11328104 and ISTCP of China Grant No. 2010DFR00700.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Qiu, J. Finite Difference Hermite WENO Schemes for Hyperbolic Conservation Laws. J Sci Comput 63, 548–572 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9905-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9905-2