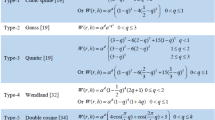Abstract
The accuracy and stability of the classical formulation of the smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) method for modelling compression of elastic solids is studied to assess its suitability for predicting solid deformation. SPH has natural advantages for simulating problems involving compression of deformable solids arising from its ability to handle large deformation without re-meshing, complex free surface behaviour and tracking of multiple material interfaces. The ‘classical SPH method’, as originally proposed by Monaghan (in Ann Rev Astron 30:543–574, 1992, Rep Prog Phys 68:1703–1759, 2005), has become broadly established as a robust method in different areas, especially involving fluid flows. However, limited attention has been paid to understanding of its numerical performance for elastic deformation problems. To address this, we evaluate the classical SPH method to explore its stability, accuracy and convergence and the effect of numerical parameters on elastic solutions using a generic uniaxial stress test. Short term transient and long term uniform state SPH solutions agree well with those from the finite element method (FEM). The SPH elastic deformation solution showed good convergence with increasing particle resolution. The tensile instability stabilisation method was found to have little impact on the solution, except for higher values of the correction factor which then produce small amplitude benign artificial banded stress patterns. The use of artificial viscosity is able to eliminate the instability and improve the accuracy of the solutions. Overall, the classical SPH method appears to be robust and suitable for accurate modelling of elastic solids under compression.




























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Monaghan, J.J.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 30, 543–574 (1992)
Monaghan, J.J.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 68, 1703–1759 (2005)
Gingold, R.A., Monaghan, J.J.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics—theory and application to non-spherical stars. MNRAS 181, 375–389 (1977)
Lucy, L.B.: A numerical approach to the testing of the fission hypothesis. Astron. J. 82, 1013–1024 (1977)
Monaghan, J.J., Price, D.J.: Variational principles for relativistic smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 328(2), 381–392 (2001)
Cleary, P.W.: Modelling confined multi-material heat and mass flows using SPH. Appl. Math. Model. 22(12), 981–993 (1998)
Cleary, P.W., Ha, J., Prakash, M., Nguyen, T.: Simulation of casting complex shaped objects using SPH. In: In San Francisco, CA, United States. pp. 317–326. Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, Warrendale, PA 15086, United States (2005)
Cummins, S.J., Rudman, M.J.: Truly incompressible SPH. In: In Washington, DC, USA. p. 8. ASME, Fairfield, NJ, USA (1998)
Cleary, P.W., Monaghan, J.J.: Conduction modelling using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J. Comput. Phys. 148(1), 227–264 (1999)
Bonet, J., Kulasegaram, S.: A simplified approach to enhance the performance of smooth particle hydrodynamics methods. Appl. Math. Comput. (N. Y.) 126(2–3), 133–155 (2002)
Cleary, P., Ha, J., Alguine, V., Nguyen, T.: Flow modelling in casting processes. Appl. Math. Model. 26(2), 171–190 (2002)
Cleary, P.W., Prakash, M., Ha, J., Stokes, N., Scott, C.: Smooth particle hydrodynamics: status and future potential. Prog. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 7(2–4), 70–90 (2007)
Libersky, L.D., Petschek, A.G.: Smooth particle hydrodynamics with strength of materials. In: Trease, H., Crowley, W.P. (eds.) Advances in the Free-Lagrange Method. Springer, Berlin (1990)
Wingate, C.A., Fisher, H.N.: Strength Modeling in SPHC. Los Alamos National Laboratory, Report No. LA-UR-93-3942 (1993)
Gray, J.P., Monaghan, J.J., Swift, R.P.: SPH elastic dynamics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 190(49–50), 6641–6662 (2001)
Cleary, P.W., Prakash, M., Ha, J.: Novel applications of smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) in metal forming. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 177(1–3), 41–48 (2006)
Das, R., Cleary, P.W.: The potential for SPH modelling of solid deformation and fracture. In: Reddy, D. (ed.) IUTAM Proceedings Book Series Volume on “Theoretical, Computational and Modelling Aspects of Inelastic Media”, pp. 287–296. Springer, Capetown (2008)
Karekal, S., Das, R., Mosse, L., Cleary, P.W.: Application of a mesh-free continuum method for simulation of rock caving processes. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 48(5), 703–711 (2011)
Cleary, P.W., Prakash, M., Das, R., Ha, J.: Modelling of metal forging using SPH. Appl. Math. Model. 36(8), 3836–3855 (2012)
Das, R., Cleary, P.W.: A mesh-free approach for fracture modelling of gravity dams under earthquake. Int. J. Fract. 179(1–2), 9–33 (2013)
Das, R., Cleary, P.W.: Effect of rock shapes on brittle fracture using Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 53(1), 47–60 (2010)
Fagan, T., Das, R., Lemiale, V., Estrin, Y.: Modelling of equal channel angular pressing using a mesh-free method. J. Mater. Sci. 47 (11), 4514–4519 (2012)
Islam, S., Ibrahim, R., Das, R., Fagan, T.: Novel approach for modelling of nanomachining using a mesh-less method. Appl. Math. Model. 36 (11), 5589–5602 (2012)
Bradley, G.L., Chang, P.C., McKenna, G.B.: Rubber modeling using uniaxial test data. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 81(4), 837–848 (2001)
Liu, W.K., Jun, S., Li, S., Adee, J., Belytschko, T.: Reproducing kernel particle methods for structural dynamics. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 38(10), 1655–1679 (1995)
Chen, J.K., Beraun, J.E., Jih, C.J.: Improvement for tensile instability in smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Comput. Mech. 23(4), 279–287 (1999)
Liu, M.B., Liu, G.R.: Restoring particle consistency in smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Appl. Numer. Math. 56(1), 19–36 (2006)
Bonet, J., Kulasegaram, S.: Correction and stabilization of smooth particle hydrodynamics methods with applications in metal forming simulations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 47(6), 1189–1214 (2000)
Bonet, J., Kulasegaram, S.: Remarks on tension instability of Eulerian and Lagrangian corrected smooth particle hydrodynamics (CSPH) methods. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 52(11), 1203–1220 (2001)
Vidal, Y., Bonet, J., Huerta, A.: Stabilized updated Lagrangian corrected SPH for explicit dynamic problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 69(13), 2687–2710 (2007)
Dyka, C.T., Ingel, R.P.: An approach for tension instability in smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Comput. Struct. 57, 573–580 (1995)
Dyka, C.T., Randles, P.W., Ingel, R.P.: Stress points for tension instability in SPH. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 40(13), 2325–2341 (1997)
Randles, P.W., Libersky, L.D.: Normalized SPH with stress points. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 48(10), 1445–1462 (2000)
Vignjevic, R., Campbell, J., Libersky, L.: A treatment of zero-energy modes in the smoothed particle hydrodynamics method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 184(1), 67–85 (2000)
Belytschko, T., Xiao, S.: Stability analysis of particle methods with corrected derivatives. Comput. Math. Appl. 43(3–5), 329–350 (2002)
Xiao, S.R., Belytschko, T.: Material stability analysis of particle methods. Adv. Comput. Math. 23(1–2), 171–190 (2005)
Shaw, A., Roy, D.: Stabilized SPH-based simulations of impact dynamics using acceleration-corrected artificial viscosity. Int. J. Impact Eng 48, 98–106 (2012)
Shaw, A., Roy, D., Reid, S.R.: Optimised form of acceleration correction algorithm within SPH-based simulations of impact mechanics. Int. J. Solids Struct. 48(25–26), 3484–3498 (2011)
Shaw, A., Reid, S.R.: Applications of SPH with the acceleration correction algorithm in structural impact computations. Curr. Sci. 97(8), 1177–1186 (2009)
Shaw, A., Reid, S.R.: Heuristic acceleration correction algorithm for use in SPH computations in impact mechanics. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198(49–52), 3962–3974 (2009)
Wang, S.L.N.: A large-deformation Galerkin SPH method for fracture. J. Eng. Math. 71(3), 305–318 (2011)
Wong, S., Shie, Y.: Large deformation analysis with Galerkin based smoothed particle hydrodynamics. CMES 36(2), 97–118 (2008)
Gray, J.P., Monaghan, J.J.: Numerical modelling of stress fields and fracture around magma chambers. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 135, 259–283 (2004)
Swegle, J.W., Hicks, D.L., Attaway, S.W.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics stability analysis. J. Comput. Phys. 116(1), 123–134 (1995)
Morris, J.P.: A study of the stability properties of smooth particle hydrodynamics. Publ. Astron. Soc. Aust. 13(1), 97–102 (1996)
Monaghan, J.J.: SPH without a tensile instability. J. Comput. Phys. 159(2), 290–311 (2000)
Melean, Y., Sigalotti, L.D.G., Hasmy, A.: On the SPH tensile instability in forming viscous liquid drops. Comput. Phys. Commun. 157(3), 191–200 (2004)
Liu, Z.S., Swaddiwudhipong, S., Koh, C.G.: High velocity impact dynamic response of structures using SPH method. Int. J. Comput. Eng. Sci. 5(2), 315–326 (2004)
Monaghan, J.J.: Simulating free surface flows with SPH. J. Comput. Phys. 110, 399–406 (1994)
Kulasegaram, S., Bonet, J., Lewis, R.W., Profit, M.: High pressure die casting simulation using a Lagrangian particle method. Commun. Numer. Methods Eng. 19(9), 679–687 (2003)
Cedric, T., Janssen, L.P.B.M., Pep, E.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics model for phase separating fluid mixtures. I. General equations. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin. Soft Matter Phys. 72, 016713 (2005)
Cleary, P.W., Ha, J., Prakash, M., Nguyen, T.: 3D SPH flow predictions and validation for high pressure die casting of automotive components. Appl. Math. Model. 30(11), 1406–1427 (2006)
Fang, J., Owens, R.G., Tacher, L., Parriaux, A.: A numerical study of the SPH method for simulating transient viscoelastic free surface flows. J. Nonnewton. Fluid Mech. 139(1–2), 68–84 (2006)
Imaeda, Y., Inutsuka, S.-I.: Shear flows in smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Astrophys. J. 569(1), 501–518 (2002)
Monaghan, J.J., Gingold, R.A.: Shock simulation by the particle method SPH. J. Comput. Phys. 52(2), 374–389 (1983)
Monaco, A.D., Manenti, S., Gallati, M., Sibilla, S., Agate, G., Guandalini, R.: SPH modeling of solid boundaries through a semi-analytic approach. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 5(1), 1–15 (2011)
Libersky, L.D., Randles, P.W., Carney, T.C., Dickinson, D.L.: Recent improvements in SPH modeling of hypervelocity impact. Int. J. Impact Eng 20(6–10 pt 2), 525–532 (1997)
Libersky, L.D., Petscheck, A.G., Carney, T.C., Hipp, J.R., Allahdadi, F.A.: High strain Lagrangian hydrodynamics—a three dimensional SPH code for dynamic material response. J. Comput. Phys. 109(1), 67–75 (1993)
Randles, P.W., Libersky, L.D.: Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: some recent improvements and applications. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 139(1–4), 375–408 (1996)
Mayrhofer, A., Rogers, B.D., Violeau, D., Ferrand, M.: Investigation of wall bounded flows using SPH and the unified semi-analytical wall boundary conditions. Comput. Phys. Commun. 184(11), 2515–2527 (2013)
Wu, B., Tan, C.P.: Sand production prediction of gas field: methodology and laboratory verification. In: SPE Asia Pacific Oil & Gas Conference and Exhibition, Melbourne, Australia (2002)
Timoshenko, S., Goodier, J.N.: Theory of Elasticity, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York (1984)
Bathe, K.J.: Finite Element Procedures. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1995)
Babuska, I., Suri, M.: On locking and robustness in the finite element method. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 29(5), 1261–1293 (1992)
Suri, M., Babuska, I., Schwab, C.: Locking effects in the finite element approximation of plate models. Math. Comput. 64(210), 461 (1995)
Ozkul, T.A., Ture, U.: The transition from thin plates to moderately thick plates by using finite element analysis and the shear locking problem. Thin-Walled Struct. 42(10), 1405–1430 (2004)
Suri, M.: Analytical and computational assessment of locking in the hp finite element method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 133(3–4), 347–371 (1996)
Hansbo, P.: New approach to quadrature for finite elements incorporating hourglass control as a special case. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 158(3–4), 301–309 (1998)
Reese, S., Wriggers, P.: Stabilization technique to avoid hourglassing in finite elasticity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 48(1), 79–109 (2000)
Fernandez-Mendez, S., Bonet, J., Huerta, A.: Continuous blending of SPH with finite elements. Comput. Struct. 83, 1448–1458 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, R., Cleary, P.W. Evaluation of Accuracy and Stability of the Classical SPH Method Under Uniaxial Compression. J Sci Comput 64, 858–897 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9948-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-014-9948-4